Craftsman Mohammad Zakir, 35, who lives in a low-lying area of Karachi’s Orangi Town, does not recall the authorities ever cleaning out the stormwater drain serving his neighborhood.
Thorani Goth in West District was flooded during the fourth bout of monsoon rain this season from Aug. 6-8.
During that — and a previous downpour late last month — water came up 1.2-1.5m inside Zakir’s home, ruining furniture, electrical equipment and important documents.
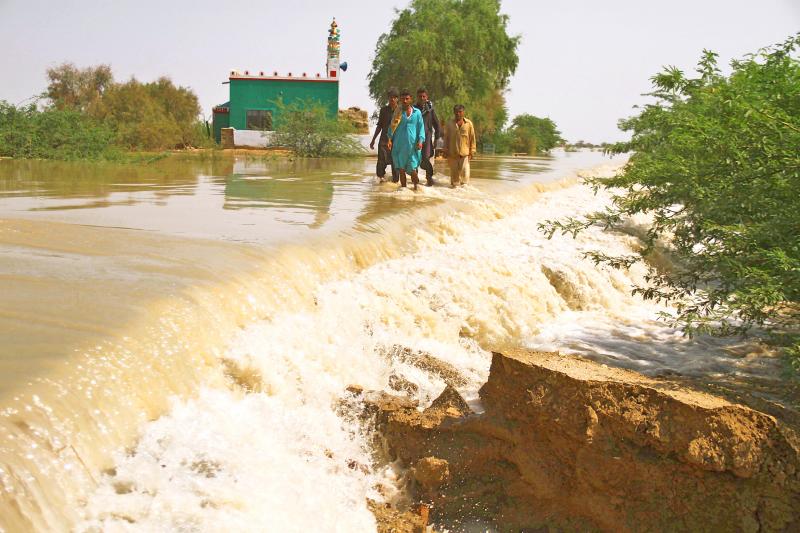

Photo: EPA-EFE
It also soaked an order of 250 women’s garments he was due to decorate with sequins and beads — his first job in five months due to the coronavirus pandemic.
“I’ll put them out to dry to see if there are water stains on them,” said the informal-sector worker.
If the clothes were ruined, he would have to bear half the cost of 250,000 Pakistani rupees (US$1,488), he added.
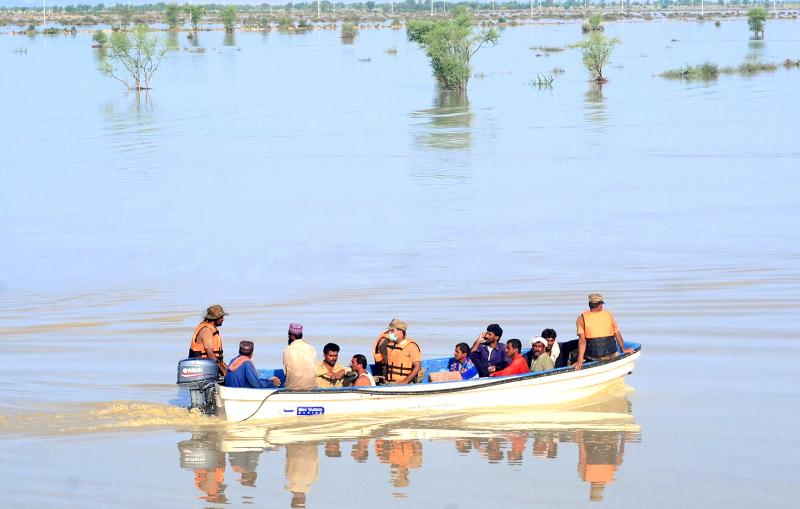

Photo: AP
Karachi Mayor Waseem Akhtar said people “are certainly not exaggerating when they say water comes up chest-high into their homes.”
The city has a network of 550 stormwater drains which zig-zag through the city and flow out into the Arabian Sea, but many are obstructed by illegal construction, waste and sludge.
Akhtar said the city authorities cleaned out the drains every year before the monsoon, except last year when the provincial government did not provide the funds for the work.
In the mayor’s four-year term, which ends this month, management of Karachi’s services have been hamstrung by disputes between different levels of government.
Meanwhile the city’s infrastructure is struggling to cope with heavy monsoon rains, as seen this year.
Sardar Sarfaraz, Karachi head of the Pakistan Meteorological Department, said rainfall of as little as 50mm could cause urban flooding in some of Karachi’s low-lying areas, with the most recent downpour easily exceeding that across the city.
Scientists are still figuring out how global warming will affect the Asian monsoon, but in many parts of the world, higher temperatures are fueling more intense bouts of rainfall.
Sarfaraz noted the trend is for more erratic weather patterns, as predicted by climate scientists.
In Karachi, the August rains killed 22 people, 11 of them by electrocution, after 10 died in July. From 2014 to last year, the city recorded more than 70 rain-related deaths, with 2018 an exception as it was largely dry.
After the havoc last month — with main roads submerged, sewage spewing from manholes and into homes, and power cuts lasting for hours — Prime Minister Imran Khan tasked the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) with sorting out the city’s drains.
The NDMA, helped by the military’s engineering wing, said it had cleaned three major drains in just under a week, clearing 42 choke points and removing more than 31,000 tonnes of sludge.
After touring the city, Sindh Information Minister Syed Nasir Hussain Shah told Pakistan’s Dawn newspaper there were no floods in the city, despite the intensity of this month’s rain, as prevention policies had been effectively implemented.
But Zakir’s experience does not back up that assertion.
ILLEGAL BUILDING
Hot sun after the monsoon rain has provided some respite for Zakir’s family and the 13 million city residents, out of a population of more than 17 million, who live in informal settlements that are prone to flooding.
Zakir blamed illegal construction along the drainage channels, adding that “the government needs to come here and bulldoze” the buildings.
“The stormwater drains, some as wide as 200 feet, have over the years, due to unauthorized construction, narrowed to just 30 feet — so what do you expect?” said Mayor Akhtar.
The main responsibility lies both with residents who have encroached on land along the drain, and the provincial government for letting it happen, said the outgoing mayor.
The province of Sindh has taken a larger share of control from the city authority but has not provided the budget owed, which a court ruling ordered it to pay, Akhtar said.
A Sindh government spokesman said it did not owe money to the Karachi Metropolitan Corporation, to which it had transferred 50 billion rupees in the last three and a half years.
Solid waste dumped into stormwater drains exacerbates the flooding. It is estimated that the mega-city generates 13,000 tonnes of garbage daily.
The Sindh Solid Waste Management Board collects 70 percent of that and takes it to two landfills, but told the Thomson Reuters Foundation it does not know what happens to the rest.
Sewage is also being dumped in storm drains, as little has been invested in rehabilitating the crumbling sewerage system for two decades despite the city’s expansion, officials said.
LONGER-TERM PLAN?
Zubair Channa, director of the Sindh government-led Solid Waste Emergency and Efficiency Project (SWEEP), funded with $100 million from the World Bank, said encroachment on most of Karachi’s large drains over a long period, coupled with their uneven width, caused disturbances in the flow of water.
Drains feeding into the big water channels are also not well maintained, making the flooding worse, noted the civil engineer.
“What is needed is a comprehensive engineering solution,” he said, rather than “firefighting” each year as the city does now.
In its first year, the SWEEP project has hired contractors to remove about 10 million cubic feet of sludge from the drains and deposit it in landfill by the end of August, he noted.
With floods causing so much devastation year after year, Mayor Akhtar said it was time “to take the firm but unpleasant decision” of pulling down illegal buildings.
Before that is done, people must be provided with an alternative, he added.
“There is enough government land that can be used for both vertical expansion as well as developing satellite towns around Karachi, where these people can be shifted,” he said.
But with Karachi run by three tiers of government dominated by three different political parties, real solutions to its problems are often lost in a war of words.
“We need the judiciary and the army to sit with experts like architects and town planners to resolve the issue,” Akhtar said.

March 2 to March 8 Gunfire rang out along the shore of the frontline island of Lieyu (烈嶼) on a foggy afternoon on March 7, 1987. By the time it was over, about 20 unarmed Vietnamese refugees — men, women, elderly and children — were dead. They were hastily buried, followed by decades of silence. Months later, opposition politicians and journalists tried to uncover what had happened, but conflicting accounts only deepened the confusion. One version suggested that government troops had mistakenly killed their own operatives attempting to return home from Vietnam. The military maintained that the

Taiwan has next to no political engagement in Myanmar, either with the ruling military junta nor the dozens of armed groups who’ve in the last five years taken over around two-thirds of the nation’s territory in a sprawling, patchwork civil war. But early last month, the leader of one relatively minor Burmese revolutionary faction, General Nerdah Bomya, who is also an alleged war criminal, made a low key visit to Taipei, where he met with a member of President William Lai’s (賴清德) staff, a retired Taiwanese military official and several academics. “I feel like Taiwan is a good example of
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades