For the authorities that brought the Mountains to Sea National Greenway (山海圳國家綠道) into existence, the route is as much about culture as it is about hiking.
Han culture dominates the coastal and agricultural flatlands of Tainan and Chiayi counties, but as the Greenway climbs along its Tribal Trail (原鄉之路) section, hikers pass through communities inhabited by members of the Tsou Indigenous community.
Leaving Chiayi County’s Dapu Village (大埔), walkers follow Provincial Highway 3 to Dapu Bridge where a sign bearing the Tsou greeting “a veo veo yu” marks the point at which the Greenway turns off to follow Qingshan Industrial Road (青山產業道路) — and the point at which the balance of cultures tips towards primarily Indigenous.
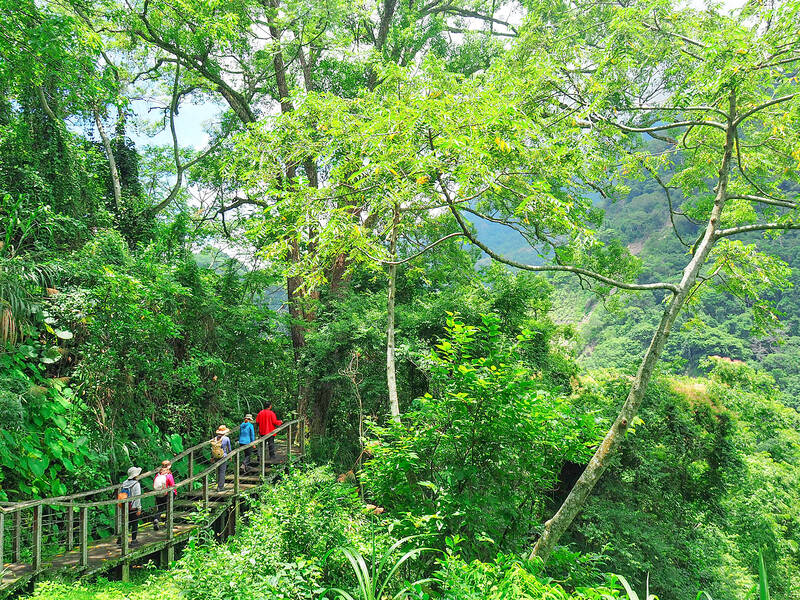

Photo: Ami Barnes
CAYAMAVANA’S PAVILIONS
A zigzagging climb brings hikers to Cayamavana (Chashan, 茶山). The village is unique among Taiwan’s indigenous settlements both for its ethnic diversity — Tsou individuals comprise the largest group here, but there are also Bunun and a scattering of Han villagers — and also for its extensive collection of pavilions.
Pavilions — more specifically thatched-roofed hufus — are scattered all around the village and are a big part of daily life.

Photo: Ami Barnes
They are where the community gathers, chats and shares food — relics of a time when the community’s dead were buried below their living quarters, necessitating that noisy socializing activities be conducted away from the home.
Cayamavana is a good place to spend the night. Stopping here makes the Dapu-to-Cayamavana day short and the following day long, but Cayamavana has more places to stay than the next village — among them, Chashan Kaiyuan Farmstead (茶山開元農場) is a welcoming option — prices start at NT$1,200, bookable by calling (09) 3277-3883.
From Cayamavana, the Greenway follows Chiayi District Road 129 for about 17 kilometers, passing through Niahosa Village (Xinmei, 新美) about halfway along this leg.
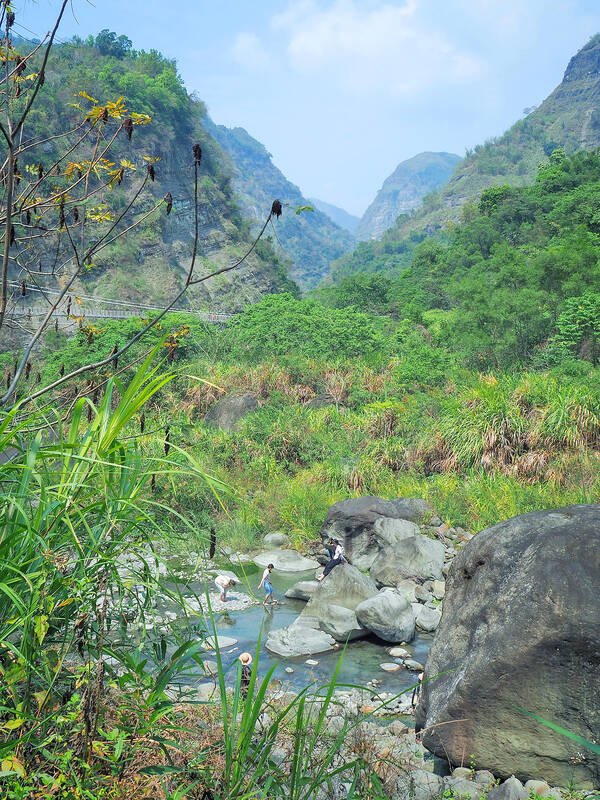

Photo: Ami Barnes
The village is relatively young, with most families having resettled there in the wake of World War II, although nearby archaeological excavations have revealed pottery, hunting paraphernalia and graves dating back around 3,800 years.
Niahosa feels a tad livelier than neighboring Cayamavana. It has a well-stocked convenience store, a coffee shop and some small eateries. There’s also an elementary school (at the latest count, populated entirely by Indigenous youths) and a couple of churches.
ECOLOGICAL PARK
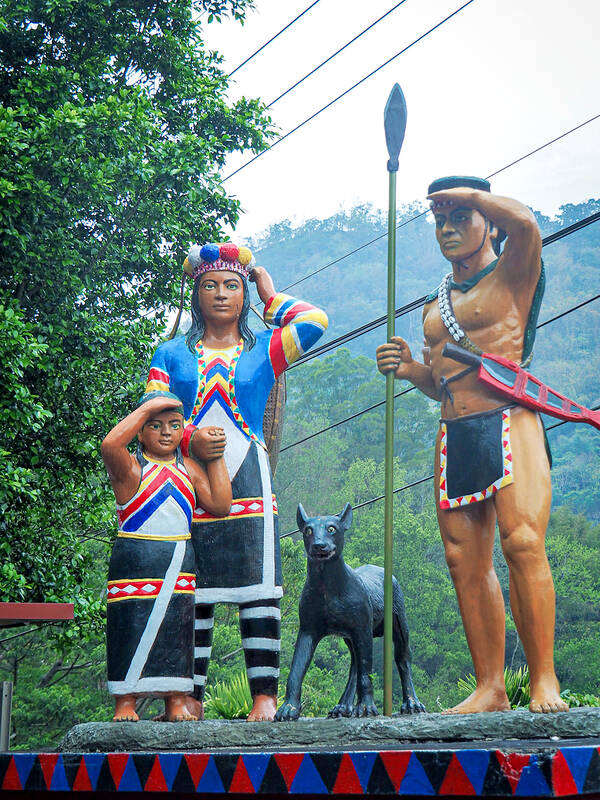

Photo: Ami Barnes
At Danayigu Nature Ecological Park (達娜伊谷自然生態公園), the Greenway finally parts ways with the road.
The route passes straight through the park and out the other side, meaning walkers must pay the entry fee (NT$150, discounted for Mountains to Sea Greenway trail passport holders).
Run by the Tsou peoples of Saviki (Shanmei Village, 山美) — it’s an example of collaborative efforts affecting real change.
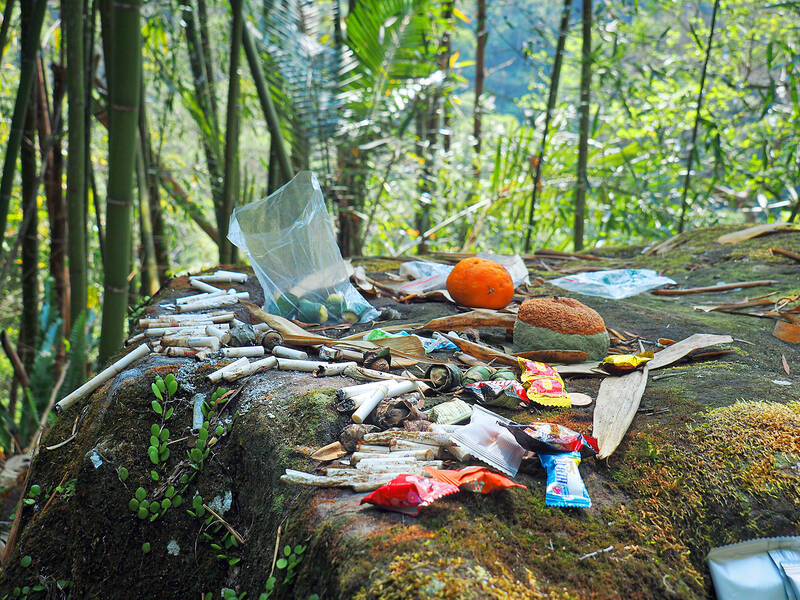

Photo: Ami Barnes
The Tsou traditionally practiced a combination of agriculture and hunting, with each family assigned an area of land comprising a stretch of riverbank and forest hunting grounds.
Ancestral lands sustained families for generations, but this system was thrown into disarray when post-World War II incomers brought destructive fishing practices such as electrofishing, stunning fish with electric currents.
It only took a couple of decades for the fish population to be all but eradicated, prompting villagers to take the drastic step of pooling their clans’ hunting grounds in order to preserve them.
The two waterways that run through the park — Zengwen River (曾文河) and Danayigu Creek (達娜伊谷溪) — were classified as shoveljaw carp conservation areas, and land to either side of the water became a hunting-prohibited nature reserve.
Fish fry from the creek’s headwaters were reintroduced to kickstart population recovery, and villagers organized patrols to ensure the new rules were followed. Within a short span, these efforts bore fruit — or rather, fish — and the cooperatively run park opened to visitors.
Passing through, hikers can visit the fish-viewing trail, learn about Tsou ways of life and refuel at stalls selling barbecued meats and local produce.
The Greenway leaves the park via an owl-adorned bridge before a lung-busting climb up Limei Refuge Trail (里美避難步道).
REMOTE NIAE’UCNA COMMUNITY
Before the Japanese colonial period, this was the primary route between Saviki and Niae’ucna (Lijia, 里佳). The Japanese constructed a new trail and this one fell into disuse until Typhoon Morakot wiped out sections of Niae’ucna’s only access road — prompting the old trail’s rebirth as an evacuation and supply route, then later a leisure trail.
Near the top, walkers can choose the slightly longer Giant Stone Slab Trail (巨石板步道) or crack on with the walk along Wuqiha Creek Industrial Road (烏奇哈溪產業道路) in search of rest in Niae’ucna — the through-hike’s most remote community.
Niae’ucna has a single homestay, Jiana Baiyi Workshop (嘉娜百藝工坊) and no official restaurant, but the homestay partners with villagers to offer hearty Indigenous-style feasts (advance booking required). Rooms are NT$2,400 per night, bookable by phoning (05) 251-1383.
Leaving the village, hikers pass Niae’ucna’s tribute stone stacked high with offerings for the locale’s guardian spirit, which appears to have a penchant for cigarettes and betel nuts.
The road is bounded by fields of tea and ginger and shaded by Formosa sweet gum trees, which — according to tribal lore — the Tsou are descended from.
Tapangu (Dabang, 達邦) and Tefya (Tefuye, 特富野) are the Greenway’s final two villages. Occupying parcels of flat land among an otherwise mountainous landscape, legend holds that the two villages sprang up in the footprints of Hamo — the Tsou creator god.
Tapangu is small and the sights densely packed. The Tsou Cultural Exhibition Hall (free to enter) sits between the school and its mountain-view running track.
West of the track, Tsou Fengguan Tribal Restaurant (鄒風館部落餐廳) serves up excellent Tsou cuisine, while at the eastern edge, a Japanese-era police dormitory serves as a reminder of the repression endured by Taiwan’s Indigenous communities.
Tapangu’s kuba — a ceremonial meeting place — is tucked between houses to the north of the running track, with thatched roofs capped with a living Dendrobium orchid and are where the community gathers for festivals. Tapangu and Tefya are the last of Taiwan’s communities with kubas.
A suspension bridge spans the river valley separating Tapangu from Tefya, and the trail on the far side ascends through creaking bamboo forests and towering camphor giants.
FARM-TO-TABLE COFFEE
Coffee growing has taken off in the region over the past decade, and as the trail approaches Tefya, it skirts several small coffee plantations and a handful of wayside cafes where the coffee must have one of the shortest farm-to-table journeys ever recorded — the plants are within literal striking distance of the tables.
The Tribal Trail continues a little further before segueing into the Greenway’s final portion — the Sacred Mountain Trail (聖山之路) — but since Tapangu and Tefya make an excellent point to break up the journey, it makes sense to pause the writing here too.

One of the biggest sore spots in Taiwan’s historical friendship with the US came in 1979 when US president Jimmy Carter broke off formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan’s Republic of China (ROC) government so that the US could establish relations with the People’s Republic of China (PRC). Taiwan’s derecognition came purely at China’s insistence, and the US took the deal. Retired American diplomat John Tkacik, who for almost decade surrounding that schism, from 1974 to 1982, worked in embassies in Taipei and Beijing and at the Taiwan Desk in Washington DC, recently argued in the Taipei Times that “President Carter’s derecognition

JUNE 30 to JULY 6 After being routed by the Japanese in the bloody battle of Baguashan (八卦山), Hsu Hsiang (徐驤) and a handful of surviving Hakka fighters sped toward Tainan. There, he would meet with Liu Yung-fu (劉永福), leader of the Black Flag Army who had assumed control of the resisting Republic of Formosa after its president and vice-president fled to China. Hsu, who had been fighting non-stop for over two months from Taoyuan to Changhua, was reportedly injured and exhausted. As the story goes, Liu advised that Hsu take shelter in China to recover and regroup, but Hsu steadfastly
You can tell a lot about a generation from the contents of their cool box: nowadays the barbecue ice bucket is likely to be filled with hard seltzers, non-alcoholic beers and fluorescent BuzzBallz — a particular favorite among Gen Z. Two decades ago, it was WKD, Bacardi Breezers and the odd Smirnoff Ice bobbing in a puddle of melted ice. And while nostalgia may have brought back some alcopops, the new wave of ready-to-drink (RTD) options look and taste noticeably different. It is not just the drinks that have changed, but drinking habits too, driven in part by more health-conscious consumers and

On Sunday, President William Lai (賴清德) delivered a strategically brilliant speech. It was the first of his “Ten Lectures on National Unity,” (團結國家十講) focusing on the topic of “nation.” Though it has been eclipsed — much to the relief of the opposing Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) and Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) — by an ill-advised statement in the second speech of the series, the days following Lai’s first speech were illuminating on many fronts, both domestic and internationally, in highlighting the multi-layered success of Lai’s strategic move. “OF COURSE TAIWAN IS A COUNTRY” Never before has a Taiwanese president devoted an entire speech to