In a cramped room with blistered walls on the edge of Harare, three sex workers sat pressed together on a frayed mattress spread across bare concrete.
This was the work station for the women, who say their trade turned perilous after US President Donald Trump abruptly cut foreign health aid earlier this year.
One of them, Sharon Mukakanhanga, reached into her bag and pulled out a pair of baby socks she used when there was nothing else between her and risk.
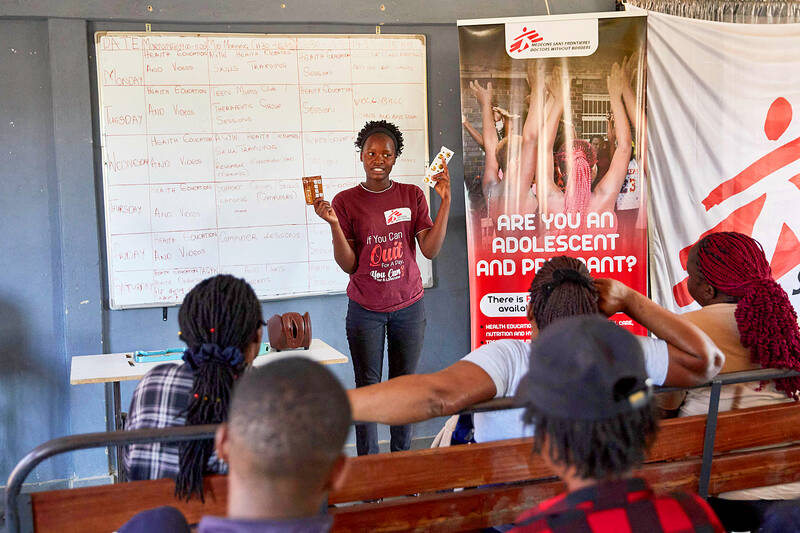

Photo: AFP
“These little socks served as condoms when I became so desperate after the American government withdrew its support from my all-time go-to safe haven,” the 43-year-old said, referring to her preferred clinic.
Mukakanhanga is among thousands of sex workers in Zimbabwe who have struggled to access HIV prevention tools since the US government cuts gutted medical centers that once provided free condoms, antiretrovirals and basic care.
For nearly two decades, the US programs, including PEPFAR, the world’s largest HIV initiative, formed a critical safety net for Zimbabwe’s fragile health system.
The first half of this year has seen 5,932 AIDS-related deaths, a rise from 5,712 in the same period last year, according to official government data.
The impact of the withdrawals was immediate, said 47-year-old HIV-positive sex worker Cecilia Ruzvidzo.
“It was a very difficult period. I literally lost my mind,” said the mother of four, who has been in the trade for nearly two decades.
She recalled leaving her most recent visit to the clinic with only 10 days of antiretrovirals.
“I could not get condoms, which are a necessity for my work. I was at risk of contracting more infections. My clients were also exposed,” she said.
With US-funded facilities being shuttered or empty, the few remaining providers say they are buckling under the pressure.
Medical charity Doctors Without Borders said its clinics in Harare suburbs such as Epworth and Mbare are stretched thin.
“They don’t know where to go. They don’t know where to seek services,” said project lead Charlotte Pignon, referring to patients, and especially sex workers.
While she did not directly link the rising deaths to the funding cuts, she said the impact of the withdrawal could not be ignored.
“It is difficult to know all the factors that are impacting those numbers, but it’s impossible to say that it’s not impacted by the US cuts either,” she said.
The scale of the fallout was still coming into focus, said Wonder Mufunda, chief executive of Harare-headquartered think tank the Centre for Humanitarian Analytics (CHA).
Mufunda said US support had previously amounted to about US$522 million, with about US$90 million directed to HIV programs.
“You wake up and you have lost such funding, there were serious disruptions,” he said, warning that deaths could rise. “It’s quite a big blow we are talking about.”
Beyond overstretched clinics, Zimbabwe’s economic free fall is pushing more people into sex work, with an estimated 40,500 women already engaged in sex work nationwide, according to CHA.
Competition had eroded the power to insist on safer sex, Cleopatra Katsande said.
Some workers were charging as little as US$0.50 per client, far less than the cost of a box of condoms, she said.
For veteran Ruzvidzo, there is no real choice.
“We knew it wasn’t safe,” she said of using baby socks as condoms. “But I had to feed my children.”
The clients did not seem to mind, she said.
“When it comes to this moment, men don’t think straight,” she said.
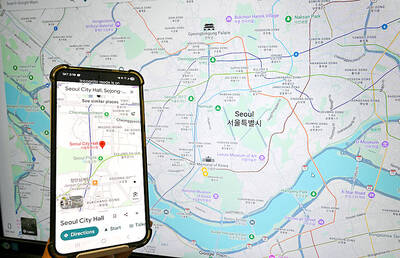
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

THE TRAGEDY OF PUNCH: Footage of the seven-month-old Japanese macaque has gone viral online after he was rejected by his mother and formed a bond with a soft toy A baby monkey in Japan has captured hearts around the world after videos of him being bullied by other monkeys and rejected by his mother went viral last week. Punch, a Japanese macaque, was born in July last year at Ichikawa City Zoo. He has drawn international attention after zookeepers gave him a stuffed orangutan toy after he was abandoned by his mother. Without maternal guidance to help him integrate, Punch has turned to the toy for comfort. He has been filmed multiple times being dragged and chased by older Japanese macaques inside the enclosure. Early clips showed him wandering alone with

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail