July 20 to July 26
For 40 years, there was a Fujian Provincial Government (福建省政府) in New Taipei City run by an appointed military governor-for-life.
This governor controlled no territory and performed no administrative duties; he and his staff were charged with researching plans for the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) to “retake” Fujian Province from the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), who seized it along with the rest of China during the Chinese Civil War.
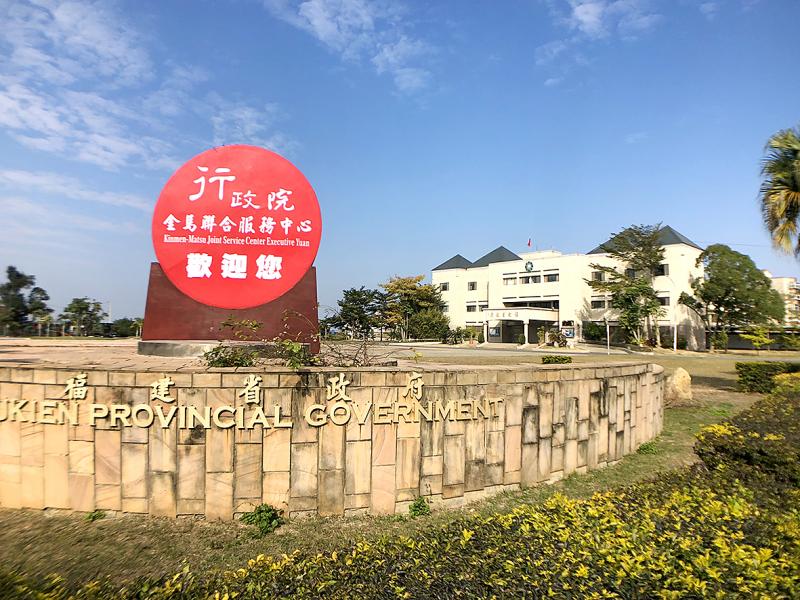

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia commons
The provincial government office was originally located in Kinmen, which along with the Matsu islands made up the only part of Fujian Province that the KMT retained — at just about 0.15 percent of the original territory.
But as Kinmen and Matsu became war zones following the 1954 First Taiwan Strait Crisis, the provincial government was relocated to today’s Sindian District (新店) in New Taipei City on July 20, 1956. Its administrative duties were transferred to the two military-run county offices that oversaw the islands.
Republic of China (ROC) Army major general Tai Chung-yu (戴仲玉), who was appointed provincial governor in 1955, held the post for 31 years until his death in 1986. The central government moved the office back to Kinmen in 1996 and completely defunded it in 2018, but they could not abolish it without changing the Constitution. As a result, the Fujian Provincial Government still exists, but in name only.

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia commons
GOVERNOR-FOR-LIFE
In August 1949, the People’s Liberation Army descended upon Fuzhou, the original seat of the Fujian Provincial Government. About 60,000 KMT troops defended the city, but they were decisively routed after a week of fighting. With his troops nearly wiped out, division commander Lee Yan-nian (李延年) eventually fled to Taiwan, where he was jailed for over a year for allegedly abandoning his post.
The KMT subsequently moved the Fujian Provincial Government to the offshore island of Kinmen and put it under military control. From there, they managed to fend off the pursuing PLA troops two months later at the Battle of Guningtou (古寧頭).
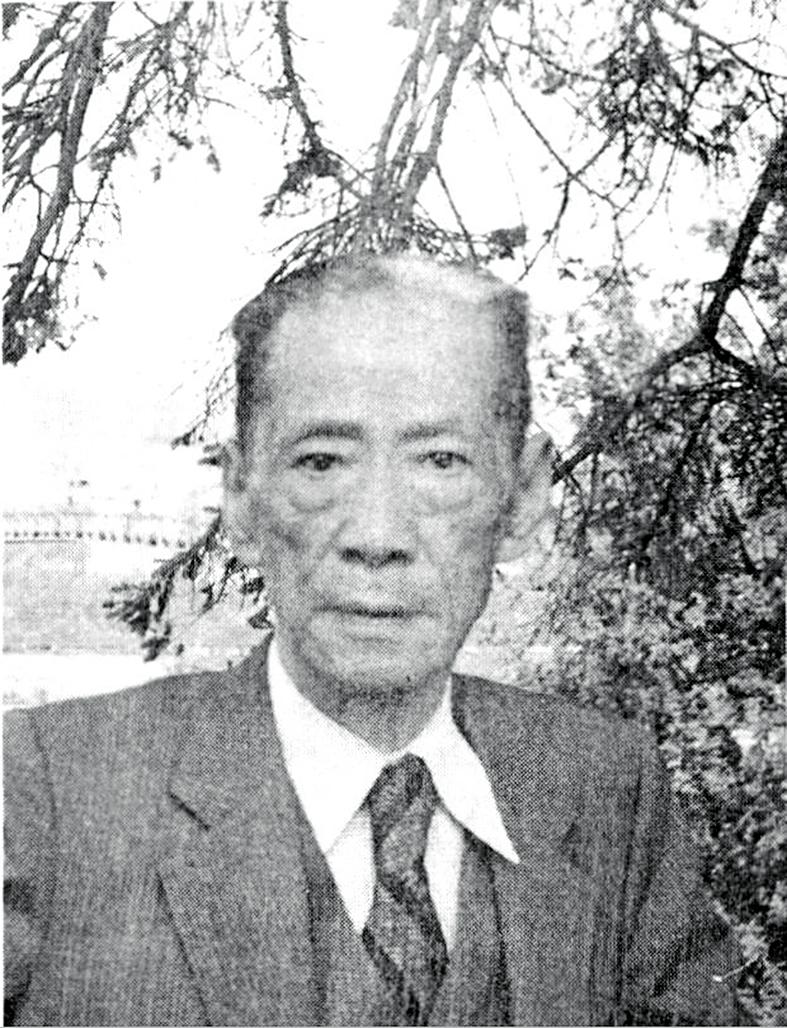

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
Since the KMT also managed to hold on to the Yijiangshan (一江山) and Dachen (大陳) islands off the coast of Zhejiang Province, it actually established a local Zhejiang Provincial Government in 1951. The office was abolished when the PLA captured the islands during the First Taiwan Strait Crisis of 1954.
The PLA also tried to take Kinmen during the same conflict by heavily shelling it for over a year, but they eventually relented when the US threatened to respond with nuclear weapons. The precarious situation prompted the KMT to designate Kinmen and Matsu as military zones in 1956, and the provincial government office was moved to Sindian.
Even the Japanese and KMT allowed limited local elections in Taiwan, but in Kinmen, the military commander who doubled as county commissioner initially appointed all positions down to the borough wardens. The first local elections were held in 1971.
Several months before he left Kinmen, Tai carved the propaganda slogan “the restoration of our nation is within reach” (中興在望) into a large boulder at Taiwu Mountain (太武山). The PLA would attack Kinmen again two years later — but by then, Tai was working in Sindian.
The Kinmen and Matsu warzone provisions state that the office in Sindian was “in charge of conducting research toward plans for retaking [Fujian] province,” but it’s unclear what exactly this “research” entailed.
FREEZING THE PROVINCE
While Martial Law ended in 1987, Kinmen and Matsu remained under military control until 1992. Just a year after the Fujian Provincial Government moved back to Kinmen, the National Assembly on July 21, 1997 amended the constitution to greatly reduce the powers the nation’s provincial governments. These changes were chiefly aimed at the Taiwan Provincial Government since its territory overlapped with the central government by 98 percent. Some say the move was politically motivated, but the official line was to streamline operations and save costs.
The central government also canceled direct provincial governor elections. These changes didn’t affect the Fujian office much because it wasn’t a functioning administrative entity and did not have elected governors.
The Fujian Provincial Government further lost its autonomy in 1998, becoming an entity under the Executive Yuan. Former secretary-general Wong Ming-chih (翁明志) told the BBC that after 1998, the office’s main function was to serve as a bridge between Kinmen, Matsu and the central government, advocating for local policy and requesting funding. For example, Wong says the office’s efforts were key to government approval of the Kinmen Bridge, which began construction in 2013 and will connect the main island with neighboring Little Kinmen (小金門) by next year.
Wong says that people sending letters from Taiwan to China’s Fujian Provincial People’s Government (福建省人民政府) looking for lost relatives would sometimes accidentally omit the “People’s,” and the mail would wind up in Kinmen.
The Fujian provincial governors appointed after 2007 all concurrently held other positions. Lo Ying-shay (羅瑩雪), for instance, also served as minister without portfolio in addition to heading the Mongolian and Tibetan Affairs Commission (蒙藏委員會). This agency was also a remnant of the days when the KMT still openly claimed the two territories along with the rest of China. It was abolished in 2017.
When the Fujian Provincial Government was defunded, the Kinmen-Matsu Joint Services Center (金馬聯合服務中心) assumed its responsibilities. The last provincial governor, Chang Ching-sen (張景森), now heads the service center.
Taiwan in Time, a column about Taiwan’s history that is published every Sunday, spotlights important or interesting events around the nation that either have anniversaries this week or are tied to current events.
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

For many centuries from the medieval to the early modern era, the island port of Hirado on the northwestern tip of Kyushu in Japan was the epicenter of piracy in East Asia. From bases in Hirado the notorious wokou (倭寇) terrorized Korea and China. They raided coastal towns, carrying off people into slavery and looting everything from grain to porcelain to bells in Buddhist temples. Kyushu itself operated a thriving trade with China in sulfur, a necessary ingredient of the gunpowder that powered militaries from Europe to Japan. Over time Hirado developed into a full service stop for pirates. Booty could

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them