When an apartment comes up for rent in Germany’s big cities, hundreds of prospective tenants often queue down the street to view it, but the acute shortage of affordable housing is getting scant attention ahead of today’s snap general election.
“Housing is one of the main problems for people, but nobody talks about it, nobody takes it seriously,” said Andreas Ibel, president of Build Europe, an association representing housing developers.
Migration and the sluggish economy top the list of voters’ concerns, but analysts say housing policy fails to break through as returns on investment take time to register, making the issue a tough one to campaign on in a short election cycle.

Photo: EPA-EFE
A single rental listing in Berlin can generate 300 viewing requests per day, and this is driving inequalities across the country as the less well-off struggle to compete in the crowded market.
Rising rents are likely to lead to more support for far-right parties like Alternative for Germany (AfD), which is currently polling second, among low-income tenants, according to researchers at Oxford, Mannheim and Zurich universities.
A growing number of people are spending 40 percent of their income on housing, the threshold for a household to be considered overburdened by rent payments, according to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Higher rents and a shortage of housing, especially social housing, are driving the crisis, but other pressures, such as rising numbers of holiday lets as well as refugee arrivals, have added to the squeeze in major cities.
“Developments such as AirBnB, or the recent influx of asylum seekers and migrants have only worsened the situation, but they are not the key cause,” German Institute for Economic Research (DIW) economist Christian Danne said.
Germany is a nation of tenants with more than 50 percent renting their homes, compared with an EU average of about 30 percent in 2023. This high level has contributed in part to the housing crunch due to rent price caps.
While limiting rent increases can help some tenants, they also worsen housing shortages, as people rarely move, fewer flats are put on the rental market, while landlords exploit loopholes charging higher prices for furnished flats, which are exempt from caps, pricing many out of city living, analysts say.
Poorer households, especially single parents, are suffering most, a DIW report said last year.
“It’s not just an issue for low-income households. Even middle-income families, as soon as a place comes on the market, they rent it without viewing it,” Danne said.
This problem is most stark in Berlin, where social housing was sold off in 2004 to plug budgets, allowing private investors to develop luxury apartments that offered a higher yield.
Second-tier cities like Hamburg, or Cologne are also experiencing extraordinary growth in asking rents according to Immoscout24, an online real-estate platform in Germany.
Plans to extend a 10-year-old rent price cap, due to expire at the end of this year, were derailed by the snap election.
The ruling coalition parties, the Social Democrats (SPD) and the Greens, have pledged to continue the cap, while the center-right Christian Democratic Union (CDU), who are expected to come first in today’s election, want to scrap it.
Analysts and real-estate developers agree that extending the price cap would not ease the housing crunch, especially for low-income households.
DIW study authors are calling for targeted support for low-income renters and the expansion of social housing.
Social housing experts say Germany could look to neighboring Austria as an example, citing the country’s commitment to social housing as a basic right. More than half of Vienna’s residents live in subsidized housing.
Germany needs 600,000 to 800,000 more homes to deal with demand, a figure that is set to rise as the pace of construction stalls, and pledges to build hundreds of thousands of new homes fall short.
The outgoing government vowed to build 400,000 new homes a year when it came to power in 2021, a quarter of which were to be state-subsidized, but only about 200,000 new homes were built during the last year, compared with 293,000 in 2021.
Paralysis in the construction sector is down to high raw material costs, a lack of land, few government incentives and excessive regulations, developers say.
“One of the biggest problems we are facing is trying to have a gold standard house, which nobody can pay for,” Ibel said, adding that this model includes strict requirements for energy efficiency.
Policymakers should explore reducing red tape and offering incentives, such as tax breaks for companies building affordable homes, developers say.
However, if politicians do not make building affordable houses a priority, the situation would only get worse, driving a wedge between the most vulnerable — low-income families and asylum seekers — who are often competing housing in the same residential zones.
“Instead of building houses, we’ll build walls to keep people out,” said Sorcha Edwards, general secretary of Housing Europe, a network of European social housing providers. “We’re just going to be causing more tensions and divisions.”
NOT JUSTIFIED: The bank’s governor said there would only be a rate cut if inflation falls below 1.5% and economic conditions deteriorate, which have not been detected The central bank yesterday kept its key interest rates unchanged for a fifth consecutive quarter, aligning with market expectations, while slightly lowering its inflation outlook amid signs of cooling price pressures. The move came after the US Federal Reserve held rates steady overnight, despite pressure from US President Donald Trump to cut borrowing costs. Central bank board members unanimously voted to maintain the discount rate at 2 percent, the secured loan rate at 2.375 percent and the overnight lending rate at 4.25 percent. “We consider the policy decision appropriate, although it suggests tightening leaning after factoring in slackening inflation and stable GDP growth,”

DIVIDED VIEWS: Although the Fed agreed on holding rates steady, some officials see no rate cuts for this year, while 10 policymakers foresee two or more cuts There are a lot of unknowns about the outlook for the economy and interest rates, but US Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell signaled at least one thing seems certain: Higher prices are coming. Fed policymakers voted unanimously to hold interest rates steady at a range of 4.25 percent to 4.50 percent for a fourth straight meeting on Wednesday, as they await clarity on whether tariffs would leave a one-time or more lasting mark on inflation. Powell said it is still unclear how much of the bill would fall on the shoulders of consumers, but he expects to learn more about tariffs

Greek tourism student Katerina quit within a month of starting work at a five-star hotel in Halkidiki, one of the country’s top destinations, because she said conditions were so dire. Beyond the bad pay, the 22-year-old said that her working and living conditions were “miserable and unacceptable.” Millions holiday in Greece every year, but its vital tourism industry is finding it harder and harder to recruit Greeks to look after them. “I was asked to work in any department of the hotel where there was a need, from service to cleaning,” said Katerina, a tourism and marketing student, who would
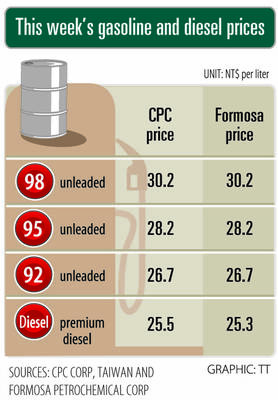
i Gasoline and diesel prices at fuel stations are this week to rise NT$0.1 per liter, as tensions in the Middle East pushed crude oil prices higher last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. International crude oil prices last week rose for the third consecutive week due to an escalating conflict between Israel and Iran, as the market is concerned that the situation in the Middle East might affect crude oil supply, CPC and Formosa said in separate statements. Front-month Brent crude oil futures — the international oil benchmark — rose 3.75 percent to settle at US$77.01