Forty years ago, Myanmar barmaid Dar San Ye stood in a river running through Yangon, squaring up to a North Korean agent gripping a live grenade.
Hours earlier on Oct. 9, 1983, a huge explosion had shattered the peace of the capital city as a Pyongyang hit team detonated bombs to try to assassinate visiting South Korean president Chun Doo-hwan.
Seventeen Korean officials, including the foreign minister, and four Burmese nationals died when the blast ripped through a mausoleum housing the remains of Myanmar’s founding father and independence hero Aung San.
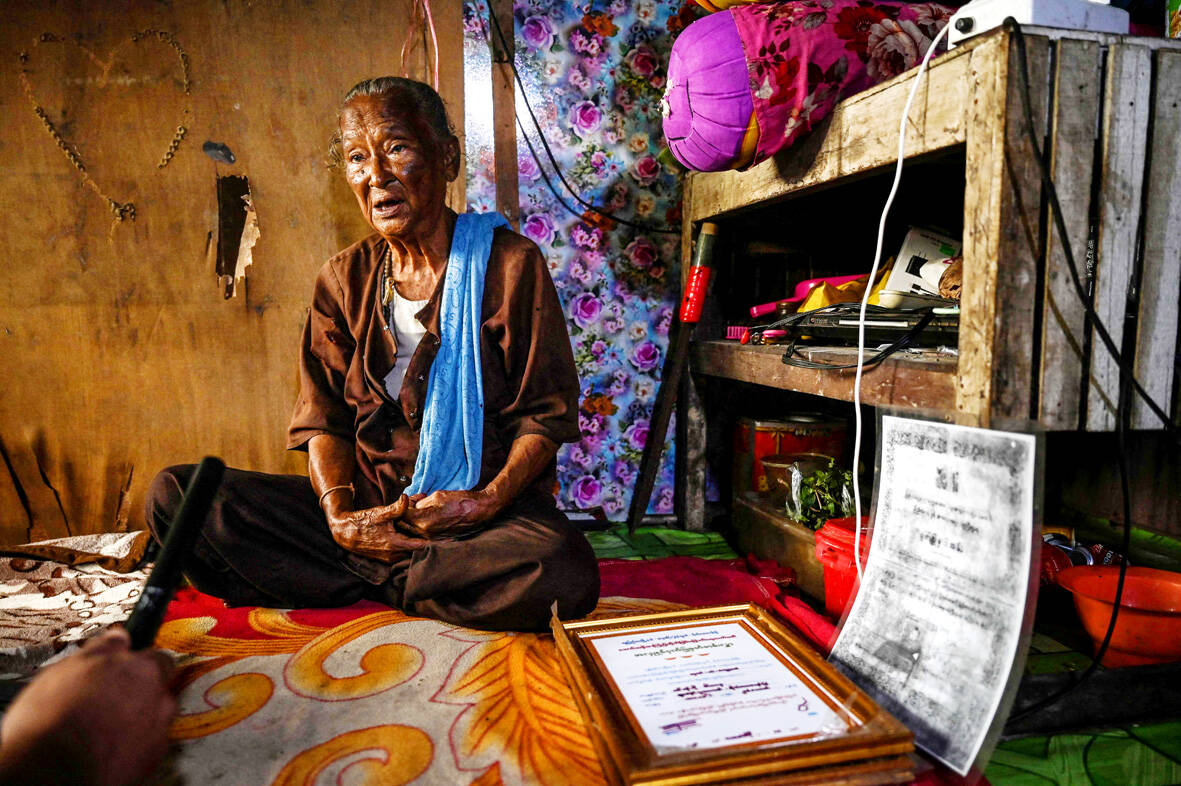

Photo: AFP
President Chun himself was not there, however, having been delayed at a previous engagement.
The bombers fled the scene, with Yangon plunged into chaos.
Now 87 years old, she spoke from her home on the outskirts of the city, recalling her role in the drama as she puffed on a cigar.
“I heard the Martyrs’ Mausoleum had been blown up by some foreigners,” she said.
Customers in her bar on the banks of the Pazundaung River could talk of little else, she said.
“I asked people if they (the attackers) had been captured... They said no,” she recalled. “I told them the bombers will be captured later because we are Buddhist Myanmar and our good spirits will guard us.”
Little did she know she would be the one to do it.
‘I PUNCHED HIM’
Dar San Ye finished her shift and returned home as evening began to fall, with the city still on edge and a hunt for the perpetrators under way. Suddenly, she heard shouts that there was a thief in the river. She rushed out and saw a crowd of around a hundred people gathered on the bank.
Pausing only to hitch up her nightdress, she waded in, not quite sure who the man in the water was.
“The guy was standing waist-deep in water,” she said. “I called him: ‘Come here! Come here!’”
“He just stared at me. I realized he wouldn’t understand Burmese. I remembered an English phrase that I used to use to make fun of English people.
“I asked him: ‘Are you my friend?’”
Desperate for sympathy as he found himself surrounded, he replied: “Yes, yes! Are you Chinese?” The barmaid recalled that he then reached out to try to shake her hand.
But when three men from the crowd joined in to help Dar San Ye, he began to fight back, pushing her and the others away and running to the end of a pier.
There he took out a grenade and pulled the pin, but it failed to detonate fully.
“His left hand was blown off. On his right hand, four fingers were blown off and only the thumb remained,” she said.
“After that, he jumped into the water again and I also jumped in... When he appeared above the water again, I punched him in the neck.”
HANGED AFTER TRIAL
The agent, Kim Jin-su, was one of the three-man hit team.
Thanks to Dar San Ye, he was captured by authorities. He refused to cooperate with interrogators and was hanged after a trial.
The two other assassins, Shin Ki-chol and Kang Min-chol, were tracked down by security forces just outside Yangon.
Shin died in the ensuing firefight but Kang was captured alive and sentenced to life in prison after confessing.
He died there after almost 25 years behind bars.
A CIA report said there was “very strong circumstantial evidence” linking Pyongyang to the mausoleum bombing.
It said alleged North Korean agents had used similar radio-detonated explosives in a 1970 plot to kill then-president Park Chung-hee as he visited a cemetery in Seoul. A delegation from Pyongyang had also visited the mausoleum less than two months before — “an excellent opportunity to survey the scene and plan an operation.”
A North Korean ship unloading aid equipment in Yangon port two weeks earlier “would be consistent with the dispatch of an agent team,” it said. A court in Myanmar — then called Burma — ruled that the attack was “the work of saboteurs acting under instructions of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea.”
Its then junta cut off diplomatic ties with Pyongyang that were not restored until more than 20 years later.
WELL-KNOWN FIGURE
Shortly after the bombing Dar San Ye and the three men who helped her were feted at a government ceremony and given clothes and money in compensation.
“Since then, they have never come to see me,” she said, with a copy of a faded and creased “Record of Honor” certificate all she has left to link her to the day.
Myanmar re-established ties with North Korea in 2007, when both countries were under a slew of Western sanctions and branded “outposts of tyranny” by the US.
Under the current junta, the rebuilt Martyr’s Mausoleum is all but closed off — barring select diplomats invited to pay their respects to Myanmar’s independence hero. Dar San Ye is a well-known figure in Yangon, and has been the subject of several documentaries and feature articles in Myanmar media.
But with most of her family dead and little other support she lives off donations from charitable neighbors that come to around 30,000-40,000 kyat (US$15-19) per day.
She has no regrets about the risk she took in the river that day.
“I tried to catch him just for my country. Once, our General Aung San was assassinated. Then his grave was destroyed again. So I went down to catch him.”
“I can’t let them insult my country.”
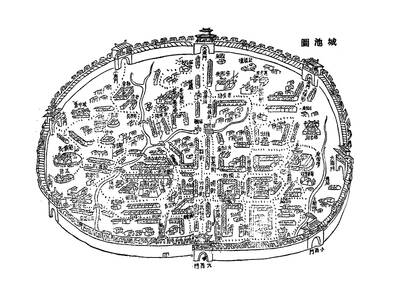
May 26 to June 1 When the Qing Dynasty first took control over many parts of Taiwan in 1684, it roughly continued the Kingdom of Tungning’s administrative borders (see below), setting up one prefecture and three counties. The actual area of control covered today’s Chiayi, Tainan and Kaohsiung. The administrative center was in Taiwan Prefecture, in today’s Tainan. But as Han settlement expanded and due to rebellions and other international incidents, the administrative units became more complex. By the time Taiwan became a province of the Qing in 1887, there were three prefectures, eleven counties, three subprefectures and one directly-administered prefecture, with

President William Lai (賴清德) yesterday delivered an address marking the first anniversary of his presidency. In the speech, Lai affirmed Taiwan’s global role in technology, trade and security. He announced economic and national security initiatives, and emphasized democratic values and cross-party cooperation. The following is the full text of his speech: Yesterday, outside of Beida Elementary School in New Taipei City’s Sanxia District (三峽), there was a major traffic accident that, sadly, claimed several lives and resulted in multiple injuries. The Executive Yuan immediately formed a task force, and last night I personally visited the victims in hospital. Central government agencies and the

Among Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) villages, a certain rivalry exists between Arunothai, the largest of these villages, and Mae Salong, which is currently the most prosperous. Historically, the rivalry stems from a split in KMT military factions in the early 1960s, which divided command and opium territories after Chiang Kai-shek (蔣介石) cut off open support in 1961 due to international pressure (see part two, “The KMT opium lords of the Golden Triangle,” on May 20). But today this rivalry manifests as a different kind of split, with Arunothai leading a pro-China faction and Mae Salong staunchly aligned to Taiwan.
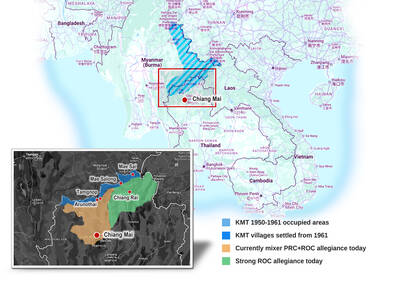
As with most of northern Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) settlements, the village of Arunothai was only given a Thai name once the Thai government began in the 1970s to assert control over the border region and initiate a decades-long process of political integration. The village’s original name, bestowed by its Yunnanese founders when they first settled the valley in the late 1960s, was a Chinese name, Dagudi (大谷地), which literally translates as “a place for threshing rice.” At that time, these village founders did not know how permanent their settlement would be. Most of Arunothai’s first generation were soldiers