Marshall Islands officials said they are ready to resume talks with the US this week on renewing a long-standing economic and security deal, provided Washington addresses grievances stemming from the testing of nuclear weapons on the Pacific archipelago more than 70 years ago.
The US detonated 67 nuclear bombs in the Marshall Islands from 1946 to 1958, and the health and environmental impacts are still felt on the islands and atolls that lie between Hawaii and the Philippines.
US special envoy Joseph Yun is scheduled to land in the capital, Majuro, tomorrow to resume negotiations on extending the 20-year Compact of Free Association, part of which expires next year.

Photo: AFP
Marshall Islands negotiators first want the US to pay more of the compensation awarded by the international Nuclear Claims Tribunal, totaling more than US$3 billion, of which about US$270 million has been paid so far.
Officials in Majuro broke off talks in September to renew the compact, a key international agreement between the US, the Marshall Islands, Micronesia and Palau.
The Marshall Islands said it would also be ready to resume talks with Yun if Washington tackled health and environmental issues stemming from its nuclear testing.
“We are ready to sign [a compact extension] tomorrow, once the key issues are addressed,” Marshall Islands Parliament Speaker Kenneth Kedi said.
“We need to come up with a dignified solution,” he said.
Kedi represents Rongelap Atoll, which is still affected by nuclear testing. He was encouraged by an agreement signed in late September by US President Joe Biden and Pacific island leaders, including Marshall Islands President David Kabua, that included references to the US commitment to addressing its nuclear past.
However, until that happens, “it casts a question mark on all the promises Washington has made,” Kedi said.
“If we can’t resolve issues from our past, how will it be going forward with other issues?” he said.
Thousands of Marshall Islanders were engulfed in a radioactive fallout cloud following the 1954 Castle Bravo nuclear test by the US military, and many subsequently experienced health problems.
Tonnes of contaminated debris from the testing was dumped in a crater on the Enewetak Atoll and capped with concrete that has since cracked, sparking health concerns.
Hundreds of islanders from the Marshall’s Bikini, Enewetak, Rongelap and Utrik atolls have also had to relocate due to nuclear contamination. Many are still unable to return home.
A study issued by the US National Cancer Institute in 2004 estimated that about 530 cancer cases had been caused by the nuclear testing.
“As Bikinians, we’ve done enough for the United States,” said Alson Kelen, chairman of the Marshall Islands’ National Nuclear Commission, who believes the US should pay the full amount of the compensation awarded.
“We’re not asking to be rich. We’re asking for funding to solve our nuclear problems ... really the funds are to mitigate and address the problems of our health, relocations and nuclear cleanups,” Kelen said.

Yemen’s separatist leader has vowed to keep working for an independent state in the country’s south, in his first social media post since he disappeared earlier this month after his group briefly seized swathes of territory. Aidarous al-Zubaidi’s United Arab Emirates (UAE)-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) forces last month captured two Yemeni provinces in an offensive that was rolled back by Saudi strikes and Riyadh’s allied forces on the ground. Al-Zubaidi then disappeared after he failed to board a flight to Riyadh for talks earlier this month, with Saudi Arabia accusing him of fleeing to Abu Dhabi, while supporters insisted he was

The Chinese Embassy in Manila yesterday said it has filed a diplomatic protest against a Philippine Coast Guard spokesman over a social media post that included cartoonish images of Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平). Philippine Coast Guard spokesman Jay Tarriela and an embassy official had been trading barbs since last week over issues concerning the disputed South China Sea. The crucial waterway, which Beijing claims historic rights to despite an international ruling that its assertion has no legal basis, has been the site of repeated clashes between Chinese and Philippine vessels. Tarriela’s Facebook post on Wednesday included a photo of him giving a
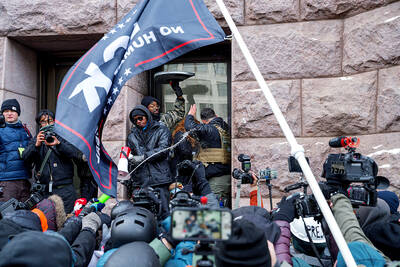
‘MOBILIZED’: While protesters countered ICE agents, Minnesota Governor Tim Walz activated the state’s National Guard to ‘support the rights of Minnesotans’ to assemble Hundreds of counterprotesters drowned out a far-right activist’s attempt to hold a small rally in support of US President Donald Trump’s latest immigration crackdown in Minneapolis, Minnesota, on Saturday, as the governor’s office announced that National Guard troops were mobilized and ready to assist law enforcement, although not yet deployed to city streets. There have been protests every day since the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) ramped up immigration enforcement in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul by bringing in more than 2,000 federal officers. Conservative influencer Jake Lang organized an anti-Islam, anti-Somali and pro-US Immigration and Customs Enforcement

NASA on Saturday rolled out its towering Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft as it began preparations for its first crewed mission to the Moon in more than 50 years. The maneuver, which takes up to 12 hours, would allow the US space agency to begin a string of tests for the Artemis 2 mission, which could blast off as early as Feb. 6. The immense orange and white SLS rocket, and the Orion vessel were slowly wheeled out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and painstakingly moved 6.5km to Launch Pad 39B. If the