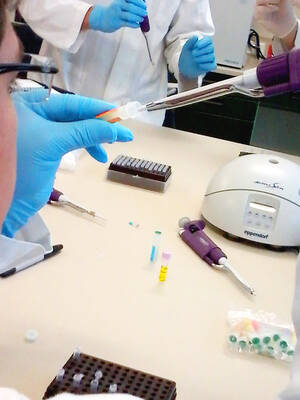
On a raft floating off Hong Kong’s rural eastern coastline, former investment banker turned scientist Yan Wa-tat patiently scrapes barnacles off some 2,000 oysters — a tiresome but crucial part of his mission to bring back pearl farming.
“The species was once abundant in Hong Kong,” the 58-year-old lamented. “We have a history of pearl fishing of over 1,000 years... but because of over-fishing in Hong Kong, we only have very few of them left,” he explained.
Yan is farming Akoya pearl oysters, a specimen prized for jewelry, hoping his research will show other fishermen that the industry could be viable.

Photo: AFP
It’s a calling that requires patience. Cultured pearls take around a year to form and every few weeks Yan has to scrape away any barnacles that might compete for food with his precious oysters.
This kind of knowledge was once ubiquitous in the region. After all, the famous waterway that sustains this part of southern China — along one of the world’s most densely populated regions — is called the Pearl River.
The world’s biggest pearl, once owned by Catherine the Great and known as the “Sleeping Lion” because of its bizarre shape, is thought to have been plucked from southern China’s waters sometime in the 1700s before Dutch traders spirited it away.

Photo: AFP
And Hong Kong — dubbed the “Pearl of the Orient” by its former colonial overlords — remains the world’s largest importer and exporter of pearls, with exports topping US$1.8 billion in 2016, according to UN trade data.
But none of them are produced locally. Over-fishing and market forces have long devastated the wild pearl farming trade in the city.
Cultured pearl farming is a relatively modern industry, and a few Hong Kong ventures rose to the challenge in the 1950s. But they struggled against Japanese competitors who came to dominate the trade. The city’s last pearl farm was shuttered in 1981.
OYSTERS AND CHIPS
Now Yan and a handful of fishermen are trying to change that — with a small cottage industry combining traditional knowledge and cutting-edge technology.
Yan worked in Hong Kong’s lucrative banking sector until his mid-50s, when he decided he wanted to do something “more interesting and also more productive for our society.”
He embarked on a doctorate at Hong Kong University’s School of Biological Sciences looking at how to resurrect the city’s pearl farming trade, something he didn’t even know existed until he stumbled across it in early research.
In his lab at Hong Kong University, Yan researches the best ways to insert a radio frequency identification (RFID) chip into an oyster’s nucleus, around which a pearl will then grow — although the exact mechanism is a closely-guarded secret.
The chips are part of the same family of technology that allows users of mobile phones, transport cards and identity badges to scan into a building or to make a purchase with a simple swipe.
Yan holds a scanning device against one of his oysters and after a small bleep sound, a set of numbers appears on an app on his smartphone.
That tech has multiple benefits. Some 10 to 20 percent of nuclei are expelled by the oyster — meaning a cultured pearl is unable to form — but this is usually only discovered when prizing them open at harvest time.
Using a chip means farmers can simply scan the shell to check if a pearl has been produced.
But serial numbers will also allow buyers to know exactly where their pearls have come from, reducing the risk of fakes or lower quality scams.
NEW HARVEST
In March, a group of local fishermen inspired by Yan’s project carried out a harvest of Akoya pearls — the first to be done in Hong Kong in years.
“I think pearl farming has a future in Hong Kong,” explained Leung Kam-ming, one of the owners of a fishing raft culturing Akoya pearl oysters in the rural Sai Kung region. “I started pearl cultivation to make some extra money.”
Leung farms around 30,000 oysters, selling each cultured pearl for around HK$100 (US$12.70). Any pearls that do not meet jewelry standards can be sold along with the oyster shells as pearl powder for Chinese medicine and cosmetics.
While culturing pearls is no longer common knowledge among the Hong Kong fishing community, Leung hopes his successful harvest will set a precedent for other fishermen to follow.
And in a rare development for densely populated Hong Kong, there is plenty of space for new oyster farms.
Yan estimates some 90 percent of the 1,000 or so fishing rafts in the city’s waters are unused because so few young people wish to join the fishing trade these days.
“If I can show to the fishermen that they can make a living, diversify their income sources, then I think they will be interested in doing this,” he predicted.
Google unveiled an artificial intelligence tool Wednesday that its scientists said would help unravel the mysteries of the human genome — and could one day lead to new treatments for diseases. The deep learning model AlphaGenome was hailed by outside researchers as a “breakthrough” that would let scientists study and even simulate the roots of difficult-to-treat genetic diseases. While the first complete map of the human genome in 2003 “gave us the book of life, reading it remained a challenge,” Pushmeet Kohli, vice president of research at Google DeepMind, told journalists. “We have the text,” he said, which is a sequence of

On a harsh winter afternoon last month, 2,000 protesters marched and chanted slogans such as “CCP out” and “Korea for Koreans” in Seoul’s popular Gangnam District. Participants — mostly students — wore caps printed with the Chinese characters for “exterminate communism” (滅共) and held banners reading “Heaven will destroy the Chinese Communist Party” (天滅中共). During the march, Park Jun-young, the leader of the protest organizer “Free University,” a conservative youth movement, who was on a hunger strike, collapsed after delivering a speech in sub-zero temperatures and was later hospitalized. Several protesters shaved their heads at the end of the demonstration. A

Every now and then, even hardcore hikers like to sleep in, leave the heavy gear at home and just enjoy a relaxed half-day stroll in the mountains: no cold, no steep uphills, no pressure to walk a certain distance in a day. In the winter, the mild climate and lower elevations of the forests in Taiwan’s far south offer a number of easy escapes like this. A prime example is the river above Mudan Reservoir (牡丹水庫): with shallow water, gentle current, abundant wildlife and a complete lack of tourists, this walk is accessible to nearly everyone but still feels quite remote.

In August of 1949 American journalist Darrell Berrigan toured occupied Formosa and on Aug. 13 published “Should We Grab Formosa?” in the Saturday Evening Post. Berrigan, cataloguing the numerous horrors of corruption and looting the occupying Republic of China (ROC) was inflicting on the locals, advocated outright annexation of Taiwan by the US. He contended the islanders would welcome that. Berrigan also observed that the islanders were planning another revolt, and wrote of their “island nationalism.” The US position on Taiwan was well known there, and islanders, he said, had told him of US official statements that Taiwan had not