The bell-shaped windows on Puji Temple are its standout feature. But temple guide Chen Yu-shun (陳裕順) is struggling with the Japanese word for this architectural motif.
“Excuse me,” he says. “My Japanese is rusty.” Suddenly it comes: “Katomado!”
The tourist that Chen is addressing nods approval. Visiting Taiwan for the second time, Miyuki Fujiwara is impressed by how convenient it is.
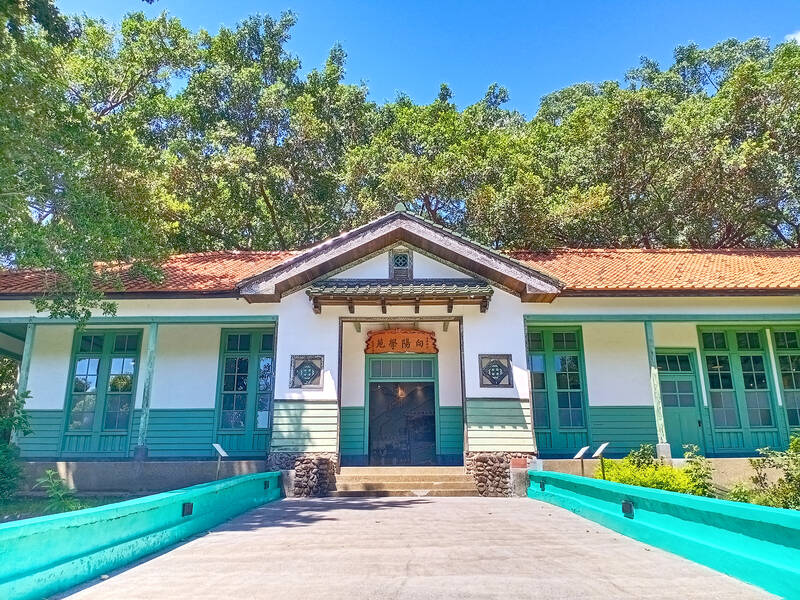

Photo: James Baron
“I am surprised by how many people speak Japanese [in Taiwan],” says Fujiwara, a native of Matsuyama City. “Even those who don’t speak much are willing to try.”
A 2017 headline in the Japan Times captures the familiarity that has bred affection among Japanese for their former colony: “Taiwan: Where Japanese go on vacation to feel at home.” Yet, while Taiwan remains a popular destination for Japanese, it has struggled to regain pre-COVID numbers, when a record 2 million-plus tourists from Japan visited in 2019.
The absence of an integrated policy to leverage Taiwan’s colonial relics is one obvious issue, and Taipei’s northernmost district, which is replete with wonderful but woefully promoted attractions, is a good example.
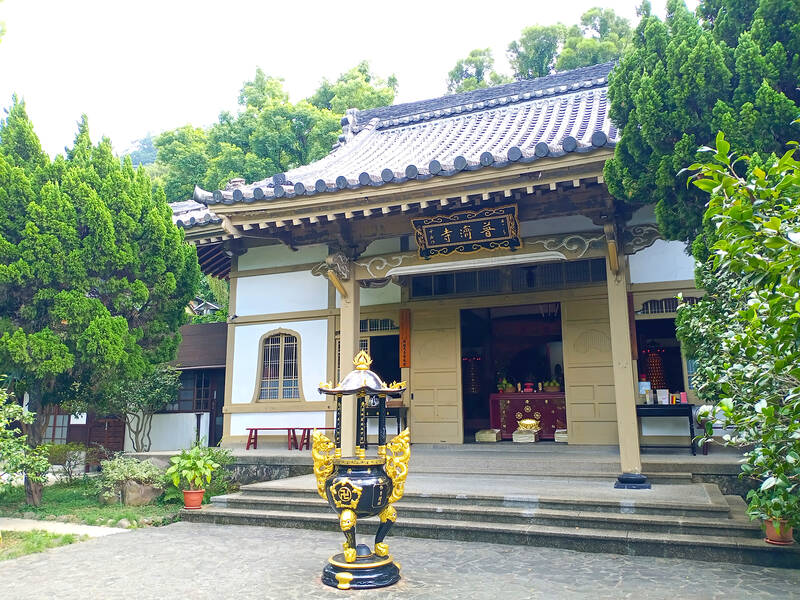

Photo: James Baron
UNDERTOURISTED
Overlooking Xinbeitou (新北投) hot spring resort area, Puji Temple (普濟寺, 112, Wenquan Rd, Beitou District, 北投區溫泉路112號) is one of the few surviving Shingon Buddhist temples in Taiwan and among Taipei’s best-preserved wooden colonial-era structures. A 10-minute uphill stroll from Xinbeitou MRT station, the temple remains scandalously undertouristed.
“Some days there are no visitors,” says Chen, who volunteers as a guide twice a week.

Photo: James Baron
Apart from Chen’s brief tour, there is no information at the site. The English and Chinese-language signboards that once lined the steps from the chozubachi — an ablution basin with ladle — at the bottom inexplicably disappeared years ago. These displays described the spread of the Vajrayana sect of Buddhism from India to Japan via China, before things came full circle, with the colonial powers bringing their mutated variant — Shingon — to Taiwan where it helped finesse relations with the imperial subjects.
The temple, which was built with funds from Japanese railway engineers in 1905, is dedicated to a special hot spring guardian incarnation of Guanyin. Another curiosity is the stone statue of Ksitigarbha in an adjoining pavilion. In Japanese culture, this deity protects the souls of aborted fetuses, and his presence here supposedly relates to Beitou’s history as a red-light district. Not that you would know any of this without searching online.
At least Puji is visitable. Opposite, the Old Bank of Taiwan Dormitory (臺灣銀行舊宿舍, 103, Wenquan Road, Beitou District, 北投區溫泉路103號) remains shuttered. After years of restoration concluded circa 2017, a land dispute prevented it opening to the public. “The [state-owned] Bank of Taiwan says its theirs, and Taipei’s Department of Cultural affairs says it’s a public heritage,” says a representative of Beitou Cultural Foundation. “There’s no resolution, so it’s off limits.”

Photo: James Baron
The site comprises three structures. The exquisitely restored building nearest the gate, which can be seen by anyone cheeky enough to vault onto the outer wall, was established as a hot spring hotel before being purchased by the bank in 1941. Behind it — across a tiny bridge over a brook — sit two grander villas with brickwork and concrete colonnades. These were originally the property of a wealthy businessman.
Thanks to a bureaucratic wrangle, this unique complex is invisible to passersby. “It’s a shame,” says the representative. “It could be a great attraction.”
Perhaps the biggest oversight is the Former Japanese Military Hospital (衛戍醫院北投分院, 60, Xinmin Rd, Beitou District, 北投區新民路60號). Constructed in 1898, this splendid turquoise bungalow hosted officers wounded in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904-5. Its tranquil setting, amid “therapeutic” onsen, and knotty banyans, was ideal for recuperation. Features include counterweighted windows and a marawai-en type veranda — providing shelter from northern Taiwan’s inclemency. A unique element is a flap from which guard dogs once patrolled.
Following a makeover, the museum re-opened in August, with a new souvenir shop and handicraft space. Proceeds from the entrance fee — discounted for district residents — fund a program helping mental health patients reintegrate into society. Patients muck in at the museum under this community-based initiative.
With zero promotion, the site gets scant attention. “Mainly school trips, locals, or people who find us accidentally,” says Chou Tai-chen (邱泰楨), a program supervisor and tour guide.
Because it’s attached to Beitou’s Tri-Service General Hospital, the museum is administered by Taiwan’s Ministry of Defense, without support from the Taipei City Government. Tours are in Chinese, with no onsite Japanese materials.
“There’s no budget,” says a Chou. “One employee speaks some Japanese, but we’d have to arrange something in advance.”
ALLIED BOMBING
At the apex of another hill is Shanguang Temple (善光寺, 20, Yinguang Lane, Wenquan Rd, Beitou District, 北投區溫泉路銀光巷20號), which dates from 1932. The pagoda here is an ossuary for ashes that purportedly contain sarira — crystals found in the remains of exemplary Buddhist masters. The site is absent from most tourist maps and, aside from the religious associations, the caretakers and local authorities seem clueless about its role in a remarkable episode from World War II.
Not so Cheng Hong-ming (鄭宏銘.), a Tamsui native with a history blog called The Battle of Fisherman’s Wharf. “Japanese families from Tamsui were evacuated to the temple during the Allied bombing of Taiwan,” says Cheng. “It was deemed safer because of its seclusion.”
Hirokawa Norio was a pupil at Tamsui Elementary School when he evacuated to Shanguang. His own blog documents his experience, which included taking cover from strafing.
In 2013, with Cheng’s assistance, Hirokawa — who died in 2021 — and other Tamsui-born Japanese, received honorary citizenship during a ceremony at Tamsui District Office. Like many wansei, as Taiwan-born Japanese were known, Hirokawa considered Taiwan home.
Cheng is unequivocal about the obscurity of this history. “Throughout the Chiang Kai-shek (蔣中正) era, erasing the history of Japan rule was a government priority,” Cheng says. He highlights the stigma of meiri — an insult for alleged Japanese lapdogs. As this was “the KMT’s political weapon of choice,” the DPP assiduously avoided actions that could spark such accusations.
But do other factors influence the lackluster handling of Japanese heritage sites?
Part two will appear on Feb. 4.
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades

March 2 to March 8 Gunfire rang out along the shore of the frontline island of Lieyu (烈嶼) on a foggy afternoon on March 7, 1987. By the time it was over, about 20 unarmed Vietnamese refugees — men, women, elderly and children — were dead. They were hastily buried, followed by decades of silence. Months later, opposition politicians and journalists tried to uncover what had happened, but conflicting accounts only deepened the confusion. One version suggested that government troops had mistakenly killed their own operatives attempting to return home from Vietnam. The military maintained that the

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them