Aug. 14 to Aug. 20
On Aug. 15, 1978, the first Tzechiang-class express train (自強號) made its official maiden voyage, traversing the newly electrified route between Taipei and Taichung. It was a British EMU100 train, a model that was used by the Taiwan Railway Company until June 2009.
It was a major milestone in Taiwan’s railroad history, which stretches back to the construction of the first railroad in 1887 under the supervision of the Qing Empire’s governor of Taiwan, Liu Ming-chuan (劉銘傳). Liu is often considered the “father of Taiwan’s railways,” but a quick Google search will reveal that there is another contender for the title — Japanese national Hasegawa Kinsuke, who was the chief engineer behind the completion of the Taiwan Trunk Line (縱貫線) in 1908, which connected Kirun (Keelung) and Takao (Kaohsiung).
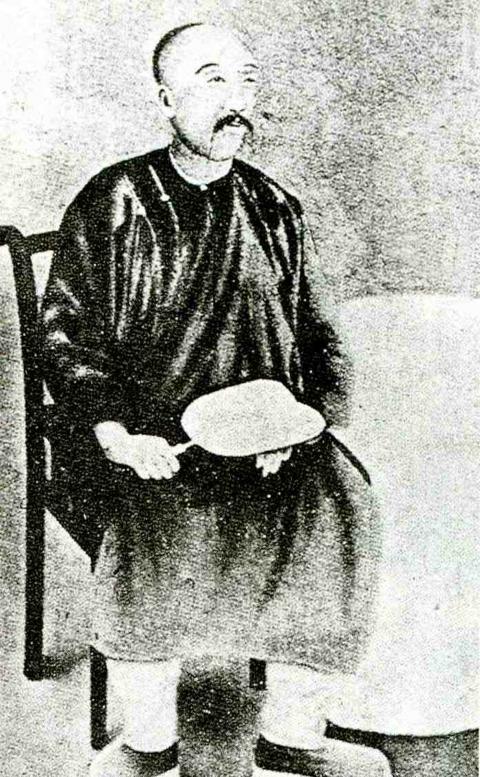

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Liu was Taiwan’s first governor when the Qing decided to separate it from Fujian Province in 1885. Long considered a backwater province, the Qing only began to take an interest in developing Taiwan in the latter half of the 19th century.
The idea of building a railroad in Taiwan was first proposed in 1877 by Fujian governor Ting Jih-chang (丁日昌), who saw Taiwan as a key defensive location — but it never materialized due to technical and financial issues.
Liu officially submitted a requested to the imperial court in April 1887 to build a north-south railroad. The court approved it a month later. Liu quickly set up the government-run Taiwan Railway Business Administration (全台鐵路商務總局) and recruited British and German engineers. Construction reportedly began June 9, the birthday of George Stephenson, who built the first public railway in the world — some dispute this claim, but the date is still officially observed as the anniversary of Taiwan’s railroad.
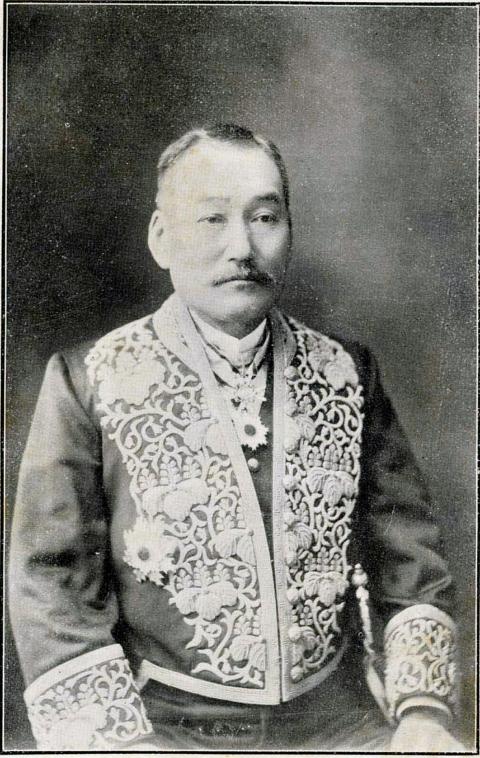

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
The first tunnel, from Taipei to Keelung, took about three years and resulted in many deaths and accidents. Upon its completion, Liu wrote a couplet which ended with “human power triumphs over God’s work” (居然人力勝神工). The first car made a test journey from Dadaocheng (大稻埕) to Xikou (錫口, today’s Songshan District, 松山) area in July 1888, drawing thousands of spectators.
Qing era railway construction ended in Hsinchu in 1894. Liu had left his post three years earlier, and his successor Shao Yu-lien (邵友濂) stopped most of Liu’s modernization programs soon after.
THE JAPANESE EFFORT
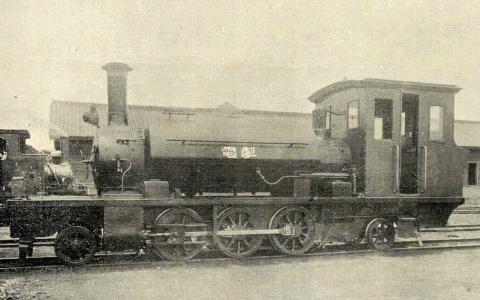
Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
A year later, the Qing ceded Taiwan to Japan. Historian Tai Pao-tsun (戴寶村) writes in the book Around the Island: The History of Taiwan’s Railway (縱貫環島:台灣鐵道) that the railroad was already in pretty bad shape when the Japanese took over and the situation was exacerbated when the retreating Qing troops sabotaged the tracks and facilities.
By July 1895, the Japanese had restored the entire railroad to working condition, using it to transport supplies in their campaign south against local resistance. Tai finds it ironic that the railroad, which was built to protect Taiwan, ended up being used by the invaders against the local population.
In the first few years, the Japanese uprooted sections of the old railroad, even abandoning the Taipei-Keelung tunnel and building a new one that was easier to traverse.
In 1899, construction began to extend the railroad further south, employing Japanese engineers and cheap Taiwanese labor. Books on Taiwanese history barely mention Hasegawa, who began his railroad career as a technician in 1877 and arrived in Taiwan in 1899 as the project’s chief engineer.
Shinpei Goto, minister of civilian affairs, wrote later in an official railroad publication, “I was the head of the railway project in name only. In fact, everything related to railroad construction was taken care of by Hasegawa. All I did was stamp paperwork.”
Hasegawa deemed the original Qing Dynasty line too steep and planned a new line south from Taihoku (Taipei). At the same time, he ordered construction to start north from Takao (Kaohsiung). During this time, he also helped build stations, branch lines (such as one to Tamsui) and connections to various ports.
The two construction camps finally met in the middle on April 20, 1908, and Hasegawa left Taiwan shortly after, having completed Liu’s vision 20 years later. A statue of Hasegawa stood in front of then-Taihoku Station from 1910 until the end of Japanese rule.
Taiwan in Time, a column about Taiwan’s history that is published every Sunday, spotlights important or interesting events around the nation that have anniversaries this week.

On Facebook a friend posted a dashcam video of a vehicle driving through the ash-colored wasteland of what was once Taroko Gorge. A crane appears in the video, and suddenly it becomes clear: the video is in color, not black and white. The magnitude 7.2 earthquake’s destruction on April 3 around and above Taroko and its reverberations across an area heavily dependent on tourism have largely vanished from the international press discussions as the news cycle moves on, but local residents still live with its consequences every day. For example, with the damage to the road corridors between Yilan and

May 13 to May 19 While Taiwanese were eligible to take the Qing Dynasty imperial exams starting from 1686, it took more than a century for a locally-registered scholar to pass the highest levels and become a jinshi (進士). In 1823, Hsinchu City resident Cheng Yung-hsi (鄭用錫) traveled to Beijing and accomplished the feat, returning home in great glory. There were technically three Taiwan residents who did it before Cheng, but two were born in China and remained registered in their birthplaces, while historians generally discount the third as he changed his residency back to Fujian Province right after the exams.

With William Lai’s (賴清德) presidential inauguration coming up on May 20, both sides of the Taiwan Strait have been signaling each other, possibly about re-opening lines of communication. For that to happen, there are two ways this could happen, one very difficult to achieve and the other dangerous. During his presidential campaign and since Lai has repeatedly expressed his hope to re-establish communication based on equality and mutual respect, and even said he hoped to meet with Chinese leader Xi Jinping (習近平) over beef noodles and bubble tea. More dramatically, as explored in the May 2 edition of this column,

Tiffany Chang (張芳瑜) is a force to be reckoned with. Crowned Miss Taiwanese American in 2022, she made history last year as the first Taiwanese winner of Miss Asia USA. She’s also a STEM student at Stanford and an aspiring philanthropist — the kind of impressive accolades that has earned her the moniker “light of Taiwan.” At the end of March, Chang returned to Taipei, to “see the people that support me because ultimately that’s what made me win.” She says her Taiwanese supporters shower her with praise: “you inspire us, and you make us feel proud of our Taiwanese heritage,”