The US on Wednesday laid out its most detailed case yet against Beijing’s “unlawful” claims in the South China Sea, rejecting the geographic and historic bases for its vast, divisive map.
In a 47-page research paper, the US Department of State’s Bureau of Oceans and International Environmental and Scientific Affairs said that China had no basis under international law for claims that have put Beijing on a collision course with the Philippines, Vietnam and other Southeast Asian nations.
“The overall effect of these maritime claims is that the PRC unlawfully claims sovereignty or some form of exclusive jurisdiction over most of the South China Sea,” the paper said, referring to the People’s Republic of China.

Photo: EPA-EFE
“These claims gravely undermine the rule of law in the oceans and numerous universally recognized provisions of international law reflected in the convention,” it said, referring to a 1982 UN treaty on the law of the sea ratified by China — but not the US.
Releasing the study, a state department statement called again on Beijing “to cease its unlawful and coercive activities in the South China Sea.”
China hit back yesterday, saying the report “distorts international law and misleads the public.”
“The US refuses to sign the treaty, but portrays itself as a judge and wantonly distorts the treaty,” Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesman Wang Wenbin (汪文斌) told a briefing in Beijing.
“In seeking its own selfish interests it uses multiple standards to carry out political manipulation,” he added.
The paper is an update of a 2014 study that similarly disputed the so-called “nine-dash line” that forms the basis for much of Beijing’s stance.
In 2016, an international court sided with the Philippines in its complaints over China’s claims.
Beijing replied by offering new justifications, including saying that China had “historic rights” over the area.
The state department paper said that such historical-based claims had “no legal basis” and that China had not offered specifics.
It also took issue with geographic justifications for China’s claims, saying that more than 100 features Beijing highlights in the South China Sea are submerged by water during high tide and therefore are “beyond the lawful limits of any state’s territorial sea.”
Beijing cites such geographic features to claim four “island groups,” which the state department study said did not meet criteria for baselines under the UN convention.
The report was issued as the US increasingly challenges China on the global stage, identifying the rising communist power as its chief long-term threat.
The South China Sea is home to valuable oil and gas deposits and shipping lanes, and Beijing’s neighbors have frequently voiced concern that their giant neighbor was seeking to expand its reach.

NATIONAL SECURITY THREAT: An official said that Guan Guan’s comments had gone beyond the threshold of free speech, as she advocated for the destruction of the ROC China-born media influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China content that threatens national security, the National Immigration Agency said yesterday. Guan Guan has said many controversial things in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” while expressing hope for expedited “reunification.” The agency received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification last year. After investigating, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and account for her actions. Guan Guan appeared as required,
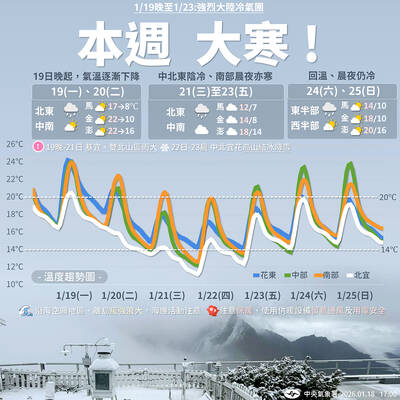
A strong cold air mass is expected to arrive tonight, bringing a change in weather and a drop in temperature, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said. The coldest time would be early on Thursday morning, with temperatures in some areas dipping as low as 8°C, it said. Daytime highs yesterday were 22°C to 24°C in northern and eastern Taiwan, and about 25°C to 28°C in the central and southern regions, it said. However, nighttime lows would dip to about 15°C to 16°C in central and northern Taiwan as well as the northeast, and 17°C to 19°C elsewhere, it said. Tropical Storm Nokaen, currently

‘NATO-PLUS’: ‘Our strategic partners in the Indo-Pacific are facing increasing aggression by the Chinese Communist Party,’ US Representative Rob Wittman said The US House of Representatives on Monday released its version of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, which includes US$1.15 billion to support security cooperation with Taiwan. The omnibus act, covering US$1.2 trillion of spending, allocates US$1 billion for the Taiwan Security Cooperation Initiative, as well as US$150 million for the replacement of defense articles and reimbursement of defense services provided to Taiwan. The fund allocations were based on the US National Defense Authorization Act for fiscal 2026 that was passed by the US Congress last month and authorized up to US$1 billion to the US Defense Security Cooperation Agency in support of the

PAPERS, PLEASE: The gang exploited the high value of the passports, selling them at inflated prices to Chinese buyers, who would treat them as ‘invisibility cloaks’ The Yilan District Court has handed four members of a syndicate prison terms ranging from one year and two months to two years and two months for their involvement in a scheme to purchase Taiwanese passports and resell them abroad at a massive markup. A Chinese human smuggling syndicate purchased Taiwanese passports through local criminal networks, exploiting the passports’ visa-free travel privileges to turn a profit of more than 20 times the original price, the court said. Such criminal organizations enable people to impersonate Taiwanese when entering and exiting Taiwan and other countries, undermining social order and the credibility of the nation’s