They have been in a committed relationship for more than 13 years, and even had a wedding in 2019. Since then, Danaya Phonphayung and Sunma Piamboon, both women, have considered themselves a married couple, even if same-sex marriages were not legally recognized.
The walls of their home in suburban Bangkok are decorated with faded photos from their happy union, filled with joy and love from their families and friends.
Today, their wedded status will be recognized by the nation as well, when a law that allows members of the LGBTQ+ community in Thailand to get married and have the same legal rights as heterosexual couples takes effect.

Photo: AP
The couple said they can’t wait to formalize their union. They plan to register their marriage at a district office near their home on the very first day that the law allows.
“I think I’ll cry,” Danaya, an office worker, said with a big smile, thinking about the moment that they will sign the paper.
“I’m so happy. It’s something that was more than I could’ve dreamed of, that suddenly this day is happening.”
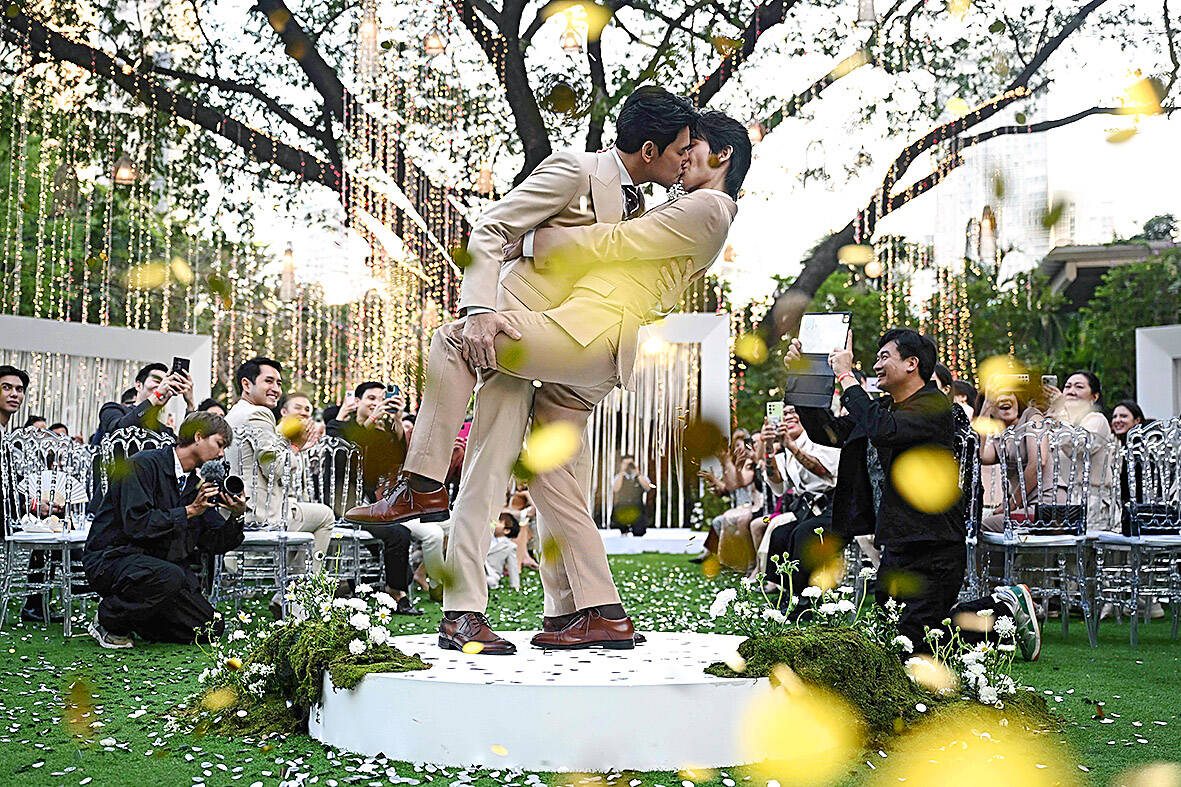

Photo: AP
“We live together. We bought a house. We bought a car. But we cannot share these things together like a married couple. When this is happening, we feel that it’s our rights that we need to secure as quickly as possible,” she said.
The marriage equality bill, which sailed through both the House of Representatives and the Senate, amended the Civil and Commercial Code to change the words “men and women” and “husband and wife” to “individuals” and “marriage partners.” It would open up access to full legal, financial and medical rights for LGBTQ+ couples.
Sunma, who owns a travel agency, said that she had realized how crucial being legally married was when Danaya was hospitalized with dengue fever, as they don’t live close to her parents.
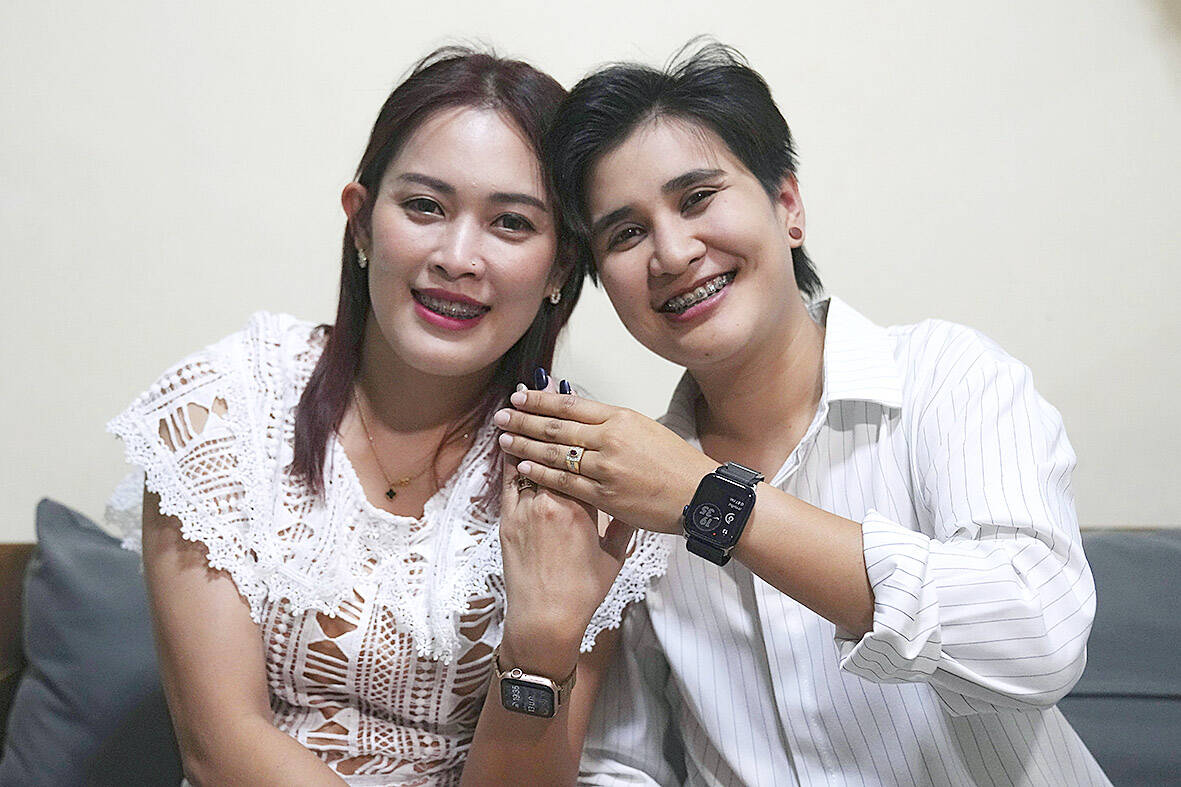

Photo: AP
“The doctors asked me who I was, and I said I was the girlfriend, and they were like, ‘so what?’”
“I couldn’t make any decision until her condition became quite serious ... I was so upset, like, if I had lost her … there would be nothing that could’ve made up for it. So, I think this is very important for both of us,” she said.
BECOMING LAW
Thailand has a reputation for acceptance and inclusivity, but struggled for decades to pass a marriage equality law. Thai society largely holds conservative values. Members of the LGBTQ+ community say they face discrimination in everyday life, although they note that things have improved greatly in recent years.
The government led by the Pheu Thai party made marriage equality one of its main goals. It made a major effort to identify itself with the annual Bangkok Pride parade in June, in which thousands of people celebrated in one of Bangkok’s busiest commercial districts.
Last week, Government House invited dozens of LGBTQ+ couples and activists for a photo op and a meeting with Prime Minister Paetongtarn Shinawatra and several high ranking officials to celebrate the law coming into effect, making Thailand the first in Southeast Asia and the third place in Asia, after Taiwan and Nepal, to legalize same-sex marriage.
“It is almost like a dream, but it’s not. So, congratulations to all,” Paetongtarn said.
“I think it’s very important that the world notice us, and know that in this small country we have this kind of thought. We have this kind of support for our people. So, we all should be proud.”
The organizers of Bangkok Pride have collaborated with relevant government agencies to hold a grand celebration in central Bangkok and facilitate couples who wish to register their marriage on the very first day. They said that more than 300 couples have registered to officially tie the knot at today’s event.
“[The law] is about returning our dignity, and confirming that we also have dignity as a human being,” said Ann “Waaddao” Chumaporn, a gender equality activist and the lead organizer of Bangkok Pride.
“That day is going to be meaningful to all the couples that have gone through this journey together. I’d like to thank everyone, every love, that has faithfully struggled so that today would finally happen.”
IMPLEMENTATION
The government and state agencies in Thailand are historically traditional in outlook. To prepare them for change, the Bangkok Metropolitan Administration said that it has organized workshops for staff of all Bangkok district offices who are in charge of handling marriage registration. They included lectures raising awareness about gender diversity and guidance on how to properly communicate with those who come for the service.
“It’s like a missing piece of the jigsaw,” Bangkok Deputy Gov. Sanon Wangsrangboon said at one of the workshops earlier this month.
“Society is ready. The law is getting ready. But the last piece of the jigsaw is the understanding from officials.”
He acknowledged there that would be problems in the beginning, but said that he hoped they would gradually improve over time.
After they register their marriage, Sunma said that she’s looking forward to having a “real marriage celebration” with her and Danaya’s families.
“It’s not just the two of us that are happy, but both of our families feel it is a big deal, and it is what everyone has been waiting for. Everyone said they are waiting for Jan. 23,” she said.

One of the biggest sore spots in Taiwan’s historical friendship with the US came in 1979 when US president Jimmy Carter broke off formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan’s Republic of China (ROC) government so that the US could establish relations with the People’s Republic of China (PRC). Taiwan’s derecognition came purely at China’s insistence, and the US took the deal. Retired American diplomat John Tkacik, who for almost decade surrounding that schism, from 1974 to 1982, worked in embassies in Taipei and Beijing and at the Taiwan Desk in Washington DC, recently argued in the Taipei Times that “President Carter’s derecognition

This year will go down in the history books. Taiwan faces enormous turmoil and uncertainty in the coming months. Which political parties are in a good position to handle big changes? All of the main parties are beset with challenges. Taking stock, this column examined the Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) (“Huang Kuo-chang’s choking the life out of the TPP,” May 28, page 12), the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) (“Challenges amid choppy waters for the DPP,” June 14, page 12) and the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) (“KMT struggles to seize opportunities as ‘interesting times’ loom,” June 20, page 11). Times like these can

JUNE 30 to JULY 6 After being routed by the Japanese in the bloody battle of Baguashan (八卦山), Hsu Hsiang (徐驤) and a handful of surviving Hakka fighters sped toward Tainan. There, he would meet with Liu Yung-fu (劉永福), leader of the Black Flag Army who had assumed control of the resisting Republic of Formosa after its president and vice-president fled to China. Hsu, who had been fighting non-stop for over two months from Taoyuan to Changhua, was reportedly injured and exhausted. As the story goes, Liu advised that Hsu take shelter in China to recover and regroup, but Hsu steadfastly
You can tell a lot about a generation from the contents of their cool box: nowadays the barbecue ice bucket is likely to be filled with hard seltzers, non-alcoholic beers and fluorescent BuzzBallz — a particular favorite among Gen Z. Two decades ago, it was WKD, Bacardi Breezers and the odd Smirnoff Ice bobbing in a puddle of melted ice. And while nostalgia may have brought back some alcopops, the new wave of ready-to-drink (RTD) options look and taste noticeably different. It is not just the drinks that have changed, but drinking habits too, driven in part by more health-conscious consumers and