The mikado pheasant, also known as “emperor’s pheasant,” is a species of pheasant endemic to Taiwan that is featured on Taiwan’s NT$1,000 bill. The mikado pheasant was once on the verge of extinction. However, thanks to the hard efforts of conservation workers, it has now returned to stable population levels. The Ministry of the Interior on Thursday shared the good news on its official Facebook page. It is a hard-won achievement that has been 30 years in the making. The ministry used the post to remind the public that if they encounter mikado pheasants while in mountainous or forest areas, they should admire the birds from a distance and refrain from disturbing them. The ministry also said that it hopes everyone will work together to protect Taiwan’s ecological diversity.
Taiwan is the only country in the world to have achieved success with a mikado pheasant breeding program. Since it was discovered that the mikado pheasant faced extinction, during 30 years of observation, the bird’s population within Yushan National Park has increased from just over 5,000 in 1986 to more than 10,000 today.
According to the Yushan National Park Administration Office, the mikado pheasant’s name was coined in 1906 when British ornithologists traveled to Yushan to collect specimens and inadvertently discovered two tail feathers of a male mikado pheasant on the headdress of a Tsou Aborigine. After being sent back to Britain for identification, the bird was announced as a new species.
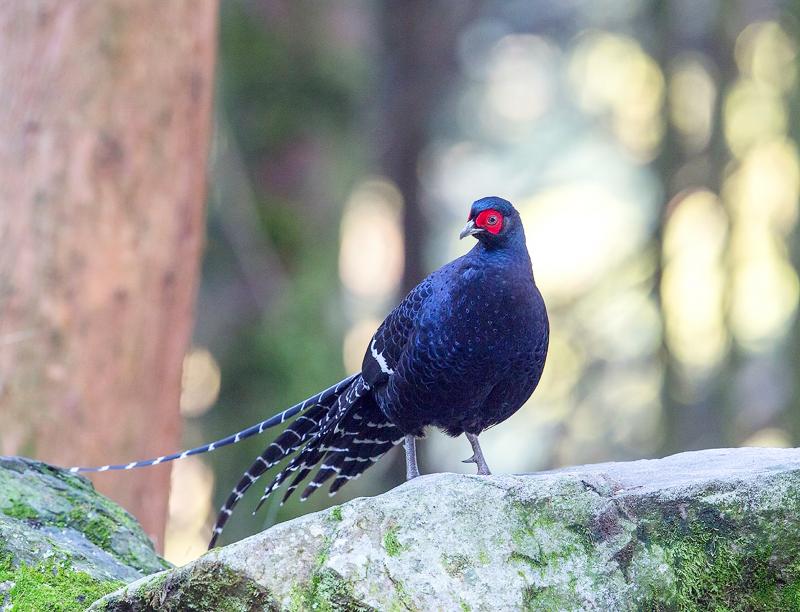

Photo courtesy of Hsieh Yu-chen 照片:謝郁震提供
The mikado pheasant often inhabits high mountains at an altitude of 1,800 to 3,300m above sea level and it likes dense fog. In addition to Yushan National Park, the mikado pheasant can also be seen at Shei-Pa National Park and Taroko National Park.
(Translated by Edward Jones)
被印在千元鈔上的台灣特有種鳥類「帝雉」原已瀕臨絕種,不過在相關單位復育人員努力下,如今已復育有成。內政部週四特別在臉書粉專分享相關訊息,表示這是經過三十年的努力,提醒民眾若在山林巧遇牠們,可以遠遠欣賞,不要刻意驚擾,也期盼大家未來共同努力守護生態多樣的台灣。

Photo courtesy of China Airlines via CNA 照片:華航提供/中央社
全世界只有台灣有的帝雉復育有成。經過三十年觀察,發現瀕臨絕種的帝雉,已經從一九八六年玉山國家公園觀測到的五千多隻,提升到目前的超過一萬隻。
根據玉山國家公園管理處,帝雉命名起源於西元一九○六年,由英國人深入玉山進行蒐集標本工作時,無意間在鄒族人的頭飾上發現了兩根雄帝雉的尾羽,經送回英國鑑定後,發表為新品種。
帝雉常棲息於海拔一千八百到三千三百公尺高山上,喜歡濃霧,不只在玉山國家公園、雪霸國家公園,還有太魯閣國家公園都可以看到牠的蹤跡。
(自由時報)

A: Wow, US climber Alex Honnold has announced that he’s going to free-climb Taipei 101 on Jan. 24. And the challenge, titled “Skyscraper Live,” will be broadcast worldwide live on Netflix at 9am. B: Oh my goodness, Taipei 101 is the world’s tallest green building. Is he crazy? A: Honnold is actually the climber in the 2019 film “Free Solo” that won an Oscar for best documentary, and was directed by Taiwanese-American Jimmy Chin and his wife. He’s a legendary climber. B: Didn’t Alain Robert, “the French Spiderman,” also attempt to scale Taipei 101 in 2004? A: Yes, but

A: There are always adventurers who want to conquer Taipei 101 as a world-class landmark. Didn’t someone once parachute from the top of it? B: Yeah, that’s right. Austrian extreme sportsman Felix Baumgartner once parachuted from the rooftop observation deck in 2007 without permission. He died earlier last year in a powered paragliding crash at the age of 56. A: Hollywood superstar Tom Cruise also almost jumped off Taipei 101 for “Mission Impossible 3.” B: What? But I didn’t see the building in the movie. A: The news says that the film’s producers applied to the Taipei City
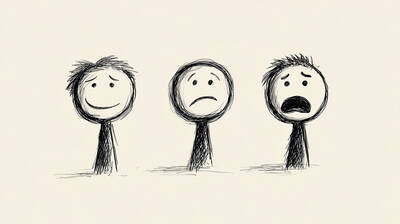
People use far more than just spoken language to communicate. Apart from using our voices to pronounce words, we also use body language, which includes countless facial expressions. Most people know that smiles and frowns indicate pleasure and displeasure, or that wide eyes with raised eyebrows typically show surprise. However, there is a lot more to learn about how facial expressions can help or hinder communication. People often unintentionally reveal their emotions through very tiny facial movements known as “microexpressions.” The term was popularized by psychologist Paul Ekman, who found that people from cultures across the world generally recognize

Nestled in the mountain region of northern Taiwan lies a small village that was once bustling due to a thriving coal industry, only to later gain fame for an entirely different reason — cats. This is Houtong Cat Village (猴硐貓村), located in Ruifang District, New Taipei City. Traditional Coal Mining and Village Transformation Houtong was originally known as “Monkey Cave” (houtong, 猴洞), a name derived from the wild monkeys that once inhabited caves in the surrounding hills. During the Japanese colonial period in the early 20th century, rich coal deposits were discovered and developed, rapidly turning Houtong into one of northern Taiwan’s