Clutching an iron hair curler radiating scorching heat, a schoolgirl torments a classmate in a desolate school gymnasium.
The curler sizzles raw flesh, as the camera pans to show scars on the victim’s body.
This scene from The Glory, an audacious South Korean drama that achieved global success, shows viewers the depth of the country’s school bullying epidemic.

Photo: AFP
While some critics have panned The Glory for its deeply disturbing scenes, some of which are based on true events — including the use of a hair curler — the drama’s unapologetic depiction of pervasive school violence has resonated within South Korean society, reigniting calls for action to address the issue.
The latest government figures show cases of school violence and bullying have surged in the last decade in South Korea. In February, President Yoon Suk-yeol vowed to end school violence and the government has moved to ensure bullying records must be more prominently reflected when applying to university.
Yet teacher organizations argue that the efforts are insufficient and that more emphasis should be placed on preventing children from becoming bullies in the first place.

Photo: AFP
MORE MALICIOUS METHODS
Keumjoo Kwak, a psychology professor at Seoul National University, says that cases of school violence and bullying in South Korea reflect the dynamics of the collectivist society, where peer pressure plays a significant role in shaping behavior.
“We form a group and torment others. The victims may be ostracized by an entire class or even by the whole school,” Kwak said.
“The bullying entails persistent and repeated harm over time, which is frequently psychological or emotional.”
She says school bullying and school violence have always existed in South Korea, but the methods used have become more sophisticated and malicious, imitating scenes from films and using social media to spread the harm.
Bullying can have a severe impact on an individual.
Lee Sang-woo, an elementary school teacher and director at the Korean Teachers and Education Workers Union (KTU), says that school violence and bullying can significantly lower a student’s self-esteem and result in social isolation and increased levels of depression and anxiety.
“Victims often believe they cannot resolve the problem of school bullying, which negatively affects their physical and mental health. It can lead to academic decline and long-term avoidance of attending school, or even dropping out,” Lee said.
In extreme cases, some turn to taking their own lives. A recent study of university students who had experienced school violence found that more than half had considered suicide.
Kwak says the competitive and high-pressure environment many students in South Korea face can intensify the problem of bullying.
She says students are subjected to intense academic pressure and long hours of studying, primarily centered on university entrance exams. This creates a highly competitive, hierarchical, and monotonous environment devoid of physical activities to expend energy — and that can lead to some individuals bullying others “as a source of amusement”.
SURGE OF BULLYING CLAIM
Taking action against violence and bullying can be difficult, but for those who do, the struggle can be long, with one in three victims unable to get any help. The number of legal disputes involving school violence has doubled in the last two years; accused bullies filed the majority of them.
A recent controversy involving lawyer Chung Sun-sin and his son’s bullying case attracted widespread attention in South Korea. The son was accused of verbally abusing a high school peer and was ordered to transfer schools.
After it was reported that Chung had used his position as a senior prosecutor and legal expert to try to reverse disciplinary action against his son, his appointment as National Office of Investigation director was withdrawn.
The Chung Sun-sin scandal is not an isolated incident, and is part of a broader trend of #MeToo-style bullying revelations that have emerged over the last few years.
The accusers, often anonymous, expose the bullying of their alleged abusers, especially when those individuals are celebrities or hold influential positions. A recent case involved the contract termination of K-pop rookie Kim Ga-ram with girl group Le Sserafim after school bullying allegations appeared online.
The director of The Glory, Ahn Gil-ho, also became embroiled in such shaming after anonymous allegations of school violence surfaced online. He later admitted to it and apologized.
‘VICTIMS NEED SUPPORT’
As part of moves to stamp out school violence, lawmakers are considering amendments to relevant laws to ensure prompt resolution of school bullying cases.
The government has also announced the inclusion of bullying records in regular university admissions and enhanced support for victims.
Teacher groups have mostly welcomed the efforts but say more needs to be done to restore relationships between students.
In a statement, the Korean Federation of Teachers Union emphasized the importance of educational solutions over punitive measures, including the creation of specialized institutions for perpetrators and education for their parents.
The Korean Federation of Teachers Associations called for compensation for teachers dealing with cases of school violence and a more nuanced approach according to each school’s situation.
Kwak at Seoul National University says victims and perpetrators must be supported to address the problem.
“Victims need counselling and support to overcome their trauma. Perpetrators need to be held accountable for their actions but also given the opportunity to change. If we leave them as they are, they will continue to harm others as adults.”
Lee from the KTU says that building a trusting relationship that encourages students to tell their teachers about bullying and periodically patrolling the school premises will help.
Kwak also points to preventive education from a young age and the need to teach empathy, cooperation, and respect for others.
“Without implementing such measures, South Korea will continue to face dreadful cases of school violence every year.”

Next week, candidates will officially register to run for chair of the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT). By the end of Friday, we will know who has registered for the Oct. 18 election. The number of declared candidates has been fluctuating daily. Some candidates registering may be disqualified, so the final list may be in flux for weeks. The list of likely candidates ranges from deep blue to deeper blue to deepest blue, bordering on red (pro-Chinese Communist Party, CCP). Unless current Chairman Eric Chu (朱立倫) can be convinced to run for re-election, the party looks likely to shift towards more hardline

Enter the Dragon 13 will bring Taiwan’s first taste of Dirty Boxing Sunday at Taipei Gymnasium, one highlight of a mixed-rules card blending new formats with traditional MMA. The undercard starts at 10:30am, with the main card beginning at 4pm. Tickets are NT$1,200. Dirty Boxing is a US-born ruleset popularized by fighters Mike Perry and Jon Jones as an alternative to boxing. The format has gained traction overseas, with its inaugural championship streamed free to millions on YouTube, Facebook and Instagram. Taiwan’s version allows punches and elbows with clinch striking, but bans kicks, knees and takedowns. The rules are stricter than the
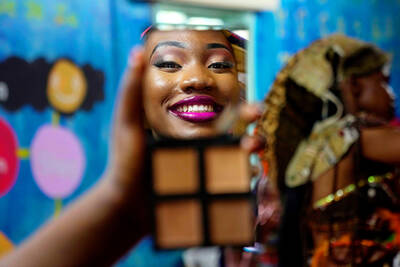
“Far from being a rock or island … it turns out that the best metaphor to describe the human body is ‘sponge.’ We’re permeable,” write Rick Smith and Bruce Lourie in their book Slow Death By Rubber Duck: The Secret Danger of Everyday Things. While the permeability of our cells is key to being alive, it also means we absorb more potentially harmful substances than we realize. Studies have found a number of chemical residues in human breast milk, urine and water systems. Many of them are endocrine disruptors, which can interfere with the body’s natural hormones. “They can mimic, block

Nearly three decades of archaeological finds in Gaza were hurriedly evacuated Thursday from a Gaza City building threatened by an Israeli strike, said an official in charge of the antiquities. “This was a high-risk operation, carried out in an extremely dangerous context for everyone involved — a real last-minute rescue,” said Olivier Poquillon, director of the French Biblical and Archaeological School of Jerusalem (EBAF), whose storehouse housed the relics. On Wednesday morning, Israeli authorities ordered EBAF — one of the oldest academic institutions in the region — to evacuate its archaeological storehouse located on the ground floor of a residential tower in