The outfall of the Linyuan ocean wetland park in Kaohsiung has recently been overflowing with bristleworms. A conservation volunteer who came into contact with a bristleworm was left in pain for between four and five days.
The Linyuan ocean wetland park is also known as “Jellyfish lake” due to its upside-down jellyfish. Recently, there has been the addition of bristleworms. Although, the two are separate species, they share a similar characteristic: both possess a mild poison. President of the Linyuan mangrove forest conservation society, Su Wen-hua, says during the summer holiday, children are occasionally seen playing in the water and called on them not to do so, in order to avoid coming into contact with bristleworms or jellyfish by accident.
Su says bristleworms are often found in salt lakes. Due to fish becoming more prevalent in the wetland park, there is an abundant supply of food for the bristleworms, which is why they are assembling in ever larger numbers. Because bristleworms like to move around in water, they currently only exist in the outfall of the Linyuan ocean wetland park. Su emphasised, bristleworms are not harmful. In fact their diet mainly consists of fish carcasses and organic detritus. For this reason they are also known as “sweepers,” since they improve they quality of water.

Photo: Hung Chen-hung, Liberty Times
照片:自由時報記者洪臣宏
A conservation volunteer, using their own body to test the poison, discovered the sting from an upside-down jellyfish will last for over a week and the bristleworm’s sting will last for between four and five days, although both are not easily provoked. Su said capturing fish is forbidden at the wetland park and he hopes that visitors will not try to flip over upside-down jellyfish or bristleworms, or play in the water, so as to avoid being stung.
(Liberty Times, translated by Edward Jones)

Photo: Hung Chen-hung, Liberty Times
照片:自由時報記者洪臣宏
高雄林園海洋濕地公園出水口最近滿布剛毛蟲,有保育志工碰觸後痛了四、五天。
林園海洋濕地公園因倒立水母而有「水母湖」之稱,最近又多了剛毛蟲,兩個不同物種卻有著一個相同特性,就是都具有微毒性。林園區紅樹林保育學會理事長蘇文華說,正值暑假偶見學童戲水,呼籲不要下水以免誤碰。
蘇文華說,剛毛蟲常見於潟湖,濕地公園的魚類愈來愈多,剛毛蟲食物來源充足,才會愈聚愈多。因喜歡在流動水域生存,目前只存在林園海洋濕地公園出水口。他強調,剛毛蟲不是害蟲,事實上牠以魚屍等腐質有機物為食,有「清道夫」之稱,可以改善水質。
有保育志工「以身試毒」,發現被倒立水母螫到會痛上一星期,剛毛蟲也會痛個四、五天,都不是好惹的。蘇文華說濕地公園禁止捕魚,他也希望遊客不要去抓倒立水母、剛毛蟲或戲水,以免被螫到。
(自由時報記者洪臣宏)

A: Which team do you think will win the championship in the 2026 World Baseball Classic? B: The previous champion Japan and runner-up the US are exceptionally strong. A: The Taiwan team was captained by Chen Chieh-hsien with a roster of 16 pitchers, 3 catchers and 11 fielders, and was quite strong, too. B: Yeah, players like Hu Chih-wei, Lin Tzu-wei, Yu Chang and Cheng Tsung-che all played in Major League Baseball. And this tournament marked the first call-up of mixed-race talent: MLB’s Stuart Fairchild. A: There are also some Taiwanese stars playing in Japan, including
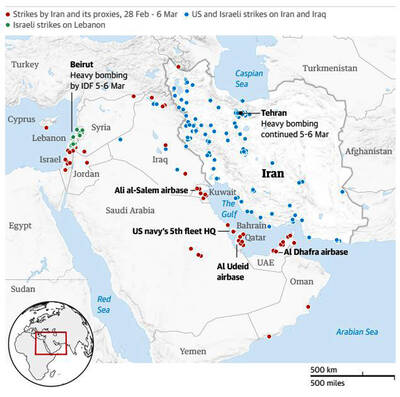
The US-Israeli war on Iran, launched on Feb. 28, has set the Middle East alight, threatening millions of people’s lives and livelihoods as the violence spreads in widening arc stretching from central Asia to the edge of Europe. The joint operation, named “Epic Fury” by the US and “Roaring Lion” by Israel, has been sold as a high-impact show of intimidating power, but its impact so far beyond the chaos and bloodshed is unclear. What is certain is that predictions that this type of war would destabilize the region have indeed rapidly materialized. What is the background to this war? For decades, the

A: Did you watch the preliminary games of the 2026 World Baseball Classic? Pool C included Australia, the Czech Republic, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan. All the games in Tokyo were absolutely intense. B: Of course. Many teams called up star players from Major League Baseball this time. Going up against players like Shohei Ohtani must come with enormous pressure. A: Japan and South Korea ultimately advanced to the quarterfinals, which are scheduled for March 14 and 15 in Miami. B: What about the semifinals and the final? A: The semifinals are set for the 16 and 17, followed

The English Lake District, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2017, is renowned for its landscapes, literary legacy and traditional farming. Yet, its esteemed status now sits at the center of a debate: is the designation protecting the region—or harming it? Conservationist Lee Schofield has sparked controversy by campaigning to revoke the Lake District’s World Heritage status. He argues that the label reinforces unsustainable farming, particularly the dominance of sheep grazing, which prevents ecological restoration and harms biodiversity. The famous Herdwick sheep, while culturally significant, contribute to overgrazing, soil erosion, and the prevention of forest recovery. Schofield clarifies that