Garbage clogs the banks of the Tigris River in Baghdad, but an army of young volunteers is cleaning it, a rare environmental project in Iraq.
With boots and gloves, they pick up soggy trash, water bottles, aluminum cans and muddy Styrofoam boxes, part of a campaign called the Cleanup Ambassadors.
“This is the first time this area has been cleaned since 2003,” shouts a passer-by about the years of conflict since a US-led invasion toppled then-Iraqi president Saddam Hussein.
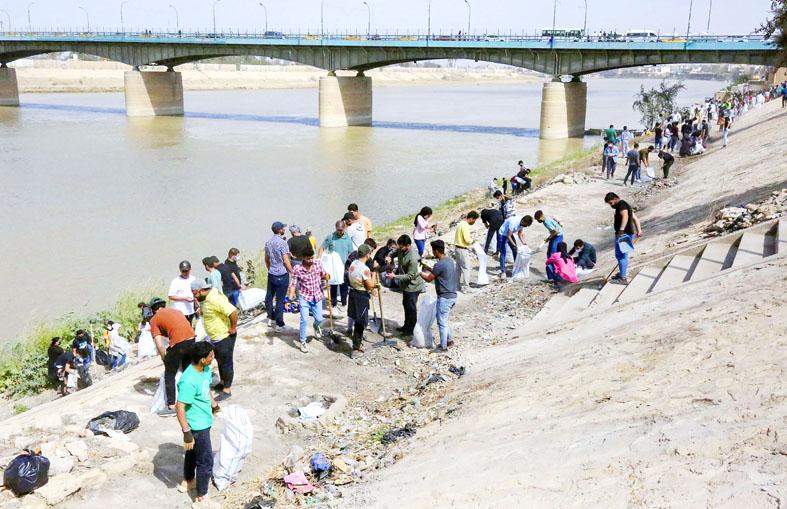

Photo: AFP
The war is over, but Iraq faces another huge threat: a host of interrelated environmental problems from climate change and rampant pollution to dust storms and water scarcity.
The 200 volunteers at work in Baghdad want to be part of the solution, removing garbage from a stretch of one of the mighty rivers that gave birth to the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia.
“It breaks my heart to see the banks of the Tigris in this state,” said one 19-year-old volunteer, who gave only her first name, Rassel, working under the city’s Al-Aimmah Bridge. “We want to change this reality. I want to make my city more beautiful.”
The task is Herculean in a country where it remains common for people to drop their trash on the ground.
The green banks of the Tigris, popular for picnics by families and groups of friends, are usually littered with waste, from single-use plastic bags to the disposable tips of hookah pipes, especially after public holidays.
“There is a lot of plastic, nylon bags and corks,” said Ali, 19, one of the cleanup event’s organizers.
The group then handed their collected waste to the Baghdad City Council, which took it away, bound for a landfill.
More often the garbage ends up directly in the Tigris. It is one of Iraq’s two major waterways, along with the Euphrates, that face a host of environmental pressures.
The rivers and their tributaries are dammed upstream in Turkey and Iran, over-used along the way, and polluted with domestic, industrial and agricultural waste.
The trash that flows downriver clogs riverbanks and wetlands, and poses a threat to terrestrial and aquatic wildlife.
When the water empties into the Persian Gulf, plastic bags are often ingested by turtles or dolphins, and block the airways and stomachs of many species, a UN report said.
In Iraq — which has experienced four decades of conflict and years of political and economic turmoil — separating and recycling waste has yet to become a priority for most people.
The country also lacks proper infrastructure for waste collection and disposal, said Azzam Alwash, head of the non-governmental group Nature Iraq.
“There are no environmentally friendly landfills, and plastic recycling is not economically viable,” he said.
Most garbage ends up in open dumps where it is burned, sending plumes of acrid smoke into the air.
This happens in Iraq’s southern Mesopotamian Marshes, one of the world’s largest inland deltas, which Saddam once had largely drained. They were in 2016 named a UNESCO World Heritage site for their biodiversity and ancient history.
Today a round-the-clock fire outside the town of Souq al-Shuyukh, which is the gateway to the marshes, burns thousands of tonnes of garbage under the open sky, sending white smoke drifting many kilometers away.
“Open burning of waste is a source of air pollution, and the real cost is the shortening of Iraqi lives,” Alwash said. “But the state has no money to build recycling facilities.”
Even worse is the air pollution caused by flaring — burning off gas that escapes during oil extraction.
This toxic cocktail has contributed to a rise in respiratory illnesses and greenhouse gas emissions, a phenomenon that UN climate experts have voiced alarm about and that the Iraqi government increasingly acknowledges.
Iraqi Minister of the Environment Jassem al-Falahi told the official Iraqi News Agency that waste incineration’s “toxic gases affect people’s lives and health.”
However, there have so far been few government initiatives to tackle Iraq’s environmental woes, and projects such as the Tigris cleanup are leading the way for now.
Ali said he hopes that their effort will have a long-term effect by helping change attitudes.
“Some people have stopped throwing their waste on the street,” Ali said, “Some have even joined us.”

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER: By showing Ju-ae’s ability to handle a weapon, the photos ‘suggest she is indeed receiving training as a successor,’ an academic said North Korea on Saturday released a rare image of leader Kim Jong-un’s teenage daughter firing a rifle at a shooting range, adding to speculation that she is being groomed as his successor. Kim’s daughter, Ju-ae, has long been seen as the next in line to rule the secretive, nuclear-armed state, and took part in a string of recent high-profile outings, including last week’s military parade marking the closing stages of North Korea’s key party congress. Pyongyang’s official Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) released a photo of Ju-ae shooting a rifle at an outdoor shooting range, peering through a rifle scope
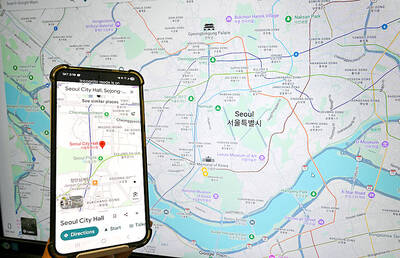
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail