Spraying a cow with pesticides, health workers target blood-sucking ticks at the heart of Iraq’s worst detected outbreak of a fever that causes people to bleed to death.
The sight of the health workers, dressed in full protective kit, is one that has become common in the Iraqi countryside, as the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) spreads, jumping from animals to humans.
This year Iraq has recorded 19 deaths among 111 CCHF cases in humans, the WHO says.
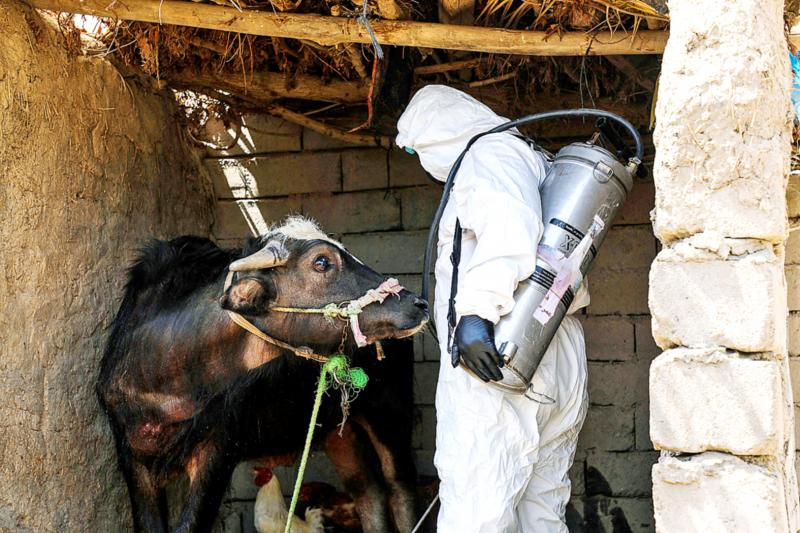
Photo: AFP
The virus has no vaccine and onset can be swift, causing severe bleeding internally and externally, and especially from the nose.
It causes death in as many as two-fifths of cases, medics say.
“The number of cases recorded is unprecedented,” said Haidar Hantouche, a health official in Dhi Qar Governate.
A poor farming region in southern Iraq, the governate accounts for nearly half of Iraq’s cases.
In previous years, cases could be counted “on the fingers of one hand,” Hantouche said.
Transmitted by ticks, hosts of the virus include wild and farmed animals such as buffalo, cattle, goats and sheep, all of which are common in Dhi Qar.
In the village of Al-Bujari, a team disinfects animals in a stable next to a house where a woman was infected. Wearing masks, goggles and overalls, the workers spray a cow and her two calves with pesticides.
A worker displays ticks that have fallen from the cow and been gathered into a container.
“Animals become infected by the bite of infected ticks,” the WHO said. “The CCHF virus is transmitted to people either by tick bites or through contact with infected animal blood or tissues during and immediately after slaughter.”
The surge of cases this year has shocked officials, as numbers far exceed recorded cases in the 43 years since the virus was first documented in Iraq in 1979.
In Dhi Qar, only 16 cases resulting in seven deaths had been recorded last year, but this year it has recorded 43 cases, including eight deaths, Hantouche said.
The numbers are still tiny compared with the COVID-19 pandemic — where Iraq has registered more than 25,200 deaths and 2.3 million recorded cases, according to WHO figures — but health workers are worried.
Endemic in Africa, Asia, the Middle East and the Balkans, CCHF’s fatality rate is between 10 and 40 percent, the WHO says.
WHO representative in Iraq Ahmed Zouiten said there were several “hypotheses” for the country’s outbreak.
They include the spread of ticks in the absence of livestock spraying campaigns during COVID-19 in 2020 and last year, and “very cautiously, we attribute part of this outbreak to global warming, which has lengthened the period of multiplication of ticks,” he said.
However, “mortality seems to be declining,” as Iraq had mounted a spraying campaign while new hospital treatments had shown “good results,” he said.
As the virus is “primarily transmitted” to people via ticks on livestock, most cases are among farmers, slaughterhouse workers and veterinarians, the WHO says.
“Human-to-human transmission can occur resulting from close contact with the blood, secretions, organs or other bodily fluids of infected persons,” it says.
Alongside uncontrolled bleeding, the virus causes intense fever and vomiting.
Medics fear there might be an explosion of cases following the Muslim festival of Eid al-Adha in July, when families traditionally slaughter an animal to feed guests.
“With the increase in the slaughter of animals, and more contact with meat, there are fears of an increase in cases during Eid,” said Azhar al-Assadi, a doctor specializing in hematological diseases in a hospital in Nasiriya.
Authorities have put in place disinfection campaigns and are cracking down on abattoirs that do not follow hygiene protocols. Several provinces have also banned livestock movement across their borders.

‘TERRORIST ATTACK’: The convoy of Brigadier General Hamdi Shukri resulted in the ‘martyrdom of five of our armed forces,’ the Presidential Leadership Council said A blast targeting the convoy of a Saudi Arabian-backed armed group killed five in Yemen’s southern city of Aden and injured the commander of the government-allied unit, officials said on Wednesday. “The treacherous terrorist attack targeting the convoy of Brigadier General Hamdi Shukri, commander of the Second Giants Brigade, resulted in the martyrdom of five of our armed forces heroes and the injury of three others,” Yemen’s Saudi Arabia-backed Presidential Leadership Council said in a statement published by Yemeni news agency Saba. A security source told reporters that a car bomb on the side of the road in the Ja’awla area in

PRECARIOUS RELATIONS: Commentators in Saudi Arabia accuse the UAE of growing too bold, backing forces at odds with Saudi interests in various conflicts A Saudi Arabian media campaign targeting the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has deepened the Gulf’s worst row in years, stoking fears of a damaging fall-out in the financial heart of the Middle East. Fiery accusations of rights abuses and betrayal have circulated for weeks in state-run and social media after a brief conflict in Yemen, where Saudi airstrikes quelled an offensive by UAE-backed separatists. The United Arab Emirates is “investing in chaos and supporting secessionists” from Libya to Yemen and the Horn of Africa, Saudi Arabia’s al-Ekhbariya TV charged in a report this week. Such invective has been unheard of

‘SHOCK TACTIC’: The dismissal of Yang mirrors past cases such as Jang Song-thaek, Kim’s uncle, who was executed after being accused of plotting to overthrow his nephew North Korean leader Kim Jong-un has fired his vice premier, compared him to a goat and railed against “incompetent” officials, state media reported yesterday, in a rare and very public broadside against apparatchiks at the opening of a critical factory. Vice Premier Yang Sung-ho was sacked “on the spot,” the state-run Korean Central News Agency said, in a speech in which Kim attacked “irresponsible, rude and incompetent leading officials.” “Please, comrade vice premier, resign by yourself when you can do it on your own before it is too late,” Kim reportedly said. “He is ineligible for an important duty. Put simply, it was

US President Donald Trump on Saturday warned Canada that if it concludes a trade deal with China, he would impose a 100 percent tariff on all goods coming over the border. Relations between the US and its northern neighbor have been rocky since Trump returned to the White House a year ago, with spats over trade and Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney decrying a “rupture” in the US-led global order. During a visit to Beijing earlier this month, Carney hailed a “new strategic partnership” with China that resulted in a “preliminary, but landmark trade agreement” to reduce tariffs — but