The US dollar and the yen bounced higher on Friday in a flight to safety, lifted by mounting fears of a global recession that has pushed the Japanese currency to fresh highs.
The euro plunged to US$1.2623 around 9pm GMT from US$1.2926 late on Thursday in New York.
The euro plummeted against the yen to ¥118.98 from ¥125.73. The greenback slid to ¥94.24 from ¥97.27.
News of a record low in eurozone business activity and Britain on the brink of recession sent shockwaves through markets, sending investors fleeing for the shelter of the dollar and yen.
The yen often rises at times of financial turmoil as dealers unwind risky bets funded with cheap Japanese credit.
“The best word to describe what’s going on right now is panic,” Credit Suisse strategist Satoru Ogasawara said. “When you don’t know what will come next, you tend to flee to the safest place.”
The euro touched another new low against the dollar since October 2006, at US$1.2497 around 9:30am GMT. On Wednesday the euro had fallen below US$1.30 for the first time since February last year.
The euro has lost more than 20 percent of its value against the dollar since striking a record high US$1.6038 in mid-July.
The pound sank to US$1.5269, the lowest level since August 2002, after official data showed the British economy shrank by 0.5 percent in the third quarter, its lowest level since 1992, after zero growth in the second quarter.
In late New York trading, the pound plunged to US$1.5900 from US$1.6216 late on Thursday.
The dollar rose to 1.1662 Swiss francs from SF1.1589.
Asian currencies slumped this week, led by South Korea’s won and Indonesia’s rupiah, as stocks slid on concern a global recession will damp demand for the region’s exports.
The won had a sixth weekly decline as the central bank said Asia’s fourth-largest economy grew 0.6 percent last quarter, the slowest pace in four years.
The won dropped 6.3 percent this week to close at 1,424 per US dollar in Seoul, near the lowest level in a decade, according to Seoul Money Brokerage Services Ltd.
The New Taiwan dollar completed its biggest weekly loss in 10 years after a government report showed the export outlook worsened more than economists expected last month.
The currency fell for an eighth day on Friday, the longest losing streak since August, after the Ministry of Economic Affairs said export orders grew at the slowest pace in six years last month as demand from the US and China cooled.
The NT dollar slumped 2.65 percent this week to NT$33.412 against the US dollar, the biggest five-day loss since the period ended Jan. 10, 1998, according to Taipei Forex Inc. The NT dollar lost 0.4 percent on Friday.
Indonesia’s rupiah fell 4.1 percent this week to 10,225 per dollar in Jakarta, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. The rupiah touched 10,315 a dollar, the weakest since October 2005.
India’s rupee fell for an 11th week after the central bank cut the economic growth outlook for the year ending March 31 to as little as 7.5 percent from an earlier estimate of 8 percent.
The currency slid as much as 0.7 percent to 50.165 per dollar, an all-time low, before closing at 49.985 in Mumbai on Friday, data compiled by Bloomberg show.
The Philippine peso lost 1.9 percent in the week to close at 48.991 per dollar in Manila, according to the Bankers Association of the Philippines. Exports make up about 40 percent of the Philippine economy.
Elsewhere, the Thai baht fell 1.3 percent versus the US dollar this week to 34.70 and the Singapore dollar dropped 1.9 percent to S$1.5105. Vietnam’s dong weakened 1.5 percent to 16,848.

NATIONAL SECURITY THREAT: An official said that Guan Guan’s comments had gone beyond the threshold of free speech, as she advocated for the destruction of the ROC China-born media influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China content that threatens national security, the National Immigration Agency said yesterday. Guan Guan has said many controversial things in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” while expressing hope for expedited “reunification.” The agency received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification last year. After investigating, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and account for her actions. Guan Guan appeared as required,
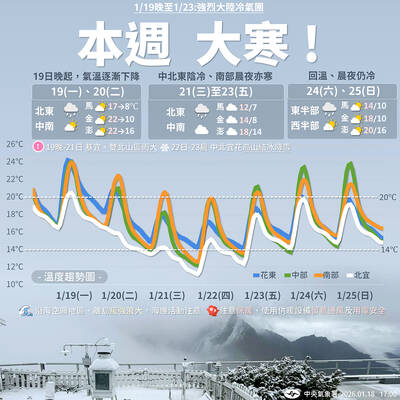
A strong cold air mass is expected to arrive tonight, bringing a change in weather and a drop in temperature, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said. The coldest time would be early on Thursday morning, with temperatures in some areas dipping as low as 8°C, it said. Daytime highs yesterday were 22°C to 24°C in northern and eastern Taiwan, and about 25°C to 28°C in the central and southern regions, it said. However, nighttime lows would dip to about 15°C to 16°C in central and northern Taiwan as well as the northeast, and 17°C to 19°C elsewhere, it said. Tropical Storm Nokaen, currently

PAPERS, PLEASE: The gang exploited the high value of the passports, selling them at inflated prices to Chinese buyers, who would treat them as ‘invisibility cloaks’ The Yilan District Court has handed four members of a syndicate prison terms ranging from one year and two months to two years and two months for their involvement in a scheme to purchase Taiwanese passports and resell them abroad at a massive markup. A Chinese human smuggling syndicate purchased Taiwanese passports through local criminal networks, exploiting the passports’ visa-free travel privileges to turn a profit of more than 20 times the original price, the court said. Such criminal organizations enable people to impersonate Taiwanese when entering and exiting Taiwan and other countries, undermining social order and the credibility of the nation’s

‘SALAMI-SLICING’: Beijing’s ‘gray zone’ tactics around the Pratas Islands have been slowly intensifying, with the PLA testing Taiwan’s responses and limits, an expert said The Ministry of National Defense yesterday condemned an intrusion by a Chinese drone into the airspace of the Pratas Islands (Dongsha Islands, 東沙群島) as a serious disruption of regional peace. The ministry said it detected the Chinese surveillance and reconnaissance drone entering the southwestern parts of Taiwan’s air defense identification zone early yesterday, and it approached the Pratas Islands at 5:41am. The ministry said it immediately notified the garrison stationed in the area to enhance aerial surveillance and alert levels, and the drone was detected in the islands’ territorial airspace at 5:44am, maintaining an altitude outside the effective range of air-defense weaponry. Following