Tashkan Khakimova, 77, crouched over a wooden weaving machine, wool speeding through her fingers, using a traditional rug-making technique in Kyrgyzstan’s remote mountainous region of Batken.
A young schoolgirl held the remaining wool next to Khakimova, dressed in a white headscarf and a velvet jacket with traditional embroidery on it. After several hundred hours of work, the wool will be transformed into a shyrdak: a traditional Kyrgyz rug.
Khakimova is one of a shrinking number of mostly elderly people living in the Central Asian country’s mountainous areas who know how to make a shyrdak. Many worry the ancient art will die out.
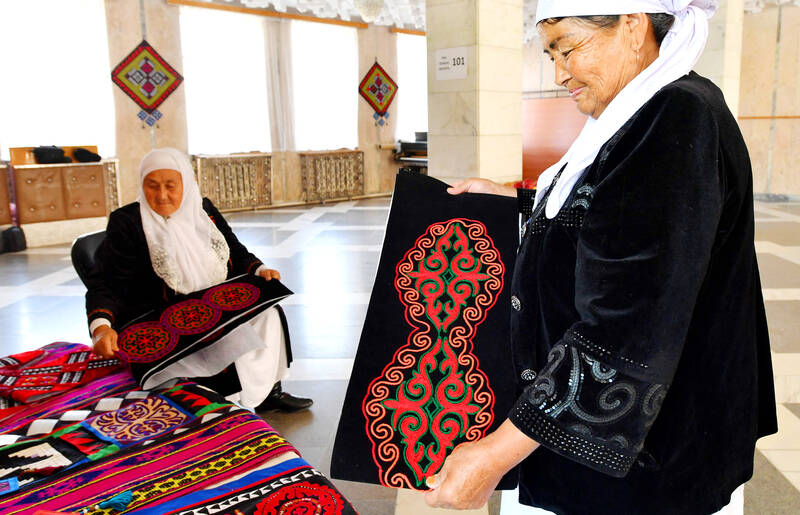

Photo: AFP
“Our parents taught us the technique, but people are forgetting it,” Khakimova said. She is part of a group of older women calling themselves the “Happy Grandmas” who meet in the small town of Kadamjay. nestled between the Alay mountains, to preserve the endangered craft and boost their meager pensions.
UNESCO has warned that the skill of making the unique rugs is “in need of urgent safeguarding,” with an abundance of synthetic carpets and the young being mostly disinterested.
The “Happy Grandmas” have a mission: to attract Kadamjay’s youngsters to learn the ancient technique. The group of around 20 women meet several times a week in the local Soviet-era house of culture, encouraging school children to learn how to weave.
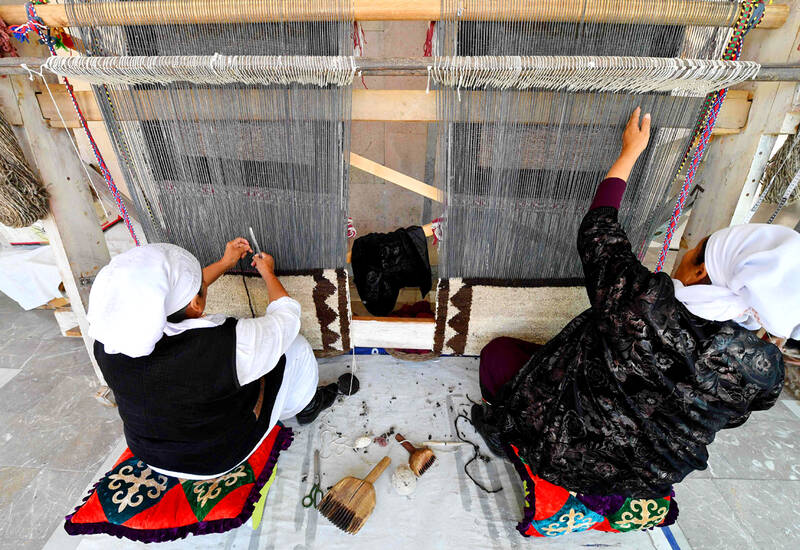

Photo: AFP
“We come here so that this craft can be passed on from generation to generation, to teach it to young people,” Khakimova said.
Rakhat Dzhoroyeva, another woman in the group, said it was important to preserve the rugs as “these are customs that we inherited from our ancestors.”
“We don’t want to sit at home with our arms crossed,” she said. “We decided to continue the tradition.”
The women use wool from their own animals to make the rugs.
“Production costs nothing,” Dzhoroyeva said, adding that wool is collected from cattle, sheep and goats and “nothing goes to waste.”
She energetically lifts threads with a comb to strengthen the knots of the brown carpet she is making. The shyrdak will then be decorated with colorful traditional patterns recalling the nomadic culture of the Kyrgyz people, before being cut out and quilted to make it more resistant.
The pensioners meet at the “House of Culture of the Metallurgists” of Kadamjay — a city built in the 1930s around a huge metals factory that is now shut down. Hoping to “attract the young,” the women take center stage in the building, with their traditional singing reverberating around the marble hall.
Curious schoolgirls walk past, with a six-year-old soon crouching down to examine the work done by the retirees.
Living in Kyrgyzstan’s poorest region, the “Happy Grandmas” also hope selling the home-made rugs will boost their pensions.
“I get around 6,000 som in pension (around US$67 a month),” Saliya Bozhoyeva, another woman in the group, said. “We can sell rugs for several hundred euros, it allows me to compensate (for) my pension.”
The rusty, abandoned metals factory — which used to employ many of the women — towers over Kadamjay. Its bankruptcy has led to unemployment and an exodus of the working population.
“My husband and I used to work at the factory, but today young people are forced to look elsewhere,” Khakimova said.
Like many families in Kyrgyzstan, her children have gone to Russia — a traditional place of employment for Central Asians — to look for work.
But the “Happy Grandmas” have some hope: there has been a renewed interest in traditional Kyrgyz carpets. Easing tensions with neighboring Uzbekistan have raised the possibility of attracting tourists to this remote region and the chance to strengthen the local economy — with some orders even coming from abroad.
“We have a lot of orders, mainly from Bishkek,” Dzhoroyeva said.
She added, joyfully: “And soon, we will send a rug to Japan.”
Google unveiled an artificial intelligence tool Wednesday that its scientists said would help unravel the mysteries of the human genome — and could one day lead to new treatments for diseases. The deep learning model AlphaGenome was hailed by outside researchers as a “breakthrough” that would let scientists study and even simulate the roots of difficult-to-treat genetic diseases. While the first complete map of the human genome in 2003 “gave us the book of life, reading it remained a challenge,” Pushmeet Kohli, vice president of research at Google DeepMind, told journalists. “We have the text,” he said, which is a sequence of

On a harsh winter afternoon last month, 2,000 protesters marched and chanted slogans such as “CCP out” and “Korea for Koreans” in Seoul’s popular Gangnam District. Participants — mostly students — wore caps printed with the Chinese characters for “exterminate communism” (滅共) and held banners reading “Heaven will destroy the Chinese Communist Party” (天滅中共). During the march, Park Jun-young, the leader of the protest organizer “Free University,” a conservative youth movement, who was on a hunger strike, collapsed after delivering a speech in sub-zero temperatures and was later hospitalized. Several protesters shaved their heads at the end of the demonstration. A

In August of 1949 American journalist Darrell Berrigan toured occupied Formosa and on Aug. 13 published “Should We Grab Formosa?” in the Saturday Evening Post. Berrigan, cataloguing the numerous horrors of corruption and looting the occupying Republic of China (ROC) was inflicting on the locals, advocated outright annexation of Taiwan by the US. He contended the islanders would welcome that. Berrigan also observed that the islanders were planning another revolt, and wrote of their “island nationalism.” The US position on Taiwan was well known there, and islanders, he said, had told him of US official statements that Taiwan had not

We have reached the point where, on any given day, it has become shocking if nothing shocking is happening in the news. This is especially true of Taiwan, which is in the crosshairs of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), uniquely vulnerable to events happening in the US and Japan and where domestic politics has turned toxic and self-destructive. There are big forces at play far beyond our ability to control them. Feelings of helplessness are no joke and can lead to serious health issues. It should come as no surprise that a Strategic Market Research report is predicting a Compound