The US is considering unilateral restrictions on China’s access to artificial intelligence (AI) memory chips and equipment capable of making those semiconductors as soon as next month, a move that would further escalate the tech rivalry between the world’s biggest economies.
The measure is designed to keep Micron Technology Inc and South Korea’s leading memorychip makers SK Hynix Inc and Samsung Electronics Co from supplying Chinese firms with so-called high-bandwidth memory (HBM) chips, people familiar with the matter said. The three firms dominate the global HBM market.
US President Joe Biden’s administration is working on several restrictions aimed at keeping vital technology out of the hands of Chinese manufacturers, including limits on sales of chipmaking equipment. This rule would deliver a new set of constraints against memory chips for AI, the latest arena of US-China competition.
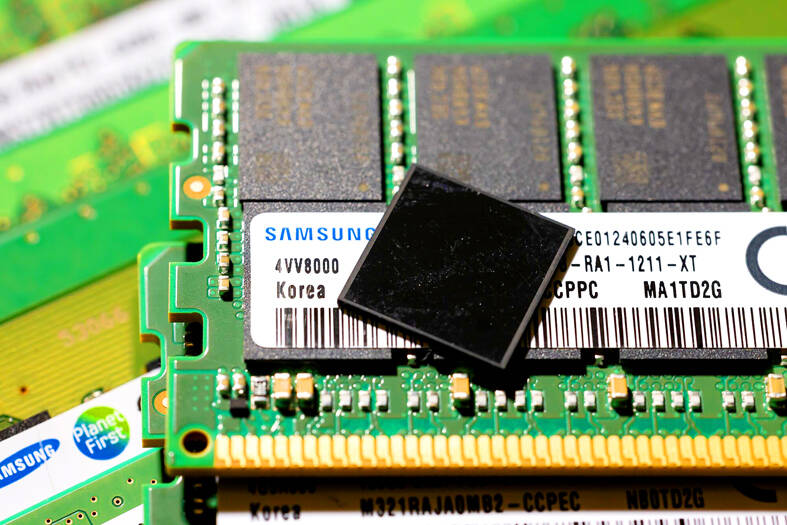
Photo: Bloomberg
If enacted, the measure would capture HBM2 and more advanced chips including HBM3 and HBM3E, the most cutting-edge AI memory chips being produced right now, as well as the tools required to make them, the sources said.
HBM chips are required to run AI accelerators like those offered by Nvidia Corp and Advanced Micro Devices Inc.
Micron would largely be unaffected as the Boise, Idaho-based chipmaker has refrained from selling its HBM products to China after Beijing banned its memory chips from critical infrastructure last year, the people said.
It is unclear what authority the US would use to restrict the South Korean firms, the people said. One possibility is the Foreign Direct Product Rule, which lets Washington impose controls on foreign-made products that use even the tiniest amount of US technology. SK Hynix and Samsung rely on US chip design software and equipment from the likes of Cadence Design Systems Inc and Applied Materials Inc.
Micron, Samsung and SK Hynix representatives declined to comment.
The new restrictions are likely to be unveiled later this month as part of a broader package that also includes sanctions against more than 120 Chinese firms and fresh limits on various types of chip equipment, with carve-outs for key allies including Japan, the Netherlands and South Korea, the people said.
As part of its comprehensive HBM-related curbs in the same export control package, the US plans to lower the threshold for what qualifies as advanced DRAM. A single HBM chip contains several DRAM dies.
New restrictions on HBM equipment and DRAM aim to deter leading Chinese memorychip maker ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc (長鑫存儲) from advancing its technology, the sources said. ChangXin is now capable of making HBM2, which first became commercially available in 2016.
Biden administration officials also plan to create a list of the critical components that China needs to keep producing semiconductors. They are also eyeing what is called a zero de-minimis rule, an even tighter standard for Foreign Direct Product Rule under which any products containing US technology would be subject to potential restrictions. A large group of US allies would be exempted from that measure, including Japan and the Netherlands.

Nvidia Corp chief executive officer Jensen Huang (黃仁勳) on Monday introduced the company’s latest supercomputer platform, featuring six new chips made by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電), saying that it is now “in full production.” “If Vera Rubin is going to be in time for this year, it must be in production by now, and so, today I can tell you that Vera Rubin is in full production,” Huang said during his keynote speech at CES in Las Vegas. The rollout of six concurrent chips for Vera Rubin — the company’s next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) computing platform — marks a strategic

REVENUE PERFORMANCE: Cloud and network products, and electronic components saw strong increases, while smart consumer electronics and computing products fell Hon Hai Precision Industry Co (鴻海精密) yesterday posted 26.51 percent quarterly growth in revenue for last quarter to NT$2.6 trillion (US$82.44 billion), the strongest on record for the period and above expectations, but the company forecast a slight revenue dip this quarter due to seasonal factors. On an annual basis, revenue last quarter grew 22.07 percent, the company said. Analysts on average estimated about NT$2.4 trillion increase. Hon Hai, which assembles servers for Nvidia Corp and iPhones for Apple Inc, is expanding its capacity in the US, adding artificial intelligence (AI) server production in Wisconsin and Texas, where it operates established campuses. This

Garment maker Makalot Industrial Co (聚陽) yesterday reported lower-than-expected fourth-quarter revenue of NT$7.93 billion (US$251.44 million), down 9.48 percent from NT$8.76 billion a year earlier. On a quarterly basis, revenue fell 10.83 percent from NT$8.89 billion, company data showed. The figure was also lower than market expectations of NT$8.05 billion, according to data compiled by Yuanta Securities Investment and Consulting Co (元大投顧), which had projected NT$8.22 billion. Makalot’s revenue this quarter would likely increase by a mid-teens percentage as the industry is entering its high season, Yuanta said. Overall, Makalot’s revenue last year totaled NT$34.43 billion, down 3.08 percent from its record NT$35.52

PRECEDENTED TIMES: In news that surely does not shock, AI and tech exports drove a banner for exports last year as Taiwan’s economic growth experienced a flood tide Taiwan’s exports delivered a blockbuster finish to last year with last month’s shipments rising at the second-highest pace on record as demand for artificial intelligence (AI) hardware and advanced computing remained strong, the Ministry of Finance said yesterday. Exports surged 43.4 percent from a year earlier to US$62.48 billion last month, extending growth to 26 consecutive months. Imports climbed 14.9 percent to US$43.04 billion, the second-highest monthly level historically, resulting in a trade surplus of US$19.43 billion — more than double that of the year before. Department of Statistics Director-General Beatrice Tsai (蔡美娜) described the performance as “surprisingly outstanding,” forecasting export growth