Enver Tohti Bughda is one of a kind — a surgeon turned bus driver. Now he travels the world, drawing attention towards organ harvesting, nuclear radiation and other public health dangers that are caused by abuses of state power in China.
“After you hear what I did,” he says, “you’ll see why I changed.”
The Medical Code of Ethics ensures doctors use their skills for the welfare of the patient. But Bughda was commanded to violate this code and instead plunder a body for its assets at the state-run hospitals of China’s western frontier. A Uighur from China’s western Xinjiang region, Bughda fled in 1998 after uncovering state secrets while doing research. He was granted asylum in the UK the following year and citizenship in 2005.
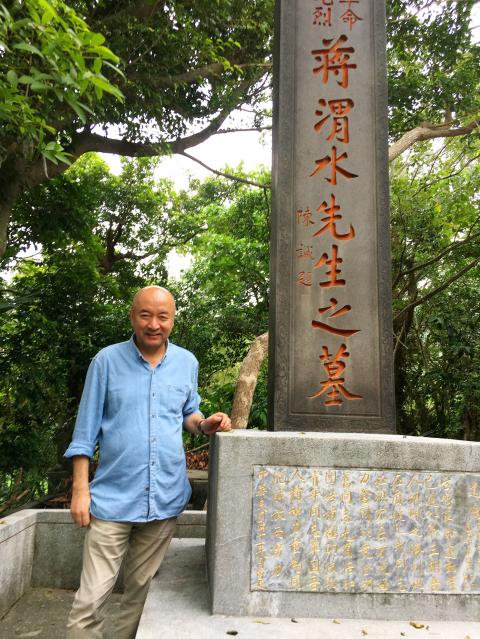

Photo courtesy of Enver Tohti Bughda
He is in Taiwan until next month for a lecture tour en route to Japan.
ORGAN FARMING
Bughda says he had his first encounter with organ harvesting when he was told to perform a very different kind of operation one night in 1995.
The chief surgeon of the Urumqi Railway Central Hospital told him to assemble a team and wait outside where a van soon pulled up and drove them to a remote area, he says.
They were parked out back, Bughda says, and could hear the sounds of shouting, whistles blowing and finally, gun shots.
“That was the signal,” he says.
The van then rushed them in and they saw six bodies lying on the ground, five dressed in prison garb, the sixth in civilian clothes, he adds.
“The backs of the prisoners heads were perforated with a bullet hole, their brains splattered on the ground,” Bughda says. “But the sixth was in civilian clothes and appeared unharmed.”
They carried this body into the back of the van and ordered Bughda to extract the man’s kidneys and liver, he says. After opening him up, Bughda says he saw the heart beating; he had been carefully shot in a way that delayed death.
“From that moment, I became an inhuman robot,” Bughda says. “After the deed was done, they boxed the organs away and told me to go home, saying ‘Remember Doc — nothing happened today,’” Bughda adds.
He says he soon realized that organ harvesting was widespread and systematic in the region.
Bughda says the number of operations has been rising in recent years. According to a report published last year by The International Coalition to End Organ Pillaging in China, there are between 60,000 to 100,000 transplants performed in the country annually.
RADIOACTIVE REGION
It was in that same year that he noticed that rates of cancer caused by nuclear radiation among Uighurs were disproportionately higher than those of the Han majority, Bughda says.
From 1964 to 1996, China carried out 48 nuclear weapons tests in Xinjiang, 23 underground, 23 atmospheric and two that failed, he says.
After a couple of years investigating, Bughda found a direct link between the cancer and the nuclear tests, and in August 1998, he and a crew of British film-makers spent several weeks undercover in Xinjiang producing Death on the Silk Road, a documentary on nuclear radiation in the region.
Bughda says the Chinese government compensates People’s Liberation Army soldiers stationed in Xinjiang, which they began providing after the tests began, proving they had known about its dangerous effects all along.
“Many locals can’t afford chemotherapy,” he says. “What I propose is similar compensation for the rest of the population.”
The final piece of the puzzle were some classified public health records.
“I invited the guard on duty out for dinner and brought along a couple of prostitutes,” he says.
Once we’d got him properly drunk, I said I needed to go to the library to get some papers for my PhD thesis and he handed over the key without a second thought, he adds.
“Reading through the documents, I knew we had a smoking gun,” he says.
June 23 to June 29 After capturing the walled city of Hsinchu on June 22, 1895, the Japanese hoped to quickly push south and seize control of Taiwan’s entire west coast — but their advance was stalled for more than a month. Not only did local Hakka fighters continue to cause them headaches, resistance forces even attempted to retake the city three times. “We had planned to occupy Anping (Tainan) and Takao (Kaohsiung) as soon as possible, but ever since we took Hsinchu, nearby bandits proclaiming to be ‘righteous people’ (義民) have been destroying train tracks and electrical cables, and gathering in villages

This year will go down in the history books. Taiwan faces enormous turmoil and uncertainty in the coming months. Which political parties are in a good position to handle big changes? All of the main parties are beset with challenges. Taking stock, this column examined the Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) (“Huang Kuo-chang’s choking the life out of the TPP,” May 28, page 12), the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) (“Challenges amid choppy waters for the DPP,” June 14, page 12) and the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) (“KMT struggles to seize opportunities as ‘interesting times’ loom,” June 20, page 11). Times like these can

Dr. Y. Tony Yang, Associate Dean of Health Policy and Population Science at George Washington University, argued last week in a piece for the Taipei Times about former president Ma Ying-jeou (馬英九) leading a student delegation to the People’s Republic of China (PRC) that, “The real question is not whether Ma’s visit helps or hurts Taiwan — it is why Taiwan lacks a sophisticated, multi-track approach to one of the most complex geopolitical relationships in the world” (“Ma’s Visit, DPP’s Blind Spot,” June 18, page 8). Yang contends that the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) has a blind spot: “By treating any
Swooping low over the banks of a Nile River tributary, an aid flight run by retired American military officers released a stream of food-stuffed sacks over a town emptied by fighting in South Sudan, a country wracked by conflict. Last week’s air drop was the latest in a controversial development — private contracting firms led by former US intelligence officers and military veterans delivering aid to some of the world’s deadliest conflict zones, in operations organized with governments that are combatants in the conflicts. The moves are roiling the global aid community, which warns of a more militarized, politicized and profit-seeking trend