China’s official data on COVID-19 deaths have always been transparent, state media late on Thursday quoted a senior health official as saying, despite the official figures being tiny compared with other countries and reports that the country’s hospitals are overwhelmed with cases of the disease.
Beijing’s release of all virus information was done “in the spirit of openness,” the official told a Chinese State Council news briefing, Xinhua news agency reported.
A national disease control body yesterday said there were about 5,500 new local cases and one death, but with the end of mass testing and the narrowing of criteria for what counts as a COVID-19 fatality, those numbers are no longer believed to reflect reality.
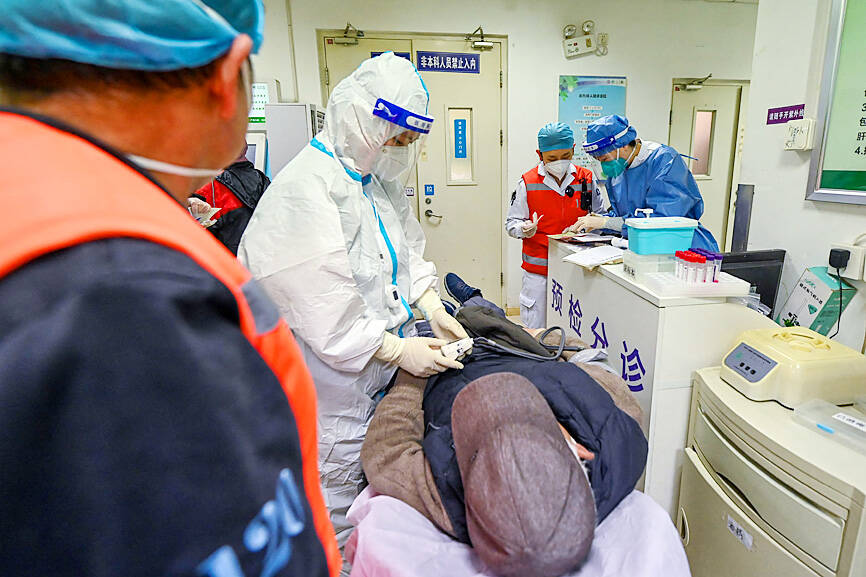
Photo: Reuters
Some experts estimate there might be as many as 9,000 daily deaths.
“China has always been publishing information on COVID-19 deaths and severe cases in the spirit of openness and transparency,” said Jiao Yahui (焦雅輝), director of the Chinese National Health Commission’s Bureau of Medical Administration.
Jiao said that China counts COVID-19 deaths as cases only if they died of respiratory failure induced by the virus after testing positive with a nucleic acid test, rather than other countries that include all deaths within 28 days of positive tests.
“China has always been committed to the scientific criteria for judging COVID-19 deaths, from beginning to end, which are in line with the international criteria,” Jiao said.
The commission last week said it would no longer release an official daily COVID-19 death toll.
Health risk analysis firm Airfinity said it currently estimates 9,000 daily deaths and 1.8 million infections per day in China, while it also expects 1.7 million fatalities across the country by the end of April.
The UK-based research company said its model was based on data from Chinese provinces, before changes to reporting infections were implemented, combined with case growth rates from other countries that tried to suppress the transmission of the virus before lifting restrictions.
China said this week it would end mandatory quarantine on arrival, after earlier this month announcing it had abandoned a raft of tough measures to contain the virus.
The world’s most populous country said it would downgrade its management of COVID-19 from Jan. 8, treating it as a Class B infection, rather than a more serious Class A infection.
Liang Wannian (梁萬年), a senior official at the commission who oversaw China’s COVID-19 response until September 2020, called the moves appropriate, scientific and law-based, Xinhua reported.
The state news agency reported Liang as saying the shift does not mean China is letting the virus go, but that is instead directing resources to the most important areas of controlling the epidemic and treating infected people.

PRECARIOUS RELATIONS: Commentators in Saudi Arabia accuse the UAE of growing too bold, backing forces at odds with Saudi interests in various conflicts A Saudi Arabian media campaign targeting the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has deepened the Gulf’s worst row in years, stoking fears of a damaging fall-out in the financial heart of the Middle East. Fiery accusations of rights abuses and betrayal have circulated for weeks in state-run and social media after a brief conflict in Yemen, where Saudi airstrikes quelled an offensive by UAE-backed separatists. The United Arab Emirates is “investing in chaos and supporting secessionists” from Libya to Yemen and the Horn of Africa, Saudi Arabia’s al-Ekhbariya TV charged in a report this week. Such invective has been unheard of

US President Donald Trump on Saturday warned Canada that if it concludes a trade deal with China, he would impose a 100 percent tariff on all goods coming over the border. Relations between the US and its northern neighbor have been rocky since Trump returned to the White House a year ago, with spats over trade and Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney decrying a “rupture” in the US-led global order. During a visit to Beijing earlier this month, Carney hailed a “new strategic partnership” with China that resulted in a “preliminary, but landmark trade agreement” to reduce tariffs — but

SCAM CLAMPDOWN: About 130 South Korean scam suspects have been sent home since October last year, and 60 more are still waiting for repatriation Dozens of South Koreans allegedly involved in online scams in Cambodia were yesterday returned to South Korea to face investigations in what was the largest group repatriation of Korean criminal suspects from abroad. The 73 South Korean suspects allegedly scammed fellow Koreans out of 48.6 billion won (US$33 million), South Korea said. Upon arrival in South Korea’s Incheon International Airport aboard a chartered plane, the suspects — 65 men and eight women — were sent to police stations. Local TV footage showed the suspects, in handcuffs and wearing masks, being escorted by police officers and boarding buses. They were among about 260 South

Chinese President Xi Jinping’s (習近平) purge of his most senior general is driven by his effort to both secure “total control” of his military and root out corruption, US Ambassador to China David Perdue said told Bloomberg Television yesterday. The probe into Zhang Youxia (張又俠), Xi’s second-in-command, announced over the weekend, is a “major development,” Perdue said, citing the family connections the vice chair of China’s apex military commission has with Xi. Chinese authorities said Zhang was being investigated for suspected serious discipline and law violations, without disclosing further details. “I take him at his word that there’s a corruption effort under