It is just a single word, but it is hard to miss in North Korea. It is splashed across countless propaganda signs, seeded through dozens of state media reports, at the beating heart of emotional pop songs and on the lips of the earnest guides who show off the grand monuments built in its honor.
The word is juche, and while it is technically a political ideology, it can seem more like a religion in its ability to inspire devotion among North Koreans and its ubiquity as a symbol of state power.
Although the usual English translation is “self-reliance,” the concept flummoxes many outsiders.

Photo: AFP
Pyongyang uses the term liberally, including in previous years at the UN, where a North Korean official was to speak yesterday at the annual General Assembly.
The nation calls nuclear bombs the “treasured sword” of juche. Newly unveiled weapons fire “juche shells.” The August test of a new rocket launcher heralded the “rapid development of the juche-oriented defense industry.”
At a Pyongyang karaoke parlor, visitors can choose to belt out at least two juche-related titles: Juche Iron is the Best and The Way of Juche is the Way of Korea.
Juche is even used to count the passing years: This year is juche 108, because it has been 108 years since national founder Kim Il-sung was born.
Although it has been around for decades, some observers believe juche has been embraced in the past few years with renewed vigor by North Korean leader Kim Jong-un, the third generation of his family to rule North Korea, as he steps out with growing confidence onto the world stage for a series of high-stakes summits over his nuclear weapons program and the international sanctions crippling his economy.
North Korea has officially “enshrined ‘self-reliance and self-development’” as the new ideological theme of the Kim Jong-un era, taking the place of his father Kim Jong-il’s military-first policies, said Joshua Pollack, a North Korea expert at the Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey and a close reader of its propaganda.
“The essence of it is that independent progress in science and technology is supposed to resolve national defense problems and economic problems alike,” he said.
Some critics call juche a successful, but vaguely defined, piece of propaganda that allows North Korea to energize its citizens with a nationalistic rallying cry amid a barrage of sanctions, while also dodging responsibility over claims of economic mismanagement.
For calamity after calamity — the collapse of the Soviet Union, the North’s major aid backer, in the 1990s; a devastating famine that same decade; relentless economic sanctions — there is always an answer and a solace: juche.
Despite the slogan, the country is heavily reliant on outside aid.
South Korea, for example, has spent about US$5.8 billion on North Korea aid and economic projects through a government fund established in 1991 to promote inter-Korean relations, according to the South’s state-run Export-Import Bank of Korea, which operates the fund.
“The ‘self-reliance’ claims of juche notwithstanding, North Korea has long survived on the largesse of the international community,” Stephan Haggard, a North Korea expert at the Peterson Institute for International Economics in Washington, has written.
Kim Jong-un has made the development of nuclear bombs and the struggling economy twin priorities of his rule, and repeated references to juche run through the propaganda centered on both efforts.
However, there is a debate among outsiders on what, exactly, the term means under Kim Jong-un’s rule — and why it is important.
North Koreans, by contrast, harbor little doubt.
“The essence of the juche idea is that man is the master of his own destiny,” Kim Chang-kyong, department head at the North Korean Social Scientists Association and an expert in juche, said in an interview in Pyongyang.
Understanding his country, he said, is impossible without understanding juche, because “all the achievements of the country are linked to the idea, which forms the guidelines of the party and state.”
At the 170m tall Tower of Juche Idea, a soaring testament to the concept built in 1982 for Kim Il-sung’s 70th birthday, guide Choe Hye-ok had a ready definition at hand: “If one believes in the local people, and relies on them, one will get the universe. This is exactly the meaning of juche.”
For many outsiders, the more it is studied, the more the word can seem less, not more, defined.
Bruce Cumings, a leading academic on North Korea, has written: “The closer one gets to [juche’s] meaning, the more it slips away.”
Asked about juche’s meaning, Pollack said: “Long story. Hotly contested.”
“There is some confusion here about juche. We tend to render it as ‘self-reliance,’ but the North Koreans never do,” he said. “They just spell it out as juche, as if to indicate it’s untranslatable.”
Kim Chang-kyong linked juche to Kim Jong-un’s ambitious construction of new skyscraper apartments, which has continued in recent years, despite strengthened sanctions.
“It is the might of juche,” he said. “Even if someone does not help us, we will build by ourselves.”
Kim Il-sung is credited with constructing juche while leading Korean guerrillas in the fight against Japanese colonizing forces, while Kim Jong-il is said to have systemized the concept.
Starting in the 1970s, juche was presented as “the highest and most up-to-date brand of progressive ideology. It justified the superiority of the North Korean leadership,” Andrei Lankov, a North Korea expert at Kookmin University in Seoul, has written.
North Korean state media claim there are juche followers worldwide and point to their interest as evidence of juche’s power.
As he worked to explain juche, Kim Chang-kyong compared it to another uniquely Korean word — kimchi, the Korean staple of fermented spicy vegetables.
“Kimchi was created in our country. But for us it is just kimchi. Nobody uses another word to describe kimchi,” he said.
“There is no way to directly translate it into English. I can only translate juche as juche,” he said.

Yemen’s separatist leader has vowed to keep working for an independent state in the country’s south, in his first social media post since he disappeared earlier this month after his group briefly seized swathes of territory. Aidarous al-Zubaidi’s United Arab Emirates (UAE)-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) forces last month captured two Yemeni provinces in an offensive that was rolled back by Saudi strikes and Riyadh’s allied forces on the ground. Al-Zubaidi then disappeared after he failed to board a flight to Riyadh for talks earlier this month, with Saudi Arabia accusing him of fleeing to Abu Dhabi, while supporters insisted he was

The Chinese Embassy in Manila yesterday said it has filed a diplomatic protest against a Philippine Coast Guard spokesman over a social media post that included cartoonish images of Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平). Philippine Coast Guard spokesman Jay Tarriela and an embassy official had been trading barbs since last week over issues concerning the disputed South China Sea. The crucial waterway, which Beijing claims historic rights to despite an international ruling that its assertion has no legal basis, has been the site of repeated clashes between Chinese and Philippine vessels. Tarriela’s Facebook post on Wednesday included a photo of him giving a
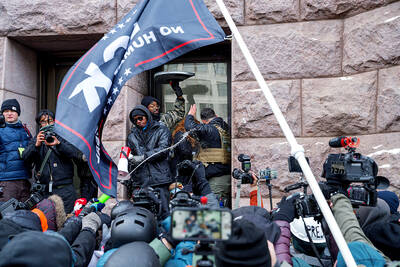
‘MOBILIZED’: While protesters countered ICE agents, Minnesota Governor Tim Walz activated the state’s National Guard to ‘support the rights of Minnesotans’ to assemble Hundreds of counterprotesters drowned out a far-right activist’s attempt to hold a small rally in support of US President Donald Trump’s latest immigration crackdown in Minneapolis, Minnesota, on Saturday, as the governor’s office announced that National Guard troops were mobilized and ready to assist law enforcement, although not yet deployed to city streets. There have been protests every day since the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) ramped up immigration enforcement in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul by bringing in more than 2,000 federal officers. Conservative influencer Jake Lang organized an anti-Islam, anti-Somali and pro-US Immigration and Customs Enforcement

NASA on Saturday rolled out its towering Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft as it began preparations for its first crewed mission to the Moon in more than 50 years. The maneuver, which takes up to 12 hours, would allow the US space agency to begin a string of tests for the Artemis 2 mission, which could blast off as early as Feb. 6. The immense orange and white SLS rocket, and the Orion vessel were slowly wheeled out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and painstakingly moved 6.5km to Launch Pad 39B. If the