Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平) was to arrive in Africa on a four-nation visit yesterday seeking deeper military and economic ties while his rival in a bitter trade war, the Trump administration, shows little interest in the world’s second most populous continent.
This is Xi’s first trip abroad since he was appointed to a second term in March with term limits removed, allowing him to rule for as long as he wants, which rang familiar to some of Africa’s long-entrenched leaders.
China is already Africa’s largest trading partner and it opened its first military base on the continent last year in the Horn of Africa nation of Djibouti, which this month launched a China-backed free trade zone it calls the largest in Africa.

Photo: Reuters
After surpassing the US in arms sales to Africa in the past few years, China this month hosted dozens of African military officials for the first China-Africa defense forum.
Xi is stopping in Senegal and then Rwanda ahead of his participation in a summit of the so-called “BRICS” emerging economies in South Africa that starts on Wednesday.
The summit comes amid the US’ trade war with China and tough trade negotiations with other key economic partners.
Last month, the foreign ministers of BRICS members Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa criticized what they called a “new wave of protectionism,” saying that US measures undermine global trade and economic growth.
Xi’s Africa visit also highlights China’s sweeping Belt and Road Initiative that envisages linking Beijing to Africa, Europe and other parts of Asia via a network of ports, railways, power plants and economic zones.
While such high-profile projects bring badly needed infrastructure and generate economic growth, US officials and others have warned that African nations are indebting themselves to China.
China’s government, banks and contractors from 2000 to 2015 loaned more than US$94 billion to African governments and state-owned companies, the China Africa Research Initiative at Johns Hopkins University said.
“Public debt in the median sub-Saharan African country rose from 34 percent of GDP in 2013 to an estimated 53 percent last year,” a report released in January by Chen Wenjie and Roger Nord of the IMF said.
From oil in nations such as Nigeria and Angola to rare minerals in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa’s natural resources are a major draw for China’s economy, the world’s second-largest behind the US.
However, China’s voracious appetite for resources such as timber and ivory has taken its toll on Africa’s environment, often with the help of corrupt local officials.
On his first visit to a West African country, Xi is to meet with Senegalese President Macky Sall.
Senegal had economic growth of 7.2 percent last year, the IMF said, adding that the nation’s largest trading partner is the EU, notably France.
The stop highlights China’s interest both in Francophone Africa and in Atlantic Ocean ports, while Senegal positions itself as a gateway to the region.
Already, a Chinese-backed industrial park has appeared outside the capital, Dakar, while rail and road links are being improved as part of an ambitious plan to reach the other end of the continent in Djibouti.
Xi then moves on to Rwanda, becoming the first Chinese president to visit the landlocked East African country, whose economy grew by 6.1 percent last year. He is to meet with Rwandan President Paul Kagame and visit a memorial for Rwanda’s 1994 genocide, which killed more than 800,000 people.
The Chinese leader is then to make his third state visit to South Africa for the BRICS summit.
South Africa’s economy, one of Africa’s largest, grew just 1.3 percent last year amid a drop in investor confidence, because of a corruption scandal around former South African president Jacob Zuma, who resigned in February.
Finally, Xi is to stop in the Indian Ocean island nation of Mauritius, whose economy grew by 3.9 percent last year.
China’s economic push is to continue in September with the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, which brings together dozens of heads of state.

NATIONAL SECURITY THREAT: An official said that Guan Guan’s comments had gone beyond the threshold of free speech, as she advocated for the destruction of the ROC China-born media influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China content that threatens national security, the National Immigration Agency said yesterday. Guan Guan has said many controversial things in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” while expressing hope for expedited “reunification.” The agency received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification last year. After investigating, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and account for her actions. Guan Guan appeared as required,
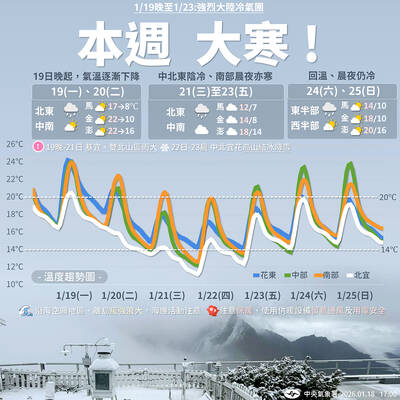
A strong cold air mass is expected to arrive tonight, bringing a change in weather and a drop in temperature, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said. The coldest time would be early on Thursday morning, with temperatures in some areas dipping as low as 8°C, it said. Daytime highs yesterday were 22°C to 24°C in northern and eastern Taiwan, and about 25°C to 28°C in the central and southern regions, it said. However, nighttime lows would dip to about 15°C to 16°C in central and northern Taiwan as well as the northeast, and 17°C to 19°C elsewhere, it said. Tropical Storm Nokaen, currently

PAPERS, PLEASE: The gang exploited the high value of the passports, selling them at inflated prices to Chinese buyers, who would treat them as ‘invisibility cloaks’ The Yilan District Court has handed four members of a syndicate prison terms ranging from one year and two months to two years and two months for their involvement in a scheme to purchase Taiwanese passports and resell them abroad at a massive markup. A Chinese human smuggling syndicate purchased Taiwanese passports through local criminal networks, exploiting the passports’ visa-free travel privileges to turn a profit of more than 20 times the original price, the court said. Such criminal organizations enable people to impersonate Taiwanese when entering and exiting Taiwan and other countries, undermining social order and the credibility of the nation’s

‘SALAMI-SLICING’: Beijing’s ‘gray zone’ tactics around the Pratas Islands have been slowly intensifying, with the PLA testing Taiwan’s responses and limits, an expert said The Ministry of National Defense yesterday condemned an intrusion by a Chinese drone into the airspace of the Pratas Islands (Dongsha Islands, 東沙群島) as a serious disruption of regional peace. The ministry said it detected the Chinese surveillance and reconnaissance drone entering the southwestern parts of Taiwan’s air defense identification zone early yesterday, and it approached the Pratas Islands at 5:41am. The ministry said it immediately notified the garrison stationed in the area to enhance aerial surveillance and alert levels, and the drone was detected in the islands’ territorial airspace at 5:44am, maintaining an altitude outside the effective range of air-defense weaponry. Following