Citizens are alarmed by the climate crisis, but most believe they are already doing more to preserve the planet than anyone else, including their government, and few are willing to make significant lifestyle changes, an international survey has found.
“The widespread awareness of the importance of the climate crisis illustrated in this study has yet to be coupled with a proportionate willingness to act,” the survey of 10 countries including the US, UK, France and Germany, observed.
Emmanuel Riviere, director of international polling at Kantar Public, said the survey, carried out in late September and published to coincide with the Cop26 climate conference in Glasgow, contained “a double lesson for governments.”
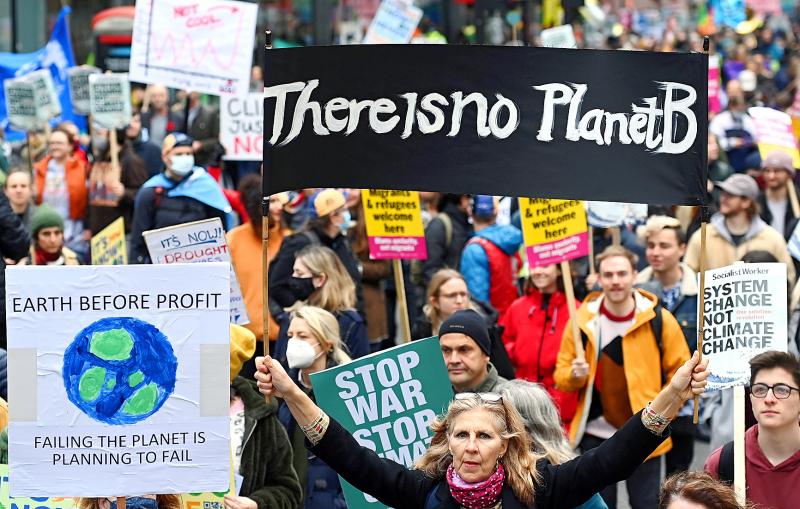

Photo: EPA-EFE
They have, first, “to measure up to people’s expectations,” Riviere said. “But they also have to persuade people not of the reality of the climate crisis — that’s done — but of what the solutions are, and of how we can fairly share responsibility for them.”
The survey found that 62 percent of people surveyed saw the climate crisis as the main environmental challenge the world was now facing, ahead of air pollution (39 percent), the impact of waste (38 percent) and new diseases (36 percent).
But when asked to rate their individual action against others’ such as governments, business and the media, people generally saw themselves as much more committed to the environment than others in their local community, or any institution.

Photo: AP
About 36 percent rated themselves “highly committed” to preserving the planet, while only 21 percent felt the same was true of the media and 19 percent of local government. A mere 18 percent felt their local community was equally committed, with national governments (17 percent) and big corporations (13 percent) seen as even less engaged.
Respondents were also lukewarm about doing more themselves, citing a wide range of reasons. Most (76 percent) of those surveyed across the 10 countries said they would accept stricter environmental rules and regulations, but almost half (46 percent) felt that there was no real need for them to change their personal habits.
Only 51 percent said they would definitely take individual climate action, with 14 percent saying they would definitely not and 35 percent torn. People in Poland and Singapore (56 percent) were the most willing to act, and in Germany (44 percent) and the Netherlands (37 percent) the least.
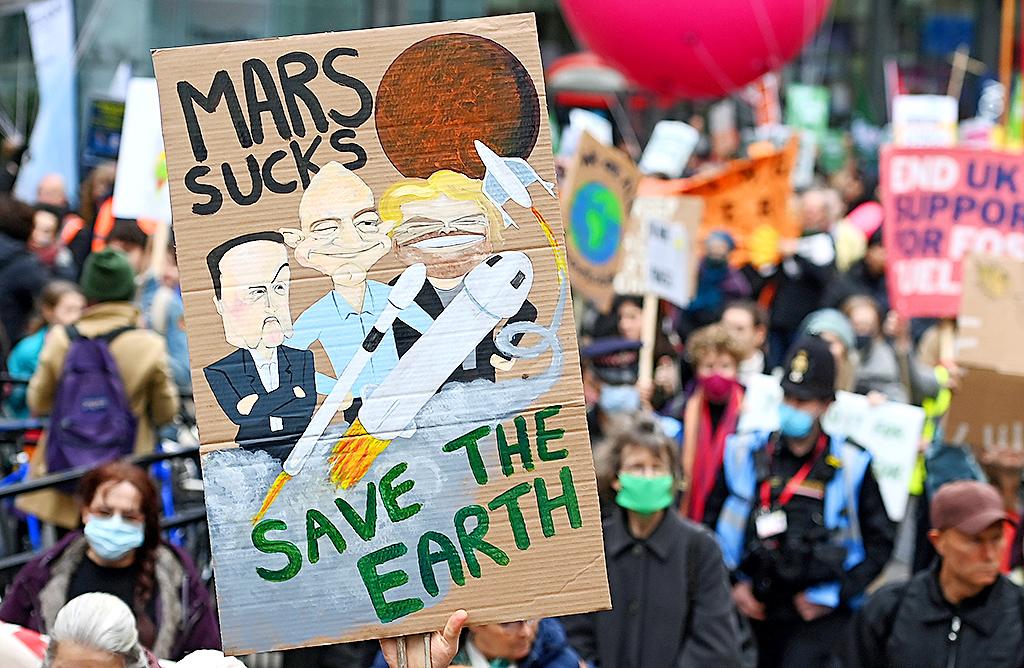

Photo: EPA-EFE
The most common reasons given for not being willing to do more for the planet were “I feel proud of what I am currently doing” (74 percent), “There isn’t agreement among experts on the best solutions” (72 percent) and “I need more resources and equipment from public authorities” (69 percent).
Other reasons for not wanting to do more included “I can’t afford to make those efforts” (60 percent), “I lack information and guidance on what to do” (55 percent), “I don’t think individual efforts can really have an impact” (39 percent), “I believe environmental threats are overestimated” (35 percent) and “I don’t have the headspace to think about it” (33 percent).
Asked which actions to preserve the planet should be prioritized, moreover, people attributed more importance to measures that were already established habits, required less individual effort or for which they bore little direct responsibility.
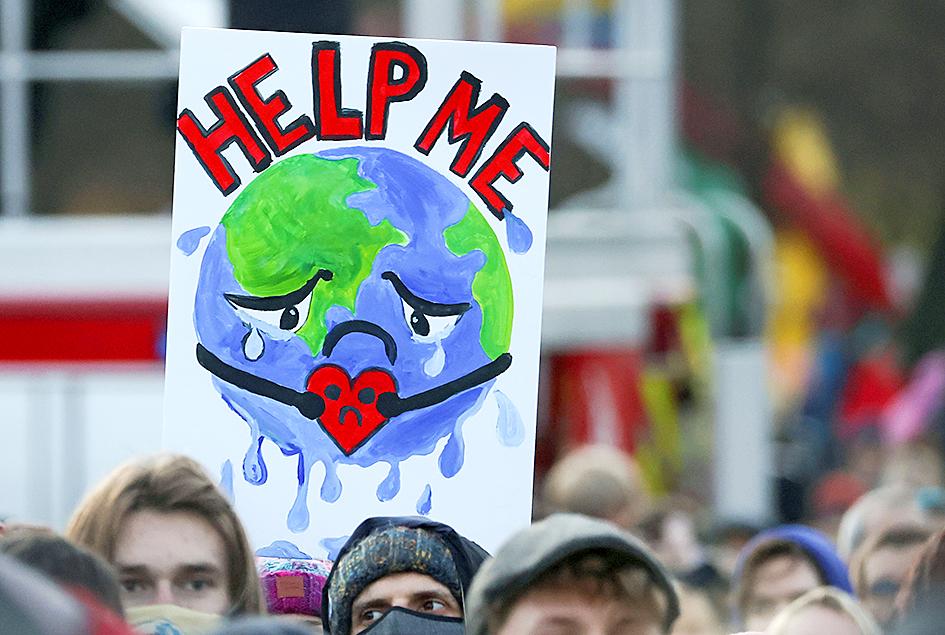

Photo: Reuters
About 57 percent, for example, said that reducing waste and increasing recycling was “very important.” Other measures seen as priorities were reversing deforestation (54 percent), protecting endangered animal species (52 percent), building energy-efficient buildings (47 percent) and replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy (45 percent).
Respondents viewed measures likely to affect their own lifestyles, however, as significantly less important: reducing people’s energy consumption was seen as a priority by only 32 percent, while favoring public transport over cars (25 percent) and radically changing our agricultural model (24 percent) were similarly unpopular.
Only 23 percent felt that reducing plane travel and charging more for products that did not respect environmental norms were important to preserve the planet, while banning fossil fuel vehicles (22 percent) and reducing meat consumption (18 percent) and international trade (17 percent) were seen as even lower priorities.
“Citizens are undeniably concerned by the state of the planet, but these findings raise doubts regarding their level of commitment to preserving it,” the study said. “Rather than translating into a greater willingness to change their habits, citizens’ concerns are particularly focused on their negative assessment of governments’ efforts.”
Representative samples of more than 1,000 people were questioned in the US, UK, Spain, France, the Netherlands, Germany, Sweden, Poland, Singapore and New Zealand.
People gave themselves the highest score for commitment everywhere except Sweden, while only in Singapore and New Zealand were national governments seen as highly engaged. The gulf between citizens’ view of their own efforts (44 percent) and that of their government (16 percent) was highest in the UK.

Dissident artist Ai Weiwei’s (艾未未) famous return to the People’s Republic of China (PRC) has been overshadowed by the astonishing news of the latest arrests of senior military figures for “corruption,” but it is an interesting piece of news in its own right, though more for what Ai does not understand than for what he does. Ai simply lacks the reflective understanding that the loneliness and isolation he imagines are “European” are simply the joys of life as an expat. That goes both ways: “I love Taiwan!” say many still wet-behind-the-ears expats here, not realizing what they love is being an
Google unveiled an artificial intelligence tool Wednesday that its scientists said would help unravel the mysteries of the human genome — and could one day lead to new treatments for diseases. The deep learning model AlphaGenome was hailed by outside researchers as a “breakthrough” that would let scientists study and even simulate the roots of difficult-to-treat genetic diseases. While the first complete map of the human genome in 2003 “gave us the book of life, reading it remained a challenge,” Pushmeet Kohli, vice president of research at Google DeepMind, told journalists. “We have the text,” he said, which is a sequence of

Every now and then, even hardcore hikers like to sleep in, leave the heavy gear at home and just enjoy a relaxed half-day stroll in the mountains: no cold, no steep uphills, no pressure to walk a certain distance in a day. In the winter, the mild climate and lower elevations of the forests in Taiwan’s far south offer a number of easy escapes like this. A prime example is the river above Mudan Reservoir (牡丹水庫): with shallow water, gentle current, abundant wildlife and a complete lack of tourists, this walk is accessible to nearly everyone but still feels quite remote.

It’s a bold filmmaking choice to have a countdown clock on the screen for most of your movie. In the best-case scenario for a movie like Mercy, in which a Los Angeles detective has to prove his innocence to an artificial intelligence judge within said time limit, it heightens the tension. Who hasn’t gotten sweaty palms in, say, a Mission: Impossible movie when the bomb is ticking down and Tom Cruise still hasn’t cleared the building? Why not just extend it for the duration? Perhaps in a better movie it might have worked. Sadly in Mercy, it’s an ever-present reminder of just