Protesters involved in the 2019-2020 pro-democracy movement in Hong Kong have been treated extraordinarily harshly by the criminal justice system compared with local and international norms, a report has found.
The surge in arrests, detentions and charges in the wake of the anti-extradition bill protests that saw millions of Hongkongers taking to the streets to oppose closer ties with mainland China meant that the criminal justice system was put under “extreme stress,” according to Jun Chan, Eric Yan-ho Lai and Thomas E Kellogg at the Center for Asian Law of Georgetown University.
“In nearly all respects, the post-2019 response has on average been more punitive than prior responses to social movements, particularly the 2014 umbrella movement,” the authors said.
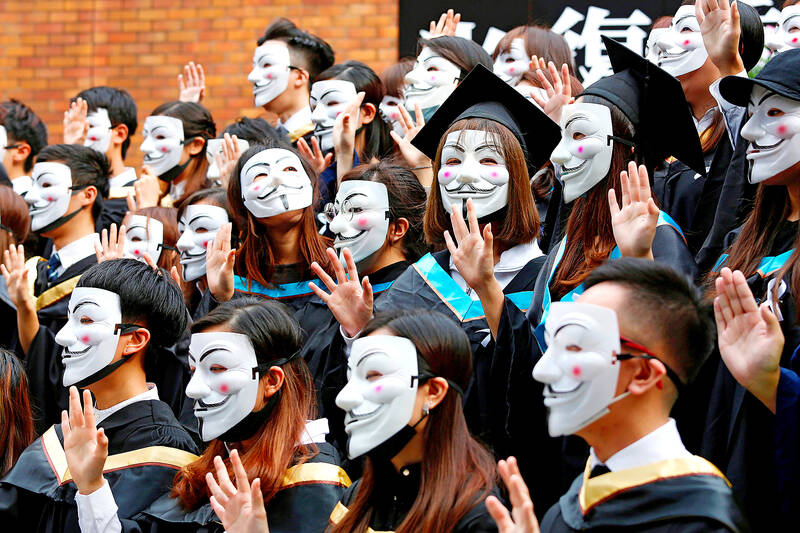

Photo: Reuters
As of August last year, more than 10,000 Hongkongers had been arrested in connection with the 2019 protest movement and nearly 3,000 prosecuted, according to government statistics. The Georgetown researchers analyzed more than 1,500 cases that had concluded by July 31, 2021.
Protesters were charged with 100 different types of offences. These included unlawful assembly, rioting, police obstruction and police assault. More than 80 percent of people convicted received custodial sentences, compared with just over 31 percent of people who were convicted on charges relating to the umbrella movement. The most common charge in the dataset was unlawful assembly, a colonial-era ordinance that allows the authorities to prosecute peaceful protesters.
The anti-extradition bill protests lasted for more than six months in 2019-2020, much longer than the umbrella movement in 2014. They were ultimately defeated in June 2020 by the imposition of a draconian national security law (NSL) that effectively banned all forms of dissent and carries a maximum of a life sentence. The Chinese and Hong Kong authorities said the law was needed to restore stability.

Photo: Bloomberg
As of September, 280 people had been arrested under the NSL, including high profile figures such as the activist Joshua Wong (黃之鋒) and the former media proprietor Jimmy Lai (黎智英). These cases are tried in separate courts, with judges hand-picked by the executive.
But most of the people swept into the criminal justice system after the protests have been charged with more ordinary offences, with many detained for several months in pre-trial detention.
Between 2019 and 2021, the average waiting time for criminal trials increased by 50 percent, to 287 days, well beyond the official target of 100 days.

Photo: Reuters
“Such long wait times suggest that the court system is flailing under the weight of a massively increased caseload,” the report said.
More than 130 of the defendants in the cases analyzed by the researchers were under 18, with the median age being 23. More than 66 percent of juvenile convictions resulted in custodial sentences, which the researchers describe as “an extraordinarily high rate of incarceration for children”.
By comparison, In England and Wales, 5 percent of juveniles who received criminal convictions in 2021 were put in custody.
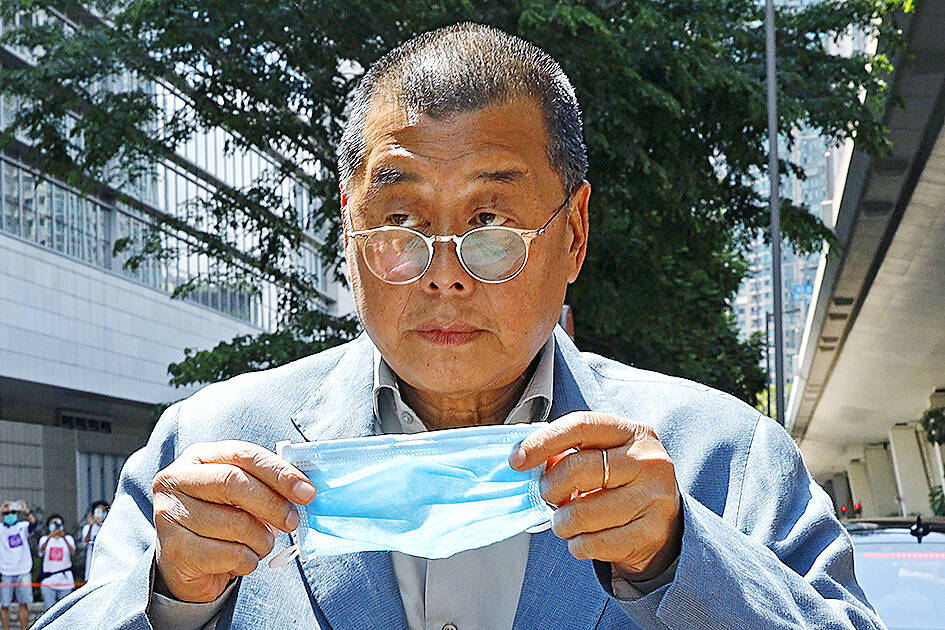

Photo: AP
Open displays of dissent in Hong Kong are now exceedingly rare. In March, a small protest about a land reclamation plan took place under close police monitoring, the first time that any kind of demonstration had been allowed since 2020.
John Lee (李家超), the city’s chief executive, has said that introducing another Hong Kong national security law, in addition to the one imposed by Beijing in 2020, is a priority for next year.

Next week, candidates will officially register to run for chair of the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT). By the end of Friday, we will know who has registered for the Oct. 18 election. The number of declared candidates has been fluctuating daily. Some candidates registering may be disqualified, so the final list may be in flux for weeks. The list of likely candidates ranges from deep blue to deeper blue to deepest blue, bordering on red (pro-Chinese Communist Party, CCP). Unless current Chairman Eric Chu (朱立倫) can be convinced to run for re-election, the party looks likely to shift towards more hardline

Sept. 15 to Sept. 21 A Bhutanese princess caught at Taoyuan Airport with 22 rhino horns — worth about NT$31 million today — might have been just another curious front-page story. But the Sept. 17, 1993 incident came at a sensitive moment. Taiwan, dubbed “Die-wan” by the British conservationist group Environmental Investigation Agency (EIA), was under international fire for being a major hub for rhino horn. Just 10 days earlier, US secretary of the interior Bruce Babbitt had recommended sanctions against Taiwan for its “failure to end its participation in rhinoceros horn trade.” Even though Taiwan had restricted imports since 1985 and enacted

Enter the Dragon 13 will bring Taiwan’s first taste of Dirty Boxing Sunday at Taipei Gymnasium, one highlight of a mixed-rules card blending new formats with traditional MMA. The undercard starts at 10:30am, with the main card beginning at 4pm. Tickets are NT$1,200. Dirty Boxing is a US-born ruleset popularized by fighters Mike Perry and Jon Jones as an alternative to boxing. The format has gained traction overseas, with its inaugural championship streamed free to millions on YouTube, Facebook and Instagram. Taiwan’s version allows punches and elbows with clinch striking, but bans kicks, knees and takedowns. The rules are stricter than the
“Far from being a rock or island … it turns out that the best metaphor to describe the human body is ‘sponge.’ We’re permeable,” write Rick Smith and Bruce Lourie in their book Slow Death By Rubber Duck: The Secret Danger of Everyday Things. While the permeability of our cells is key to being alive, it also means we absorb more potentially harmful substances than we realize. Studies have found a number of chemical residues in human breast milk, urine and water systems. Many of them are endocrine disruptors, which can interfere with the body’s natural hormones. “They can mimic, block