Eventually, it seems, every senseless waste of life gets its own gauzy tear-jerker. That’s about the only way to justify The Flowers of War (金陵十三釵), in which veteran Chinese director Zhang Yimou (張藝謀) revisits the Nanjing Massacre of 1937 by making something resembling a backstage musical, with breaks for the occasional ghastly murder or rape.
There’s nothing that says the atrocity blockbuster has to be a disaster in its own right; films like Gone With the Wind and Gallipoli have their good points. But long before its 2 1/2 hours are up, The Flowers of War is sunk by the disproportion between the events being portrayed and Zhang’s distanced, strangely frivolous treatment of them — in essence, his refusal to take a point of view on one of the most gruesome chapters in Chinese history.
Flowers has received bountiful publicity for being expensive, state-approved and Oscar-submitted, buzz that got louder in December when the film’s British star, Christian Bale, was forcibly prevented from visiting a Chinese activist lawyer being held under house arrest.

Photo courtesy of BVI
But fears that Zhang would take a one-dimensional, patriotic approach to the Japanese invasion and occupation of Nanjing, while not entirely unfounded, are misplaced. Other recent Chinese films have displayed more sentimental nationalism, jingoism and demonization of the
Japanese enemy.
His real approach to the events of 1937 is to use them as a backdrop for the kind of deluxe, Hollywood-inspired melodrama that has made him an art-house favorite. In the process he fails to deliver on most of the elements — grandeur, historical sweep, genuine pathos — that would have made the film worthwhile.
Given the right story, as in Raise the Red Lantern (大紅燈籠高高掛組) or House of the Flying Daggers (十面埋伏), Zhang’s almost clinical attention to pretty surfaces and soap-opera mechanics can have entertaining results. In Flowers, though, you can feel him at war with his material, never settling on a tone or a compelling or even coherent narrative. (The screenplay is by Liu Heng (劉恆) and Geling Yan (嚴歌苓), based on a novel by Yan.)
Zhang’s distance from the larger story of the massacre is embodied in his decision to set most of the film within the compound of a fictional European church. The result is an artificial, back-lot atmosphere; the opening scenes, set in the streets, take place in an actual fog of war, with smoke (and at one point the dust from a large mound of flour) isolating the characters from the real world of Nanjing.
Bale plays John Miller, a disreputable American vagabond who happens to be a mortician; as the film begins he is making his way through the fighting toward the church, where he is to be paid to conduct a burial. Also on the move are two groups of a dozen or so young women, the flowers of the title. They are, as a matter of production design if not credible history, visually coded: convent students in severe blue jackets and prostitutes in seductive, rainbow-hued silken dresses.
All of these parties take refuge in the church, with Miller, who dons the robes of a dead priest, bridging the Manichaean divide between the suspicious students upstairs and the contemptuous, defensive prostitutes hiding in the basement. (They quickly transform their cellar into a seraglio; you can practically smell the perfume.) It’s a contrived, hothouse state of affairs, summed up in a scene Zhang likes so much that he repeats it: the laughing prostitutes sashaying across the churchyard in slow motion, oblivious to the impending tragedy.
There will be tragedy, of course, though when it comes it takes a weirdly oblique form. One group eventually performs what appears to be an ultimate sacrifice, full of sexual and social overtones, but this happens off-camera, if it happens at all. The coyness can be explained, perhaps, in terms of the film’s structure — the story is narrated by one of the students, and what we see may correspond to her selective, romanticized memories — but it cannot really be excused.
On-screen, meanwhile, the camera ventures into the outside world in occasional scenes that seem timed to goose the action and remind us that we’re watching a war movie. In one of Zhang’s few outright concessions to the notion of Chinese supremacism, a lone officer (Tong Dawei, 佟大為) draws a contingent of Japanese soldiers away from the church in an act of hyperbolic heroism. Later, in a surrender to gross sentimentality, two prostitutes leave the church on the sort of insane mercy mission that happens only in movies, with particularly disturbing consequences. Aside from that sequence Zhang is restrained in his depictions of Japanese brutality, which mostly take the form of threats and intimidation.
Bale, turning in a respectable if oddly chipper performance under the circumstances, has the unfortunate task of playing a character who doesn’t really add up. Miller’s conversion from opportunist to savior may be another stock element of this sort of movie, but the scene meant to showcase his transformation is rushed and ineffective. Having made an American the central figure in his film, Zhang reduces him to wrangling flocks of nubile women, like Cary Grant in a much more violent Father Goose.
The Flowers of War suffers greatly in comparison to several far superior, less hyped movies about the Nanjing Massacre, including the harrowing drama City of Life and Death (南京!南京!), directed by Lu Chuan (陸川), and the documentary Nanking, by Bill Guttentag and Dan Sturman. Those filmmakers came armed with points of view. Zhang, retreating into the mists of old movies, has declined to take the field.

The Nuremberg trials have inspired filmmakers before, from Stanley Kramer’s 1961 drama to the 2000 television miniseries with Alec Baldwin and Brian Cox. But for the latest take, Nuremberg, writer-director James Vanderbilt focuses on a lesser-known figure: The US Army psychiatrist Douglas Kelley, who after the war was assigned to supervise and evaluate captured Nazi leaders to ensure they were fit for trial (and also keep them alive). But his is a name that had been largely forgotten: He wasn’t even a character in the miniseries. Kelley, portrayed in the film by Rami Malek, was an ambitious sort who saw in

It’s always a pleasure to see something one has long advocated slowly become reality. The late August visit of a delegation to the Philippines led by Deputy Minister of Agriculture Huang Chao-ching (黃昭欽), Chair of Chinese International Economic Cooperation Association Joseph Lyu (呂桔誠) and US-Taiwan Business Council vice president, Lotta Danielsson, was yet another example of how the two nations are drawing closer together. The security threat from the People’s Republic of China (PRC), along with their complementary economies, is finally fostering growth in ties. Interestingly, officials from both sides often refer to a shared Austronesian heritage when arguing for

Among the Nazis who were prosecuted during the Nuremberg trials in 1945 and 1946 was Hitler’s second-in-command, Hermann Goring. Less widely known, though, is the involvement of the US psychiatrist Douglas Kelley, who spent more than 80 hours interviewing and assessing Goring and 21 other Nazi officials prior to the trials. As described in Jack El-Hai’s 2013 book The Nazi and the Psychiatrist, Kelley was charmed by Goring but also haunted by his own conclusion that the Nazis’ atrocities were not specific to that time and place or to those people: they could in fact happen anywhere. He was ultimately
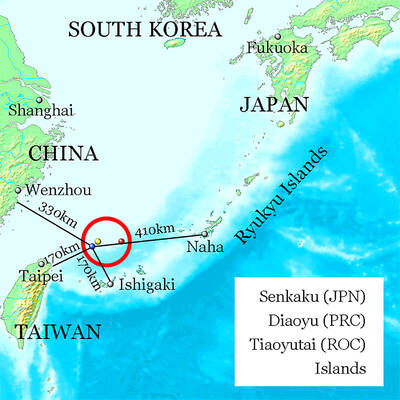
Last week gave us the droll little comedy of People’s Republic of China’s (PRC) consul general in Osaka posting a threat on X in response to Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi saying to the Diet that a Chinese attack on Taiwan may be an “existential threat” to Japan. That would allow Japanese Self Defence Forces to respond militarily. The PRC representative then said that if a “filthy neck sticks itself in uninvited, we will cut it off without a moment’s hesitation. Are you prepared for that?” This was widely, and probably deliberately, construed as a threat to behead Takaichi, though it