When entrepreneur Lee Hee-tae told his parents he was going into the porn business, he urged them not to worry about social disapproval in conservative South Korea and to think about the money instead.
The financial case, he said, was clear: built-in domestic demand plus a growing global fascination with South Korea, thanks to booming K-pop and K-drama exports.
However, due to deeply conservative social mores, South Korea’s adult industry is a minnow compared to neighboring Japan.

Photo: AFP
It produces around 2,000 adult movies a year, compared with what Lee’s research indicates is 2,000 a day made by Tokyo’s US$36.5-billion-dollar behemoth.
That, Lee said, is not only a lost opportunity but a personal tragedy for many South Koreans who are unable to properly discuss sex, desire and sexuality because of its “taboo” nature.
“I’d like South Korea to be more open about sex,” said Lee, whose adult content company Play Joker recently moved from making movies towards hosting live events.

Photo: AFP
While not illegal, the production of pornography is closely regulated in South Korea, with authorities requiring that images of genitalia be heavily blurred.
The country is also grappling with a molka, or spycam, epidemic of illicitly filmed videos that include everything from women in public restrooms to leaked sex videos from K-pop stars.
Lee argued that the two phenomena are linked and said allowing a thriving local adult content industry would help prevent spycam crimes.
Local women’s groups disagree.
“Their claim that the so-called ‘free sexual culture’ will help prevent the spread of illegal adult content is a blatant fallacy,” the Suwon Women’s Hotline said in a statement last month.
“It is nothing more than an attempt to further spread the culture of sexual violence.”
PORN FOR WOMEN?
Lee said some people might “watch molka because they don’t understand adult content,” and so don’t understand there is a difference between professional pornography and illicit footage, he said.
Lee’s company has produced around 500 adult films so far, the majority of them filmed in Japan using Japanese actors.
The bulk of them target male viewers but he can see an industry-wide trend with companies making more content specifically aimed at women, he said, adding that many Japanese producers have popular female-focused content.
On South Korea’s adult cable channel “a surprising trend has emerged where the viewership from 11 am to 12:30pm has significantly increased,” he said, prompting industry research.
“It turns out women tune in after sending husbands to work and kids to school,” he said.
However, Lee said South Korea has a web of social taboos and regulations that are “keeping the industry from reaching its full potential”.
For example, putting a porn actor in a school uniform violates child protection laws. Or featuring a flight attendant uniform guarantees the production can “expect full-blown protest from flight attendants’ unions”.
“Thanks to K-pop, Korea’s national brand has grown... and there are many countries now looking for Korean adult content,” he said, but the existing industry is unable to meet demand.
ADULTS-ONLY FESTIVAL
Lee decided to focus on live events as a way to change attitudes but his attempt to hold South Korea’s largest sex festival in April encountered online vitriol and legal challenges. Women’s groups branded the proposed festival in Suwon, south of Seoul, a “sex-exploitation event” and decried it as “quasi-prostitution.”
Suwon authorities canceled the event amid the backlash. After he found a new site in the capital, Seoul officials threatened to shut off the electricity and cancel the venue’s licenses.
That eventually forced Lee to cancel, causing what he said were significant financial losses.
Lee is taking both Suwon authorities and some women’s groups to court, seeking damages. The fallout has prompted some new lawmakers to question whether officials were right to cancel.
“What is wrong with hosting an adult-only festival?” incoming opposition lawmaker Chun Ha-ram, who won office last month in parliamentary elections, wrote in a Facebook post. “Authorities should take their hands off this. Unless it’s blatantly illegal, state power has no right to interfere in the cultural sphere.”
Such signs indicate the tide may be turning, at least a little, Lee said. He is planning another, larger event for June and said this time he won’t back down.
South Korea needs to be less prudish about adult content, he said.
“I would like to remind people that we are all created through sex.”

Late last month Philippines Foreign Affairs Secretary Theresa Lazaro told the Philippine Senate that the nation has sufficient funds to evacuate the nearly 170,000 Filipino residents in Taiwan, 84 percent of whom are migrant workers, in the event of war. Agencies have been exploring evacuation scenarios since early this year, she said. She also observed that since the Philippines has only limited ships, the government is consulting security agencies for alternatives. Filipinos are a distant third in overall migrant worker population. Indonesia has over 248,000 workers, followed by roughly 240,000 Vietnamese. It should be noted that there are another 170,000

Hannah Liao (廖宸萱) recalls the harassment she experienced on dating apps, an experience that left her frightened and disgusted. “I’ve tried some voice-based dating apps,” the 30-year-old says. “Right away, some guys would say things like, ‘Wanna talk dirty?’ or ‘Wanna suck my d**k?’” she says. Liao’s story is not unique. Ministry of Health and Welfare statistics show a more than 50 percent rise in sexual assault cases related to online encounters over the past five years. In 2023 alone, women comprised 7,698 of the 9,413 reported victims. Faced with a dating landscape that can feel more predatory than promising, many in
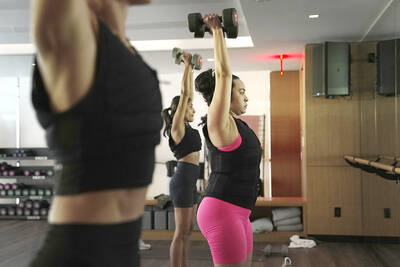
“This is one of those rare bits of TikTok fitness advice with a lot of truth behind it,” says Bethan Crouse, performance nutritionist at Loughborough University. “Sometimes it’s taken a bit too literally, though! You see people chugging protein drinks as they’re scanning out of their gym.” Crouse recommends the athletes she works with consume 20-30g of protein within 30-60 minutes of finishing a resistance training session. “The act of exercising our muscles increases the breakdown of muscle proteins,” she says. “In order to restore, or hopefully improve them — and get gains such as increased muscle mass or strength —
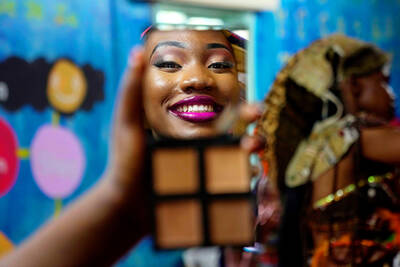
“Far from being a rock or island … it turns out that the best metaphor to describe the human body is ‘sponge.’ We’re permeable,” write Rick Smith and Bruce Lourie in their book Slow Death By Rubber Duck: The Secret Danger of Everyday Things. While the permeability of our cells is key to being alive, it also means we absorb more potentially harmful substances than we realize. Studies have found a number of chemical residues in human breast milk, urine and water systems. Many of them are endocrine disruptors, which can interfere with the body’s natural hormones. “They can mimic, block