Holding an oversized carrot, a brawny, shirtless man promotes a supplement he claims can enlarge male genitalia — one of countless AI-generated videos on TikTok peddling unproven sexual treatments.
The rise of generative AI has made it easy — and financially lucrative — to mass-produce such videos with minimal human oversight, often featuring fake celebrity endorsements of bogus and potentially harmful products.
In some TikTok videos, carrots are used as a euphemism for male genitalia, apparently to evade content moderation policing sexually explicit language.
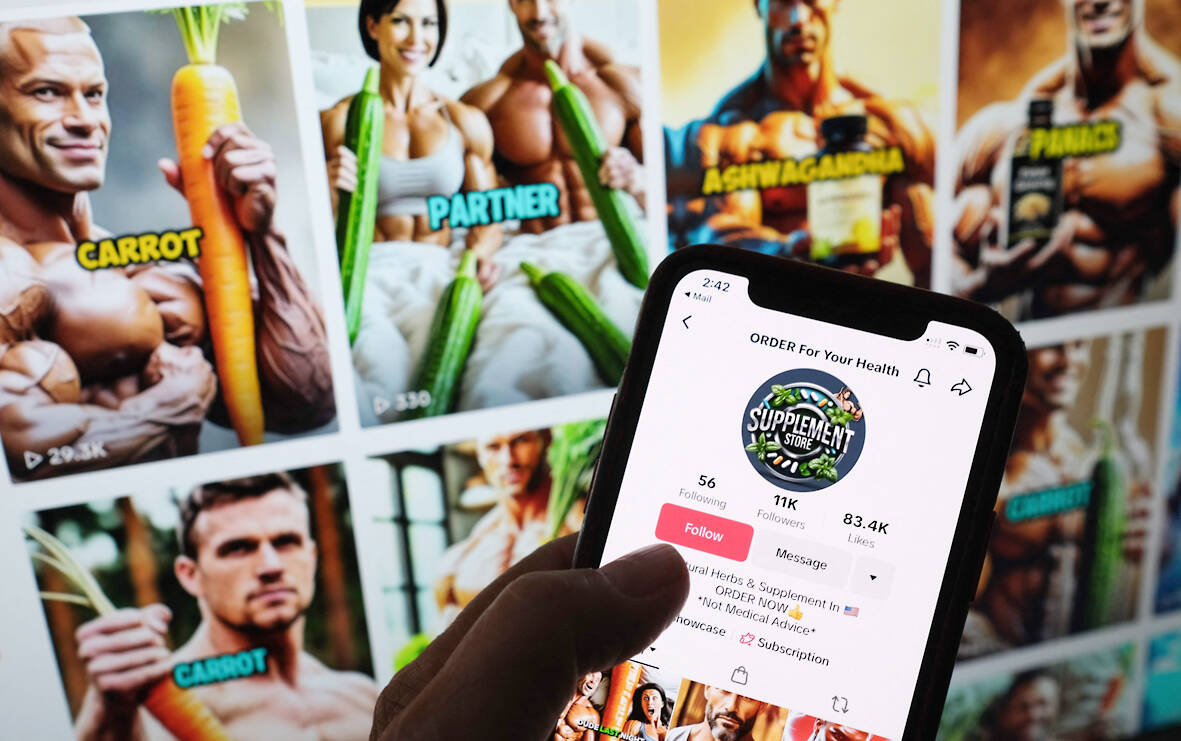
Photo: AFP
“You would notice that your carrot has grown up,” the muscled man says in a robotic voice in one video, directing users to an online purchase link.
“This product will change your life,” the man adds, claiming without evidence that the herbs used as ingredients boost testosterone and send energy levels “through the roof.”
The video appears to be AI-generated, according to a deepfake detection service recently launched by the Bay Area-headquartered firm Resemble AI.
“As seen in this example, misleading AI-generated content is being used to market supplements with exaggerated or unverified claims, potentially putting consumers’ health at risk,” said Zohaib Ahmed, Resemble AI’s chief executive and co-founder.
“We’re seeing AI-generated content weaponized to spread false information.”
‘CHEAP WAY’
The trend underscores how rapid advances in artificial intelligence have fueled what researchers call an AI dystopia, a deception-filled online universe designed to manipulate unsuspecting users into buying dubious products.
They include everything from unverified — and in some cases, potentially harmful — dietary supplements to weight loss products and sexual remedies.
“AI is a useful tool for grifters looking to create large volumes of content slop for a low cost,” said misinformation researcher Abbie Richards.
“It’s a cheap way to produce advertisements,” she added.
Alexios Mantzarlis, director of the Security, Trust and Safety Initiative at Cornell Tech, has observed a surge of “AI doctor” avatars and audio tracks on TikTok that promote questionable sexual remedies.
Some of these videos, many with millions of views, peddle testosterone-boosting concoctions made from ingredients such as lemon, ginger and garlic.
More troublingly, rapidly evolving AI tools have enabled the creation of deepfakes impersonating celebrities such as actress Amanda Seyfried and actor Robert De Niro.
“Your husband can’t get it up?” Anthony Fauci, former director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, appears to ask in a TikTok video promoting a prostate supplement.
But the clip is a deepfake, using Fauci’s likeness.
‘PERNICIOUS’
Many manipulated videos are created from existing ones, modified with AI-generated voices and lip-synced to match what the altered voice says.
“The impersonation videos are particularly pernicious as they further degrade our ability to discern authentic accounts online,” Mantzarlis said.
Last year, Mantzarlis discovered hundreds of ads on YouTube featuring deepfakes of celebrities — including Arnold Schwarzenegger, Sylvester Stallone and Mike Tyson — promoting supplements branded as erectile dysfunction cures.
The rapid pace of generating short-form AI videos means that even when tech platforms remove questionable content, near-identical versions quickly reappear — turning moderation into a game of whack-a-mole.
Researchers say this creates unique challenges for policing AI-generated content, requiring novel solutions and more sophisticated detection tools.
Fact checkers have repeatedly debunked scam ads on Facebook promoting treatments — including erectile dysfunction cures — that use fake endorsements by Ben Carson, a neurosurgeon and former US cabinet member.
Yet many users still consider the endorsements legitimate, illustrating the appeal of deepfakes. “Scammy affiliate marketing schemes and questionable sex supplements have existed for as long as the Internet and before,” Mantzarlis said.
“As with every other bad thing online, generative AI has made this abuse vector cheaper and quicker to deploy at scale.”

The Lee (李) family migrated to Taiwan in trickles many decades ago. Born in Myanmar, they are ethnically Chinese and their first language is Yunnanese, from China’s Yunnan Province. Today, they run a cozy little restaurant in Taipei’s student stomping ground, near National Taiwan University (NTU), serving up a daily pre-selected menu that pays homage to their blended Yunnan-Burmese heritage, where lemongrass and curry leaves sit beside century egg and pickled woodear mushrooms. Wu Yun (巫雲) is more akin to a family home that has set up tables and chairs and welcomed strangers to cozy up and share a meal

Dec. 8 to Dec. 14 Chang-Lee Te-ho (張李德和) had her father’s words etched into stone as her personal motto: “Even as a woman, you should master at least one art.” She went on to excel in seven — classical poetry, lyrical poetry, calligraphy, painting, music, chess and embroidery — and was also a respected educator, charity organizer and provincial assemblywoman. Among her many monikers was “Poetry Mother” (詩媽). While her father Lee Chao-yuan’s (李昭元) phrasing reflected the social norms of the 1890s, it was relatively progressive for the time. He personally taught Chang-Lee the Chinese classics until she entered public

Last week writer Wei Lingling (魏玲靈) unloaded a remarkably conventional pro-China column in the Wall Street Journal (“From Bush’s Rebuke to Trump’s Whisper: Navigating a Geopolitical Flashpoint,” Dec 2, 2025). Wei alleged that in a phone call, US President Donald Trump advised Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi not to provoke the People’s Republic of China (PRC) over Taiwan. Wei’s claim was categorically denied by Japanese government sources. Trump’s call to Takaichi, Wei said, was just like the moment in 2003 when former US president George Bush stood next to former Chinese premier Wen Jia-bao (溫家寶) and criticized former president Chen

President William Lai (賴清德) has proposed a NT$1.25 trillion (US$40 billion) special eight-year budget that intends to bolster Taiwan’s national defense, with a “T-Dome” plan to create “an unassailable Taiwan, safeguarded by innovation and technology” as its centerpiece. This is an interesting test for the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT), and how they handle it will likely provide some answers as to where the party currently stands. Naturally, the Lai administration and his Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) are for it, as are the Americans. The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) is not. The interests and agendas of those three are clear, but