A record number of super-rich people are abandoning Norway for low-tax nations after the center-left government increased wealth taxes to 1.1 percent.
More than 30 Norwegian billionaires and multimillionaires left Norway last year, according to research by the newspaper Dagens Naeringsliv.
That was more than the total number of super-rich people who left the nation during the previous 13 years, it said.
Even more super-rich individuals are expected to leave this year because of the increase in wealth tax in November last year, costing the government tens of millions of lost tax receipts.
Many have moved to Switzerland, where taxes are much lower. They include billionaire fisher turned industrial tycoon Kjell Inge Rokke, who moved to the Italian-speaking canton of Lugano, close to his favored hangout Lake Como and fashion capital Milan.
Rokke, 64, is the fourth-richest Norwegian, with an estimated fortune of about 19.6 billion kroner (US$1.9 billion).
In an open letter, he said: “I’ve chosen Lugano as my new residence — it is neither the cheapest nor has the lowest taxes — but in return, it is a great place with a central location in Europe... For those close to the company and to me, I am just a click away.”
His relocation is costing Norway about 175 million kroner in lost tax revenue a year. Last year, Rokke was the nation’s highest taxed individual.
Dagens Naeringsliv calculated that he has paid about 1.5 billion kroner in tax since 2008.
His move to Switzerland follows a relatively small increase in tax aimed at the nation’s super-rich, who face wealth taxes at both the local and state level. That includes a municipal tax of 0.7 percent on assets in excess of 1.7 million kroner for individuals, or 3.4 million kroner for couples. There is also a state wealth tax rate of 0.3 percent on assets above 1.7 million kroner.
The Norwegian government in November last year raised the state rate to 0.4 percent for assets above 20 million kroner for individuals and 40 million kroner for couples, taking the maximum wealth tax rate to 1.1 percent.
Ole Gjems-Onstad, a professor emeritus at Norwegian Business School, said he estimated that those who had left the nation had a combined fortune of at least 600 billion kroner.
“In my opinion it is a little bit like Brexit. Norway has no great tradition of self-harm and the flood of entrepreneurs moving abroad has come as something of a shock,” Gjems-Onstad said. “Some politicians are, as you know, blaming the wealthy people moving, but I think many ordinary people quite simply do not like that our best investors are leaving.”
Tord Ueland Kolstad, a retail estate and Salmon farming investor, with a fortune of about 1.5 billion kroner, has moved from Bodo in northern Norway to Lucerne in Switzerland.
“This was not what I wanted, but the toughened and increased tax rules of the current government means that I, as the founder and responsible owner, have no choice,” he told Norwegian broadcaster TV 2.
Kolstad said the increase in the wealth tax meant he would pay just over 6 million kroner, which he complained would mean he would need to pay himself a dividend of 10 million kroner to take into account increased dividend tax.
“This is unfortunately the reality of today’s tax policy. It is unjustifiable to impose such costs on the company when you want to create new jobs,” he said.
Kolstad told the Norwegian newspaper Aftenposten that when he first arrived in Switzerland he did not have any friends there.
“But now there are several of us [Norwergians], so we meet every now and then for coffee,” he said.
Erlend Grimstad, a state secretary in the Norwegian Ministry of Finance, told the Guardian he hoped that wealthy Norwegians would return “in time.”
“If you have enjoyed success and become rich in Norway, we hope you will stay and continue taking part in Norwegian society,” he said.
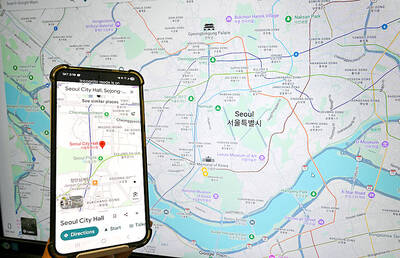
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

THE TRAGEDY OF PUNCH: Footage of the seven-month-old Japanese macaque has gone viral online after he was rejected by his mother and formed a bond with a soft toy A baby monkey in Japan has captured hearts around the world after videos of him being bullied by other monkeys and rejected by his mother went viral last week. Punch, a Japanese macaque, was born in July last year at Ichikawa City Zoo. He has drawn international attention after zookeepers gave him a stuffed orangutan toy after he was abandoned by his mother. Without maternal guidance to help him integrate, Punch has turned to the toy for comfort. He has been filmed multiple times being dragged and chased by older Japanese macaques inside the enclosure. Early clips showed him wandering alone with

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail