They are one of the easier legumes to digest and fetch a higher crop price than wheat, yet mung beans are not mainstream in the western world. But, while the vigna radiata has been nourishing populations across India and Asia for millennia, in recent decades enterprising scientists have started investigating the legume’s potential to improve food security and farmers’ incomes.
Since its inception 50 years ago, the World Vegetable Centre (also known as WorldVeg) in Tainan has collected more than 8,000 “accessions,” or varieties, of mung bean seeds, genebank manager, Maarten van Zonneveld, says. Much like other species, such as humans and dogs, plants — including mung beans — need genetic diversity to create robust offspring. Diversity also enables selective crossing of different varieties to create new lines with desirable traits.
CHALLENGES
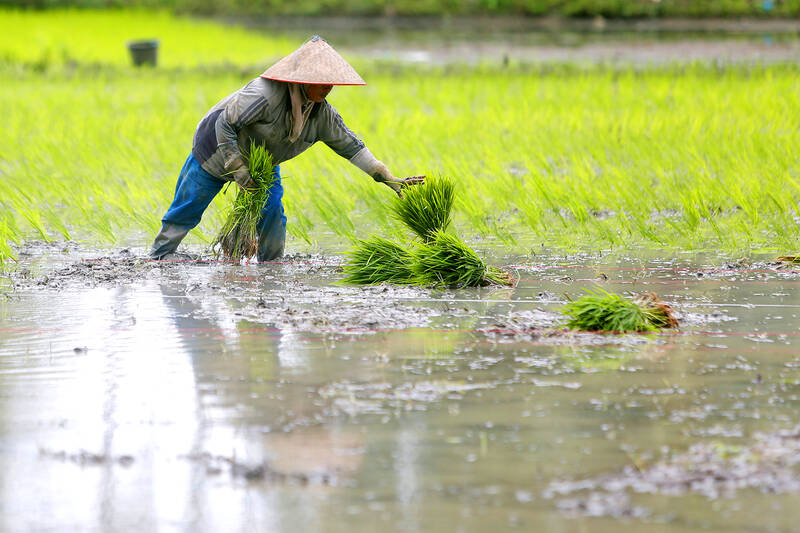

Photo: EPA-EFE
Like many of the best things in life, growing the mung bean — also known as moong bean, green gram, golden gram, black gram and Jerusalem pea — has its challenges.
Shanice Van Haeften, is a mung bean researcher at the University of Queensland. Once, while teaching a primary school science workshop in the farming region of Queensland’s Western Downs region, a student told her: “Oh yeah, my dad calls them mongrel beans because we tried to plant them and they didn’t grow well.”
Van Haeften, who completed a fellowship at WorldVeg last year, says mung bean crops can be “kind of wild and hard to manage,” and sensitive to pests, diseases and the weather (biotic and abiotic stresses, in more scientific terms).
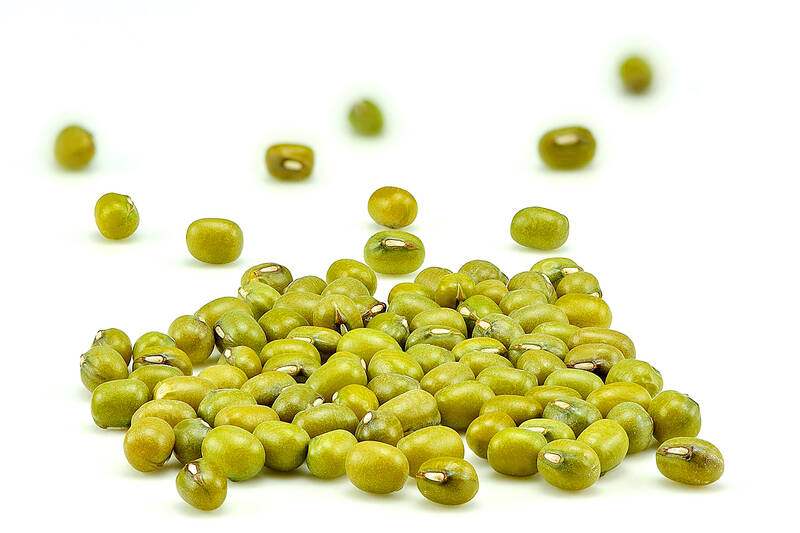

Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons
But at the International Mungbean Improvement Network (Imin), led by WorldVeg with partners including the Australian Center for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR), new varieties are being bred to overcome many of the trials that have plagued farmers.
GROWING A BETTER BEAN
In the case of mung beans, careful screening has revealed varieties with greater resistance to pathogens like powdery mildew, anthracnose and fusarium wilt, and pests such as cowpea aphid, thrips and stem fly. A wild beach variety could help breed lines that can tolerate salinity and improved lines have shortened the bean’s growing time.
“We have got varieties that mature in 50 days,” the regional director of Imin in South and Central Asia, Dr Ramakrishnan Nair, says. This makes mung beans — one of the only summer rotation options among legumes — ideal to plant between other crops such as rice or wheat, enriching the soil with nitrogen and supplementing smallholder farmers’ incomes.
Van Zonneveld says: “So, if you have your short season mung bean, it helps you diversify and if some other crop fails it still gives you some return.”
And although mung beans already have high heat tolerance, Nair says they’ve even been able to improve that.
“One of our lines will be released very soon in Tajikistan where the temperatures go up to 45C.”
In Australia, Van Haeften says mung beans are one of the highest value grain crops, attracting about US$1,100 a ton — three times higher than wheat. Currently 90 percent is exported to India and broader Asia, but she thinks demand will increase domestically. The CSIRO has predicted that Australia’s retail plant protein market will skyrocket from US$150 million in 2019 to US$6 billion by 2030.
“The plant-based market is meant to just completely explode, and even further by 2050,” says Van Haeften. “So even though mung bean isn’t a major crop now, I think it has the potential to grow exponentially.”
Not only do mung beans contain the myriad nutritional benefits of legumes in general, as a rich source of protein, fibre, antioxidant polyphenols and essential vitamins and minerals, they also have a few special qualities.
SPECIAL QUALITIES
Mung beans are easy to digest, for instance — good news if you suffer from bloating after eating beans. That not only makes them a less embarrassing choice for people with sensitive guts, it also makes their protein more available to the body. In Bangladesh, Nair says, people mix mung bean powder with milk powder to make a nutritious, tummy-friendly drink for children.
They are also low in phytates, the compounds in legumes that can reduce absorption of iron, a vital nutrient that is commonly deficient in developed and developing countries. In one of Nair’s projects exploring varieties with enhanced nutritional properties, he says researchers discovered a line that takes up more than double the iron from good soil, which they are crossing with improved lines to help address malnutrition in Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda.
In traditional Chinese medicine, mung beans are believed to have a cooling effect on the body, and have been used for thousands of years to treat fever and heatstroke as well as other conditions including hypertension, gastrointestinal problems and inflammation. This belief is baring out in research.
“The seed coat has got some goodies,” says Nair, “like two compounds particularly which help to reduce the body’s heat.”

The Taipei Times last week reported that the rising share of seniors in the population is reshaping the nation’s housing markets. According to data from the Ministry of the Interior, about 850,000 residences were occupied by elderly people in the first quarter, including 655,000 that housed only one resident. H&B Realty chief researcher Jessica Hsu (徐佳馨), quoted in the article, said that there is rising demand for elderly-friendly housing, including units with elevators, barrier-free layouts and proximity to healthcare services. Hsu and others cited in the article highlighted the changing family residential dynamics, as children no longer live with parents,
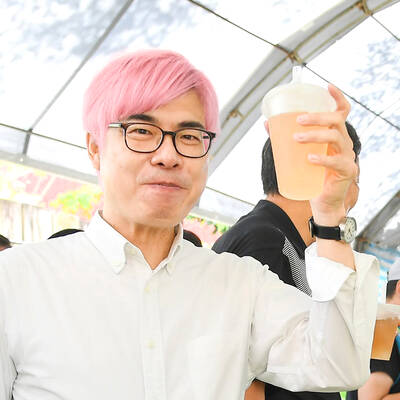

It is jarring how differently Taiwan’s politics is portrayed in the international press compared to the local Chinese-language press. Viewed from abroad, Taiwan is seen as a geopolitical hotspot, or “The Most Dangerous Place on Earth,” as the Economist once blazoned across their cover. Meanwhile, tasked with facing down those existential threats, Taiwan’s leaders are dying their hair pink. These include former president Tsai Ing-wen (蔡英文), Vice President Hsiao Bi-khim (蕭美琴) and Kaohsiung Mayor Chen Chi-mai (陳其邁), among others. They are demonstrating what big fans they are of South Korean K-pop sensations Blackpink ahead of their concerts this weekend in Kaohsiung.

Taiwan is one of the world’s greatest per-capita consumers of seafood. Whereas the average human is thought to eat around 20kg of seafood per year, each Taiwanese gets through 27kg to 35kg of ocean delicacies annually, depending on which source you find most credible. Given the ubiquity of dishes like oyster omelet (蚵仔煎) and milkfish soup (虱目魚湯), the higher estimate may well be correct. By global standards, let alone local consumption patterns, I’m not much of a seafood fan. It’s not just a matter of taste, although that’s part of it. What I’ve read about the environmental impact of the
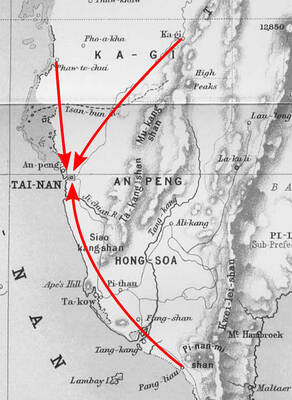
Oct 20 to Oct 26 After a day of fighting, the Japanese Army’s Second Division was resting when a curious delegation of two Scotsmen and 19 Taiwanese approached their camp. It was Oct. 20, 1895, and the troops had reached Taiye Village (太爺庄) in today’s Hunei District (湖內), Kaohsiung, just 10km away from their final target of Tainan. Led by Presbyterian missionaries Thomas Barclay and Duncan Ferguson, the group informed the Japanese that resistance leader Liu Yung-fu (劉永福) had fled to China the previous night, leaving his Black Flag Army fighters behind and the city in chaos. On behalf of the