FBI statistics on Monday confirmed what residents of big cities like Philadelphia, Houston, Cleveland and Las Vegas have seen on the streets: Violent crime in the US is on the rise, posting its biggest one-year percentage increase since 1991.
In Philadelphia, homicides jumped from 330 in 2004 to 377 last year, a 14 percent increase, according to the FBI. Murders climbed from 272 to 334 in Houston, a 23 percent rise, and from 131 to 144 in Las Vegas, a 10 percent increase.
Jeffrey Sedgwick, director of the US Justice Department's Bureau of Justice Statistics, cautioned that it is not yet clear whether the FBI numbers reflect a real increase, or what statisticians call "statistical noise."
Sedgwick said it is possible that crime rates in the US are approaching a floor below which it may be difficult or even impossible to go. "I'm not sure it's reasonable to expect you can always drive the crime rate down," he said.
Some criminal justice experts said the statistics reflect the nation's complacency in fighting crime. Crime dropped dramatically during the 1990s, and some cities have since abandoned effective programs that emphasized prevention, the putting of more cops on the street, and controls on the spread of guns.
"We see that budgets for policing are being slashed and the federal government has gotten out of that business," said James Alan Fox, a criminal justice professor at Northeastern University in Boston. Still, Fox said, "We're still far better off than we were during the double-digit crime inflation we saw in the 1970s."
In Philadelphia, which has had more than 160 murders this year, the police department has responded by creating a special unit charged with roaming the streets in the dangerous hours between 10pm and 3am. The program, which is expected to start soon, will shift 46 officers from other assignments.
Philadelphia police Captain Benjamin Naish said more people appear to be settling disputes with guns.
"I think that everybody continues to be frustrated within the government, within the department," he said. Philadelphia police have stressed that the number of killings is still below the averages in the mid-1990s and far below the 525 homicides in 1990.
The overall national increase in violent crime was modest, 2.5 percent, which equates to more than 1.4 million crimes. Nevertheless, that was the largest percentage increase since 1991.
Nationally, murders rose 4.8 percent, meaning there were more than 16,900 victims last year. That would be the most since 1998 and the largest percentage increase in 15 years.
Los Angeles and New York were among several big cities that saw murder numbers drop.

Yemen’s separatist leader has vowed to keep working for an independent state in the country’s south, in his first social media post since he disappeared earlier this month after his group briefly seized swathes of territory. Aidarous al-Zubaidi’s United Arab Emirates (UAE)-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) forces last month captured two Yemeni provinces in an offensive that was rolled back by Saudi strikes and Riyadh’s allied forces on the ground. Al-Zubaidi then disappeared after he failed to board a flight to Riyadh for talks earlier this month, with Saudi Arabia accusing him of fleeing to Abu Dhabi, while supporters insisted he was

The Chinese Embassy in Manila yesterday said it has filed a diplomatic protest against a Philippine Coast Guard spokesman over a social media post that included cartoonish images of Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平). Philippine Coast Guard spokesman Jay Tarriela and an embassy official had been trading barbs since last week over issues concerning the disputed South China Sea. The crucial waterway, which Beijing claims historic rights to despite an international ruling that its assertion has no legal basis, has been the site of repeated clashes between Chinese and Philippine vessels. Tarriela’s Facebook post on Wednesday included a photo of him giving a
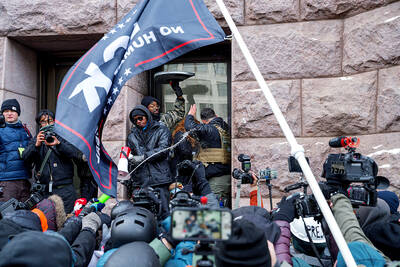
‘MOBILIZED’: While protesters countered ICE agents, Minnesota Governor Tim Walz activated the state’s National Guard to ‘support the rights of Minnesotans’ to assemble Hundreds of counterprotesters drowned out a far-right activist’s attempt to hold a small rally in support of US President Donald Trump’s latest immigration crackdown in Minneapolis, Minnesota, on Saturday, as the governor’s office announced that National Guard troops were mobilized and ready to assist law enforcement, although not yet deployed to city streets. There have been protests every day since the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) ramped up immigration enforcement in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul by bringing in more than 2,000 federal officers. Conservative influencer Jake Lang organized an anti-Islam, anti-Somali and pro-US Immigration and Customs Enforcement

NASA on Saturday rolled out its towering Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft as it began preparations for its first crewed mission to the Moon in more than 50 years. The maneuver, which takes up to 12 hours, would allow the US space agency to begin a string of tests for the Artemis 2 mission, which could blast off as early as Feb. 6. The immense orange and white SLS rocket, and the Orion vessel were slowly wheeled out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and painstakingly moved 6.5km to Launch Pad 39B. If the