Every year, the French consume about 4,000 tonnes of frog legs — the equivalent of 40 blue whales — but nearly all of the amphibian limbs that land on French plates come from abroad, as wild harvesting of the protected creatures is all but banned and their cultivation strictly controlled.
One of France’s handful of frog farmers, Patrice Francois, provides cuisses de grenouille to the kitchens of Michelin-starred restaurants and neighborhood bistros alike.
Yet, the 100,000 animals being raised at his greenhouses in Pierrelatte in southeast France hardly make a dent in the demand for a delicacy that helped earn the French the nickname “frogs,” at least in the English-speaking world.
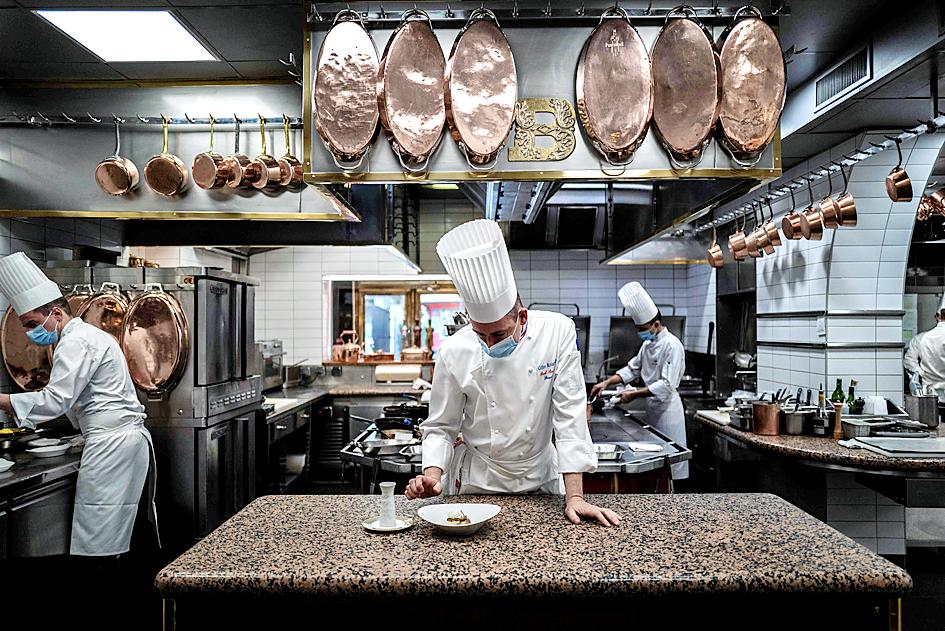

Photo: AFP
“Raising frogs is hard,” Francois told reporters, amid a deafening chorus of croaks coming from dozens of “ponds” teeming with marsh frogs, his farm’s specialty.
“It is starting to work out, but I am not yet making a living from it,” said the 56-year-old, who started France’s first frog farm 10 years ago.
To make ends meet, he also sells fish in Roanne, about 230km north.
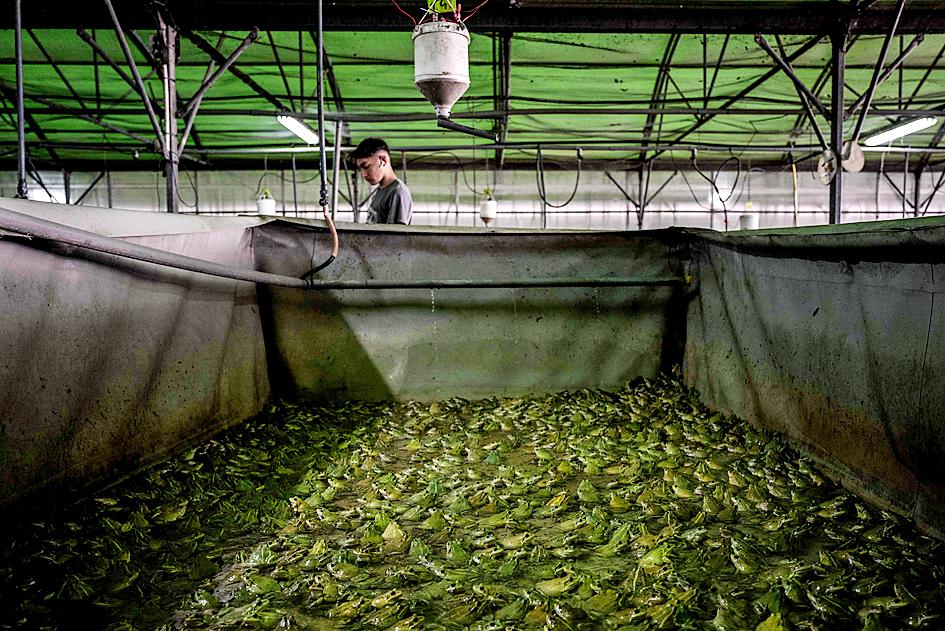

Photo: AFP
From the incubation of the eggs through raising the tadpoles and fattening up the adults, it takes about one year to produce a frog weighing 50g to 100g, each yielding two hind legs much smaller than chicken thighs.
“We control the entire production chain, from breeding to slaughter after anesthesia by cold, then butchery and shipping,” Francois said.
However, there are many hurdles along the way.
For mating to happen, conditions have to be just right, with the weather and even the lunar cycle affecting the creatures’ amorous moods.
Each fertilization by a male frog of a female’s deposited eggs can have a success rate of zero to 100 percent, depending on conditions, Francois said.
For 1 million eggs produced on the farm, about 100,000, or 10 percent, eventually mature into frogs.
The animals are easily stressed — which is harmful to their health and growth — and can suffocate if too many are grouped together.
The frogs must be grouped by size to prevent the larger ones from cannibalizing the smaller ones.
Five farms in France produce about 10 tonnes of frog meat per year, the French Ministry of Agriculture said, an amount that could reach 20 or even 50 tonnes as soon as this year.
Frogs have been eaten in France for centuries, particularly in the country’s east, but have been a protected species since 2007, because of rapidly declining numbers.
Only small wild harvests for domestic consumption are allowed, with large fines for anyone trying to catch them for sale.
Ninety-nine percent of frogs consumed in the country come from abroad — shipped alive or refrigerated from Albania, Turkey, Bulgaria, Egypt, Belgium and Italy, while frozen ones are shipped by Indonesia, Vietnam and India, the ministry said.
Frogs are also eaten in other European countries such as Belgium, in the southern US and in parts of Asia.
A 2010 study showed that global consumption was 800 million to 3.2 billion frogs, with the US and the EU the largest importers, and Indonesia and China the main exporters.
Conservationists have said that that many frog species are at risk of extinction, driven in large part by human appetites.
In key exporter Turkey, harvested species might become extinct by 2032, a study published this year by Cambridge University Press said.
Among Francois’ top clients is the storied two-Michelin-starred Paul Bocuse restaurant, near Lyon in eastern France, which boasts frog legs on its autumn menu.
Chef Gilles Reinhardt said that the restaurant long had no choice but to rely on imports.
“But nothing beats these ultra-fresh French frogs. The clients love them,” he said. “The meat is much more delicate, the frogs fleshier and firmer ... while still tender.”

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a

China yesterday held a low-key memorial ceremony for the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, with Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平) not attending, despite a diplomatic crisis between Beijing and Tokyo over Taiwan. Beijing has raged at Tokyo since Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi last month said that a hypothetical Chinese attack on Taiwan could trigger a military response from Japan. China and Japan have long sparred over their painful history. China consistently reminds its people of the 1937 Nanjing Massacre, in which it says Japanese troops killed 300,000 people in what was then its capital. A post-World War II Allied tribunal put the death toll
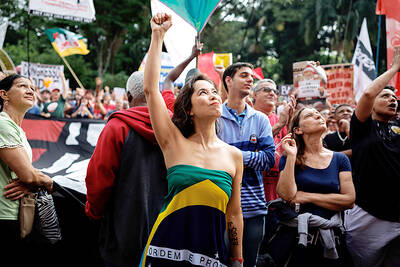
‘NO AMNESTY’: Tens of thousands of people joined the rally against a bill that would slash the former president’s prison term; President Lula has said he would veto the bill Tens of thousands of Brazilians on Sunday demonstrated against a bill that advanced in Congress this week that would reduce the time former president Jair Bolsonaro spends behind bars following his sentence of more than 27 years for attempting a coup. Protests took place in the capital, Brasilia, and in other major cities across the nation, including Sao Paulo, Florianopolis, Salvador and Recife. On Copacabana’s boardwalk in Rio de Janeiro, crowds composed of left-wing voters chanted “No amnesty” and “Out with Hugo Motta,” a reference to the speaker of the lower house, which approved the bill on Wednesday last week. It is

FALLEN: The nine soldiers who were killed while carrying out combat and engineering tasks in Russia were given the title of Hero of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea North Korean leader Kim Jong-un attended a welcoming ceremony for an army engineering unit that had returned home after carrying out duties in Russia, North Korean state media KCNA reported on Saturday. In a speech carried by KCNA, Kim praised officers and soldiers of the 528th Regiment of Engineers of the Korean People’s Army (KPA) for “heroic” conduct and “mass heroism” in fulfilling orders issued by the ruling Workers’ Party of Korea during a 120-day overseas deployment. Video footage released by North Korea showed uniformed soldiers disembarking from an aircraft, Kim hugging a soldier seated in a wheelchair, and soldiers and officials