Nov. 4 to Nov. 10
Apollo magazine (文星) vowed that it wouldn’t play by the rules in its first issue — a bold statement to make in 1957, when anyone could be jailed for saying the wrong thing.
However, the introduction to the inaugural Nov. 5 issue also defined the magazine as a “lifestyle, literature and art” publication, and the contents were relatively tame for the first four years, writes Tao Heng-sheng (陶恒生) in “The Apollo magazine that wouldn’t play by the rules” (不按牌理出牌的文星雜誌).
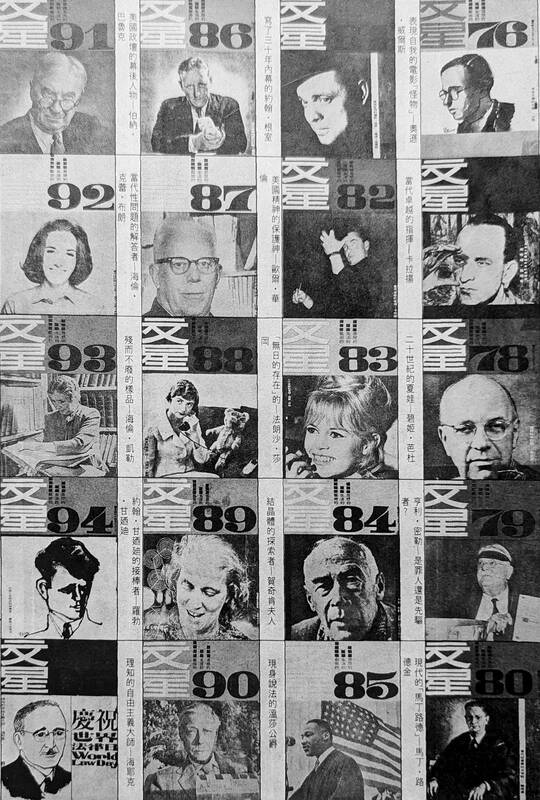

Photo courtesy of National Central Library
In 1961, the magazine changed its mission to “thought, lifestyle and art” and adopted a more critical tone with the joining of outspoken essayist Li Ao (李敖), who boasted in a later essay that prior to his arrival, Apollo “did not incite trends, did not create talking points, did not affect public opinion and did not make the old fogeys’ blood boil.”
That December, Apollo ran then-Academia Sinica president Hu Shih’s (胡適) speech, “Social change necessary for the growth of science” (科學發展所需要的社會改革), which criticized dated Eastern traditions and ways of thinking that he believed were holding the nation back.
“This is no blind condemnation of the ancient civilizations of the East, nor blind worship of the modern civilizations of the West,” Hu emphasized, but this article ignited an intense battle of words regarding Eastern versus Western ideals that lasted for years and left an impression on many young intellectuals.

Photo courtesy of National Central Library
In 1965, Apollo attracted the attention of government censors, who confiscated three issues that year. The Dec. 1 edition directly slammed the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) for abuse of power and authoritarianism. The magazine was banned for a year, but further attempts to reinstate it were rejected until its brief revival in 1986.
GENERATIONAL STRUGGLE
Apollo was founded by Hsiao Meng-neng (蕭孟能), whose father Hsiao Tung-tzu (蕭同茲) was a communications officer for the KMT who in 1932 relaunched the Central News Agency (CNA) as a news service separate from party headquarters. After relocating to Taiwan in 1949, the younger Hsiao set up a bookshop in Taipei that reprinted Western publications and carried foreign magazines.

Photo courtesy of National Central Library
He launched Apollo with former CNA Taipei director Yeh Ming-hsun (葉明勳) as publisher, and noted literary couple Hsia Cheng-ying (夏承楹) and Lin Hai-yin (林海音) (see: “Taiwan in Time: The miner of literary gems,” Nov. 26, 2017) as chief editors.
Current Taiwan Fact Check Center CEO Eve Chiu (邱家宜) writes in “Apollo and the 1962 Chinese-Western culture debate” (文星與1962年的中西文化論戰) that at first, “not playing by the rules” likely just referred to being bold enough to start a publication when scores of magazines were shutting down. They lost money for the first three years, broke even in the fourth and finally took off after shifting gears in late 1961. Soon, they were selling up to 12,000 copies per issue. In mid-1962, they doubled the pages from 40 to 80 and also doubled the price from NT$4 to NT$8.
It was a precarious time to amp up the editorial rhetoric; in 1960, Free China (自由中國) was shut down for advocating the launch of an opposition party and its founder Lei Chen (雷震) was thrown in jail for actually attempting to do so. Chiu writes that this event, coupled with the growing hopelessness in “reclaiming China,” left Taiwan’s young mainlander intellectuals feeling disillusioned and uneasy, even becoming resentful against the older generation who held onto power, refused to own up to their failures and silenced those who spoke out.
Lei’s arrest left little room for political discourse, and with few avenues to express their frustrations, things finally boiled over. Chiu writes that instead of a cultural struggle, the debate was more of a generational struggle as the young writers pushed back against their elders, who in their eyes lost China to the communists because they stubbornly refused to modernize and adopt Western ideas. Although there was a long way to go, Chiu writes that this was the beginning of the loosening of the KMT’s authority over national ideology.
CHAMPIONING HU
Hu was from the older generation, but he had been a proponent of modernization since the 1920s. In fact, his arguments were nothing new; his speech mainly reemphasized the points he made 35 years earlier that Easterners needed to let go of their superiority complex and welcome the beneficial parts of Western culture. Science and technology are not merely for material gain, but are “highly idealistic and spiritual values” that aim to better the human condition by eradicating “ignorance, superstition and slavery to the forces of nature,” he said.
Critics found fault with his notion that such values are “sadly underdeveloped in Oriental civilizations.”
“What spirituality is there in a civilization that tolerated such cruel and inhuman institutions such as footbinding for women for over a thousand years?” he asked. “What spiritual values are there in a civilization that considers life as painful and not worth living and glorifies poverty and mendicancy and sanctifies disease as an act of the gods?”
Philosopher Hsu Fu-kuan (徐復觀) was the first to strike back, calling Hu in an editorial the “shame of all Easterners.” In response, Apollo put Hu on the cover of the next issue with Li Ao penning a mostly positive profile of him. It included several pieces rebuking Hsu, one calling him an “antiquated patriot.” The following issue came out swinging with Li Ao slamming a number of prominent scholars, while other writers defended Hu’s ideas. Hu died of a heart attack in February 1962.
This topic was still ongoing in the final issue, which included a piece criticizing the classism in Confucianism and another discussing how traditional Chinese culture impedes scientific development. It also included a scathing editorial, presumably penned by Li, that objected to government interference with previous editions and demanded the KMT restore constitutional rule and democracy.
Of course this did not sit well with the authorities. They raided the office and confiscated the freshly-printed copies of the following issue. Both the magazine and bookstore shut down.
BRIEF REVIVAL
Twenty years and eight months after its initial demise, Apollo came back to life on Sept. 1, 1986.
“What sort of spiritual nourishment can we provide to today’s youth?” Hsiao asked in the editor’s words. “The sheer enthusiasm I felt 20 years ago to ‘not play by the rules’ has been reignited.”
It was a completely different Taiwan by then; the KMT’s one-party rule would end later that month and martial law would be lifted the following year. But the same questions of modernization and social change endured, wrote the editorial board, who stated their goal to introduce all sorts of global trends to the readers while exploring what it means to be “Chinese” within this context.
Tao writes that the contents of the new Apollo were higher in quality and more mature, but it failed to connect with young readers. Hsiao ended the magazine again in June 1988, citing financial concerns and his own health.
“In this highly politicized era, there seems to be fewer people who care about culture and ideology from a long-term perspective,” he writes in the final issue. “While Taiwan has become more open and lively on the surface, the entire society has become embroiled in political gossip. Star politicians have become idols and heroes, and political scandals and societal clashes have become the main source of stimulation for the masses.”
“It seems that society is moving further from our ideals. That’s the real reason Apollo can no longer continue.”
Taiwan in Time, a column about Taiwan’s history that is published every Sunday, spotlights important or interesting events around the nation that either have anniversaries this week or are tied to current events.
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

For many centuries from the medieval to the early modern era, the island port of Hirado on the northwestern tip of Kyushu in Japan was the epicenter of piracy in East Asia. From bases in Hirado the notorious wokou (倭寇) terrorized Korea and China. They raided coastal towns, carrying off people into slavery and looting everything from grain to porcelain to bells in Buddhist temples. Kyushu itself operated a thriving trade with China in sulfur, a necessary ingredient of the gunpowder that powered militaries from Europe to Japan. Over time Hirado developed into a full service stop for pirates. Booty could

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them