A global target of having 30 percent of the oceans become protected areas by 2030 is looking more fragile than ever, with little progress and the US backing away, conservationists said.
“With less than 10 percent of the ocean designated as MPAs [marine protected areas] and only 2.7 percent fully or highly protected, it is going to be difficult to reach the 30 percent target,” said Lance Morgan, head of the Marine Conservation Institute in Seattle.
The institute maps the MPAs for an online atlas, updating moves to meet the 30 percent goal that 196 countries signed onto in 2022, under the Kunling-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.

Photo: AFP
The ambition is notably at risk, because “we see countries like the US reversing course and abandoning decades of bipartisan efforts” to protect areas of the Pacific Ocean, Morgan said.
That referred to an April executive order by US President Donald Trump authorizing industrial-scale fishing in big swathes of an MPA in that ocean.
There are 16,516 declared MPAs in the world, covering just 8.4 percent of the oceans.
However, not all are created equal: Some forbid all forms of fishing, while others place no roles, or almost none, on what activities are proscribed or permitted.
“Only a third of them have levels of protection that would yield proper benefits” for fish, said Joachim Claudet, a socioecology marine researcher at the French National Centre for Scientific Research.
Daniel Pauly, a professor of fisheries science at the University of British Columbia, said “the marine protected areas have not really been proposed for the protection of biodiversity,” but “to increase fish catches.”
A proper MPA “exports fish to non-protected zones, and that should be the main reason that we create marine protected areas — they are needed to have fish,” he said.
When fish populations are left to reproduce and grow in protected areas, there is often a spillover effect that sees fish stocks outside the zones also rise, as several scientific journals have noted, especially around a no-fishing MPA in Hawaiian waters that is the biggest in the world.
One 2022 study in the Science journal showed a 54 percent increase in yellowfin tuna around that Hawaiian MPA, an area now threatened by Trump’s executive order, Pauly said.
For such sanctuaries to work, there need to be fishing bans over all or at least some of their zones, Claudet said.
However, MPAs with such restrictions account for just 2.7 percent of the ocean’s area, and are almost always in parts that are far from areas heavily impacted by human activities.
In Europe, for instance, “90 percent of the marine protected areas are still exposed to bottom trawling,” said Alexandra Cousteau, a spokesperson for the non-governmental organization Oceana. “It’s ecological nonsense.”
Pauly said that “bottom trawling in MPAs is like picking flowers with a bulldozer... They scrape the seabed.”
Oceana said French MPAs suffered intensive bottom trawling, 17,000 hours’ worth last year, as did those in British waters, with 20,600 hours.
The NGO is calling for a ban on the technique, which involves towing a heavy net along the sea floor, churning it up. Governments need to back words with action, or else these areas would be no more than symbolic markings on a map, said Jacob Armstrong, head of the WWF’s European office for the oceans.

THE TRAGEDY OF PUNCH: Footage of the seven-month-old Japanese macaque has gone viral online after he was rejected by his mother and formed a bond with a soft toy A baby monkey in Japan has captured hearts around the world after videos of him being bullied by other monkeys and rejected by his mother went viral last week. Punch, a Japanese macaque, was born in July last year at Ichikawa City Zoo. He has drawn international attention after zookeepers gave him a stuffed orangutan toy after he was abandoned by his mother. Without maternal guidance to help him integrate, Punch has turned to the toy for comfort. He has been filmed multiple times being dragged and chased by older Japanese macaques inside the enclosure. Early clips showed him wandering alone with
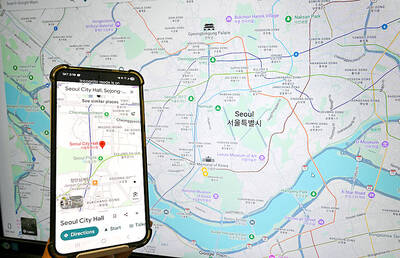
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail