Scientists yesterday announced a milestone in neurobiological research with the mapping of the entire brain of an adult fruit fly, a feat that might provide insight into the brains of other organisms and even people.
The research detailed more than 50 million connections between more than 139,000 neurons — brain nerve cells — in the insect, a species whose scientific name is Drosophila melanogaster and is often used in neurobiological studies. The research sought to decipher how brains are wired and the signals underlying healthy brain functions. It could also pave the way for mapping the brains of other species.
“You might be asking why we should care about the brain of a fruit fly. My simple answer is that if we can truly understand how any brain functions, it’s bound to tell us something about all brains,” said Princeton University professor of neuroscience and computer science Sebastian Seung, one of the co-leaders of the work published in a series of studies in the journal Nature.
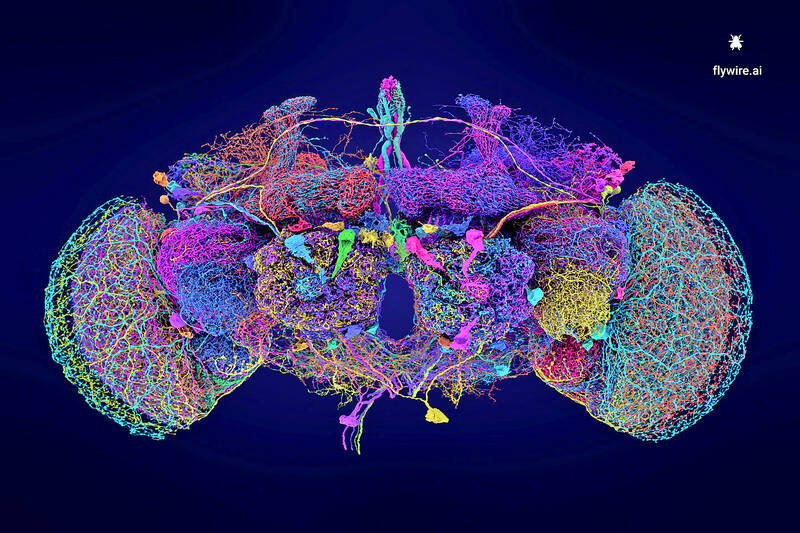
Photo: AFP / Tyler Sloan and Amy Sterling FlyWire, Princeton University
While some people might be more interested in swatting flies than studying them, some of the researchers found aesthetic satisfaction peering at the fruit fly brain, less than 1mm wide.
“It’s beautiful,” University of Cambridge neuroscientist and research coleader Gregory Jefferis said.
The map devised by the researchers provided a wiring diagram, known as a connectome, for the brain of an adult fruit fly. Similar research previously was conducted with simpler organisms, such as the worm Caenorhabditis elegans and the fruit fly’s larval stage. The adult fruit fly presented more complicated behaviors to study through its brain wiring.
“One of the major questions we’re addressing is how the wiring in the brain, its neurons and connections, can give rise to animal behavior,” said Princeton neuroscientist Mala Murthy, another of the coleaders of the research.
“And flies are an important model system for neurosciences. Their brains solve many of the same problems we do... They’re capable of sophisticated behaviors like the execution of walking and flying, learning and memory behaviors, navigation, feeding and even social interactions, which is a behavior that we studied in my lab at Princeton,” Murthy added.
One of the studies analyzed brain circuits underlying walking and discovered how flies halt.
Another analyzed the fly’s taste network and grooming circuits behind behavior such as when it uses a leg to remove dirt from its antennae. Another looked at the visual system including how the fly’s eyes process motion and color information. Still another one analyzed connectivity through the brain, discovering a large assemblage of “hub neurons” that may speed up information flow.
The researchers fashioned a map tracking the organization of the hemispheres and behavioral circuits inside the fly’s brain. They also identified the full set of cell classes in its brain, pinpointing different varieties of neurons and chemical connections — synapses — between these nerve cells, and looked at the types of chemicals secreted by the neurons.
The work was conducted by a large international collaboration of scientists known as the FlyWire Consortium.

Swedish campaigner Greta Thunberg was deported from Israel yesterday, the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs said, the day after the Israeli navy prevented her and a group of fellow pro-Palestinian activists from sailing to Gaza. Thunberg, 22, was put on a flight to France, the ministry said, adding that she would travel on to Sweden from there. Three other people who had been aboard the charity vessel also agreed to immediate repatriation. Eight other crew members are contesting their deportation order, Israeli rights group Adalah, which advised them, said in a statement. They are being held at a detention center ahead of a

A Chinese scientist was arrested while arriving in the US at Detroit airport, the second case in days involving the alleged smuggling of biological material, authorities said on Monday. The scientist is accused of shipping biological material months ago to staff at a laboratory at the University of Michigan. The FBI, in a court filing, described it as material related to certain worms and requires a government permit. “The guidelines for importing biological materials into the US for research purposes are stringent, but clear, and actions like this undermine the legitimate work of other visiting scholars,” said John Nowak, who leads field

Former Nicaraguan president Violeta Chamorro, who brought peace to Nicaragua after years of war and was the first woman elected president in the Americas, died on Saturday at the age of 95, her family said. Chamorro, who ruled the poor Central American country from 1990 to 1997, “died in peace, surrounded by the affection and love of her children,” said a statement issued by her four children. As president, Chamorro ended a civil war that had raged for much of the 1980s as US-backed rebels known as the “Contras” fought the leftist Sandinista government. That conflict made Nicaragua one of

NUCLEAR WARNING: Elites are carelessly fomenting fear and tensions between nuclear powers, perhaps because they have access to shelters, Tulsi Gabbard said After a trip to Hiroshima, US Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard on Tuesday warned that “warmongers” were pushing the world to the brink of nuclear war. Gabbard did not specify her concerns. Gabbard posted on social media a video of grisly footage from the world’s first nuclear attack and of her staring reflectively at the Hiroshima Peace Memorial. On Aug. 6, 1945, the US obliterated Hiroshima, killing 140,000 people in the explosion and by the end of the year from the uranium bomb’s effects. Three days later, a US plane dropped a plutonium bomb on Nagasaki, leaving abut 74,000 people dead by the