It is not just rocket fuel propelling the US’ first moonshot after a half-century lull. Rivalry with China’s flourishing space program is helping drive NASA’s effort to get back into space in a bigger way as both nations push to put people back on the moon and establish the first lunar bases.
US intelligence, military and political leaders make clear that they see a host of strategic challenges to the US in China’s space program, in an echo of the US-Soviet rivalry that prompted the 1960s’ race to the moon.
That is as China is quickly matching US civil and military space accomplishments, and notching new ones of its own.
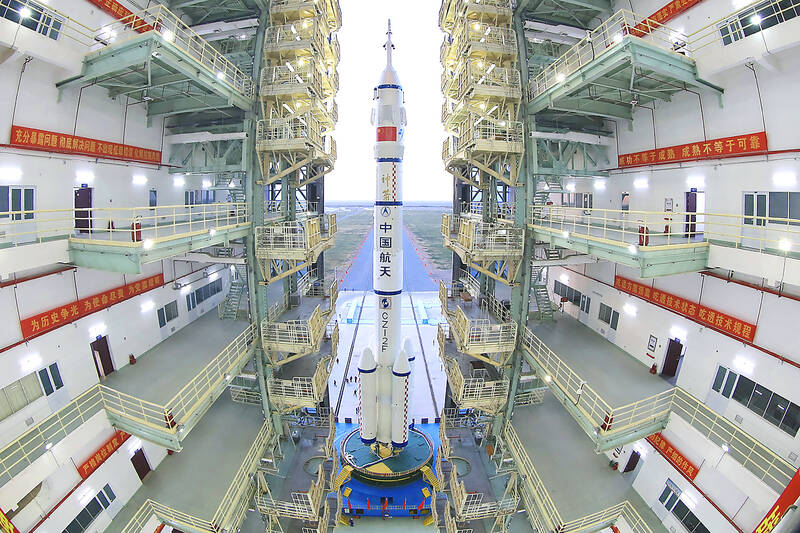

Photo: AP
On the military side, the US and China trade accusations of weaponizing space.
Senior US defense officials warn that China and Russia are building capabilities to take out the satellite systems that underpin US intelligence, military communications and early warning networks.
There is also a civilian side to the space race.
Photo: AP
The US is wary of China taking the lead in space exploration and commercial exploitation, and pioneering the technological and scientific advances that would put China ahead in power in space and in prestige on Earth.
“In a decade, the United States has gone from the unquestioned leader in space to merely one of two peers in a competition,” US Senator Jim Inhofe said this week at a US Senate Armed Services hearing. “Everything our military does relies on space.”
At another hearing last year, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson brandished an image transmitted by a Chinese rover that had just plunked down on Mars.
“The Chinese government ... they’re going to be landing humans on the moon” soon, Nelson said. “That should tell us something about our need to get off our duff.”
NASA is awaiting a new launch date this month or next month for its Artemis I uncrewed test moonshot. Technical problems scrubbed the first two launch attempts in the past few weeks.
China likewise aims to send astronauts to the moon this decade, as well as establish a robotic research station there.
The US and China intend to establish bases for intermittent crews on the moon’s south pole after that.
Russia has aligned with China’s moon program, while 21 nations have joined a US-initiated effort meant to bring guidelines and order to the civil exploration and development of space.
The parallel efforts come 50 years after US astronauts last pulled shut the doors on an Apollo module and blasted away from the moon, in December 1972.
Some space policy experts bat down talk of a new space race, seeing big differences from then-US president John F. Kennedy’s Cold War drive to outdo the Soviet Union’s Sputnik and be the first to get people on the moon.
This time, the US and China see moon programs as a stepping stone in phased programs toward exploring, settling and potentially exploiting the resources, and other untapped economic and strategic opportunities offered by the moon, Mars and space at large.
Beyond the gains in technology, science and jobs that accompany space programs, Artemis promoters point to the potential of mining minerals and frozen water on the moon, or using the moon as a base to go prospecting on asteroids.
The administration of former US president Donald Trump in particular emphasized the mining prospects.
There is potential in tourism and other commercial efforts.
And for space more broadly, Americans alone have tens of thousands of satellites overhead in what the US Space Force says is a US$500 billion global space economy.
Satellites guide GPS, process credit card purchases, help keep TV, radio and cellphone feeds going, and predict weather. They ensure the military and intelligence community’s ability to keep track of perceived threats.
In a world where China and Russia are collaborating to try to surpass the US in space, and where some point to private space efforts led by US billionaires as rendering costly NASA rocket launches unnecessary, Washington would regret leaving the glory and strategic advantages from developing the moon and space solely to the likes of Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平) and Tesla magnate Elon Musk, Artemis proponents say.
The moon programs signal that “space is going to be an arena of competition on the prestige front, demonstrating advanced technical expertise and know-how, and then also on the military front as well,” said Aaron Bateman, a professor of history and international affairs at George Washington University and a member of the Space Policy Institute.
“People who are supportive of Artemis and people who see it as a tool of competition, they want the United States to be at the table in shaping the future of exploration on other celestial bodies,” Bateman said.

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER: By showing Ju-ae’s ability to handle a weapon, the photos ‘suggest she is indeed receiving training as a successor,’ an academic said North Korea on Saturday released a rare image of leader Kim Jong-un’s teenage daughter firing a rifle at a shooting range, adding to speculation that she is being groomed as his successor. Kim’s daughter, Ju-ae, has long been seen as the next in line to rule the secretive, nuclear-armed state, and took part in a string of recent high-profile outings, including last week’s military parade marking the closing stages of North Korea’s key party congress. Pyongyang’s official Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) released a photo of Ju-ae shooting a rifle at an outdoor shooting range, peering through a rifle scope
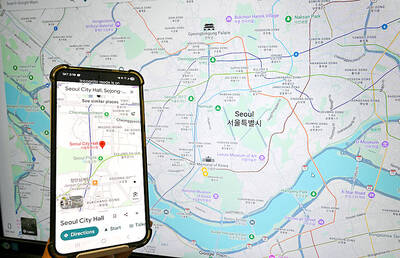
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

India and Canada yesterday reached a string of agreements, including on critical mineral cooperation and a “landmark” uranium supply deal for nuclear power, the countries’ leaders said in New Delhi. The pacts, which also covered technology and promoting the use of renewable energy, were announced after Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney hailed a fresh start in the relationship between their nations. “Our ties have seen a new energy, mutual trust and positivity,” Modi said. Carney’s visit is a key step forward in ties that effectively collapsed in 2023 after Ottawa accused New Delhi