The experimental coronavirus treatment remdesivir has failed in its first randomized clinical trial, inadvertently released results showed on Thursday, dampening expectations for the closely watched drug.
A draft summary went online briefly on the WHO Web site and was first reported by the Financial Times and health news Web site Stat, which posted a screenshot.
However, Gilead Sciences, the company behind the medicine, disputed how the now-deleted post had characterized the findings, saying that the data showed a “potential benefit.”
Photo: AFP
The Chinese trial involved 237 patients, with 158 on the drug and 79 in a control group, the summary said, adding that remdesivir was stopped early in 18 patients because of side effects.
The authors said that remdesivir was “not associated with a difference in time to clinical improvement” compared with the control.
After a month, 13.9 percent of the patients on remdesivir had died, compared with 12.8 percent of those in the control group. The difference is not statistically significant.
The WHO told the Financial Times that the draft is undergoing peer review and was published early in error.
“We believe the post included inappropriate characterizations of the study,” a Gilead spokesman told reporters, adding that it was terminated early due to low enrollment and was therefore not statistically meaningful.
“As such, the study results are inconclusive, though trends in the data suggest a potential benefit for remdesivir, particularly among patients treated early in disease,” the spokesman said.
The study does not represent the final word on the matter, and there are several large-scale trials in advanced stages that should soon provide a clearer picture.
Remdesivir, which is administered intravenously, was among the first drugs suggested as a treatment for the novel coronavirus and as such has great hopes riding on it.
Last week, Stat reported that it had shown significant efficacy at a Chicago hospital where patients who are part of one of the major trials are being treated.
The US National Institutes of Health also reported it that had proven effective in a small experiment on monkeys.
Remdesivir, which previously failed in trials against Ebola, belongs to a class of drugs that act on the virus directly — as opposed to controlling the abnormal and often lethal autoimmune response it causes. It mimics one of the four building blocks of RNA and DNA, and gets absorbed into the virus’ genome, which in turn stops the pathogen from replicating.
Anti-malarial drugs hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine have also been widely used on COVID-19 on a so-called “compassionate basis” pending results from large trials, with early studies decidedly mixed.
Other therapies that are being studied include collecting antibodies from COVID-19 survivors and injecting them in patients, or harvesting antibodies from genetically engineered mice that were deliberately infected.
Separately in France, new research shows that nicotine could protect people from contracting COVID-19.
The findings came after researchers at a top Paris hospital examined 343 COVID-19 patients, as well as 139 people with the illness who had milder symptoms.
They found that a low number of them smoked, compared with smoking rates of about 35 percent in France’s general population.
“Among these patients, only 5 percent were smokers,” said Zahir Amoura, the study’s coauthor and a professor of internal medicine.
The research echoed similar findings published in the New England Journal of Medicine last month suggesting that 12.6 percent of 1,000 people infected in China were smokers.
That was a much lower figure than the number of regular smokers in China’s general population, about 26 percent, WHO data showed.
The theory is that nicotine could adhere to cell receptors, therefore blocking the novel coronavirus from entering cells and spreading in the body, said neurobiologist Jean-Pierre Changeux from France’s Pasteur Institute, who also coauthored the study.
The researchers are awaiting approval from health authorities to carry out further clinical trials.
The researchers are looking into whether nicotine could help to prevent “cytokine storms,” a rapid overreaction of the immune system that scientists think could play a key role in fatal COVID-19 cases.
However, with further research needed, experts are not encouraging people to pick up smoking or use nicotine patches as a protective measure against the virus.
“We must not forget the harmful effects of nicotine,” French Director-General for Health Jerome Salomon said.
“Those who do not smoke should absolutely not use nicotine substitutes,” which cause side effects and addiction, he said.

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER: By showing Ju-ae’s ability to handle a weapon, the photos ‘suggest she is indeed receiving training as a successor,’ an academic said North Korea on Saturday released a rare image of leader Kim Jong-un’s teenage daughter firing a rifle at a shooting range, adding to speculation that she is being groomed as his successor. Kim’s daughter, Ju-ae, has long been seen as the next in line to rule the secretive, nuclear-armed state, and took part in a string of recent high-profile outings, including last week’s military parade marking the closing stages of North Korea’s key party congress. Pyongyang’s official Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) released a photo of Ju-ae shooting a rifle at an outdoor shooting range, peering through a rifle scope
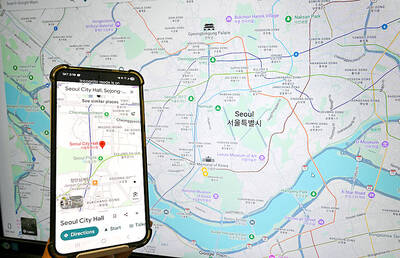
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail