Hazardous, forced work conditions sometimes akin to slavery have been detected on about 500 industrial fishing vessels worldwide, but identifying those responsible for abuses at sea is hampered by a lack of transparency and regulatory oversight, a new report concluded.
The research by the Financial Transparency Coalition, a Washington-based nonprofit organization that tracks illicit money flows, is the most comprehensive attempt to date to identify the companies operating vessels where tens of thousands of workers every year are estimated to be trapped in unsafe conditions.
The report, published on Wednesday, found that a quarter of vessels suspected of abusing workers are flagged to China, whose distant water fleet dominates fishing on the high seas, traditionally lawless areas beyond the jurisdiction of any single country. Vessels from Taiwan, Russia, Spain, Thailand and South Korea were also accused of mistreatment of fishers.
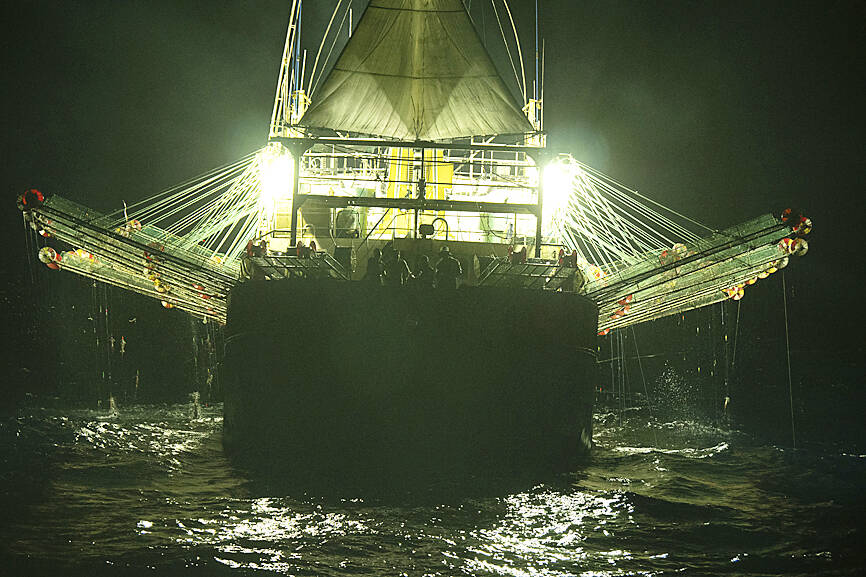

Photo: Sea Shepherd via AP
Forced labor in the seafood industry is a rarely seen but common phenomenon, one increasingly recognized as a “widespread human rights crisis,” the report says.
The Associated Press in 2015 uncovered the plight of thousands of migrant workers from Myanmar, Cambodia and Laos who were abused while employed on Thai vessels whose catch often ended up in the US.
Globally, as many as 128,000 fishers face threats of violence, debt bondage, excessive overtime and other conditions indicative of forced labor, the UN’s International Labor Organization said.
The US and European companies are under increasing pressure to clean up supply chains in labor-intensive industries where worker abuse is widespread. The Financial Action Task Force set up by the G7 countries has identified illegal logging and mining as a key driver of money laundering and encouraged its members to set up publicly available databases to raise awareness about the financial flows that fuel environmental crimes.
However, the seafood industry has so far escaped the same scrutiny, in part because governments often lack the tools to regulate what takes place hundreds of kilometers from land. This week, US President Joe Biden’s administration decided to abandon a planned expansion of the flagship Seafood Import Monitoring Program used to prevent illegal fishing and forced labor on foreign vessels, which supply about 80 percent of the seafood US citizens eat.
“We are once again seeing the heartbreaking reality of what is happening on some commercial fishing vessels out at sea and it’s completely unacceptable,” Beth Lowell, vice president of the conservation group Oceana based in the US, said about the report, in which she had no role. “Forced labor and other human rights abuses should not be the cost for a seafood dinner.”
Offenders are frequently licensed by governments like Panama and Belize with reputations for financial secrecy and minimal oversight of their fleets. Of the vessels suspected of abuse and whose ownership could be identified by the Financial Transparency Coalition, 18 percent flew so-called flags of convenience companies use to avoid careful examination and hide their shareholder structure.
The report identified two Chinese companies — ZheJiang Hairong Ocean Fisheries Co (浙江海融遠洋漁業) and Pingtan Marine Enterprises Ltd (平潭海洋實業) — as the worst offenders, with 10 and seven vessels respectively, accused of human rights violations. A third company, Chinese state-owned China National Fisheries Corp (中國水產), had five.

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER: By showing Ju-ae’s ability to handle a weapon, the photos ‘suggest she is indeed receiving training as a successor,’ an academic said North Korea on Saturday released a rare image of leader Kim Jong-un’s teenage daughter firing a rifle at a shooting range, adding to speculation that she is being groomed as his successor. Kim’s daughter, Ju-ae, has long been seen as the next in line to rule the secretive, nuclear-armed state, and took part in a string of recent high-profile outings, including last week’s military parade marking the closing stages of North Korea’s key party congress. Pyongyang’s official Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) released a photo of Ju-ae shooting a rifle at an outdoor shooting range, peering through a rifle scope
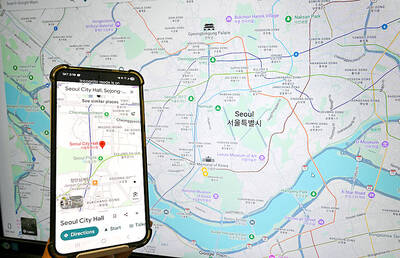
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail