Elon Musk’s SpaceX is about to take its most daring leap yet with a round-the-world test flight of its mammoth Starship.
It’s the biggest and mightiest rocket ever built at 120 meters, with the lofty goals of ferrying people to the moon and Mars.
Monday’s launch attempt was called off because of a stuck valve in the first-stage booster and there could be another try this week from South Texas. Musk’s company got the OK from the Federal Aviation Administration on Friday.

Photo: Reuters
It will be the first launch with Starship’s two sections together. No one will be on board. Early versions of the sci-fi-looking upper stage rocketed several miles into the stratosphere a few years back, crashing four times before finally landing upright in 2021. The towering first-stage rocket booster, dubbed Super Heavy, will soar for the first time.
For this demo, SpaceX won’t attempt any landings of the rocket or the spacecraft. Everything will fall into the sea.
“I’m not saying it will get to orbit, but I am guaranteeing excitement. It won’t be boring,” Musk promised at a Morgan Stanley conference last month. “I think it’s got, I don’t know, hopefully about a 50 percent chance of reaching orbit.”
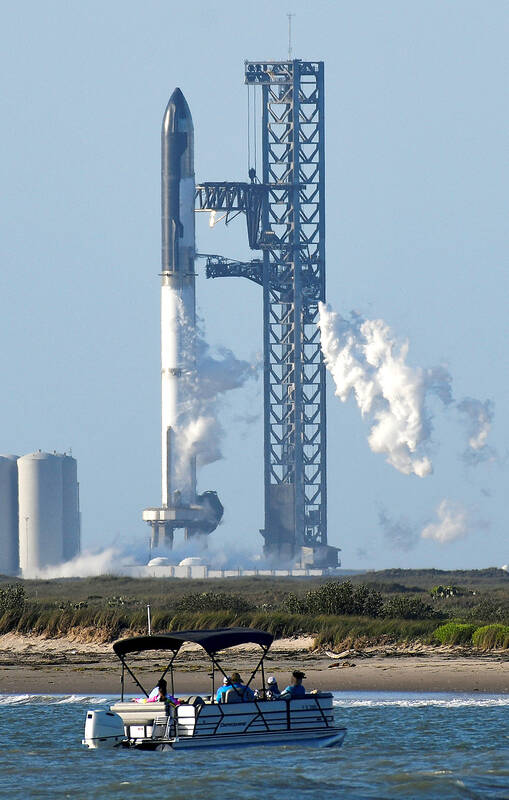

Photo: Reuters
Here’s the rundown on Starship’s debut:
SUPERSIZE ROCKET
The stainless steel Starship has 33 main engines and 16.7 million pounds of thrust. All but two of the methane-fueled, first-stage engines ignited during a launch pad test in January — good enough to reach orbit, Musk noted.
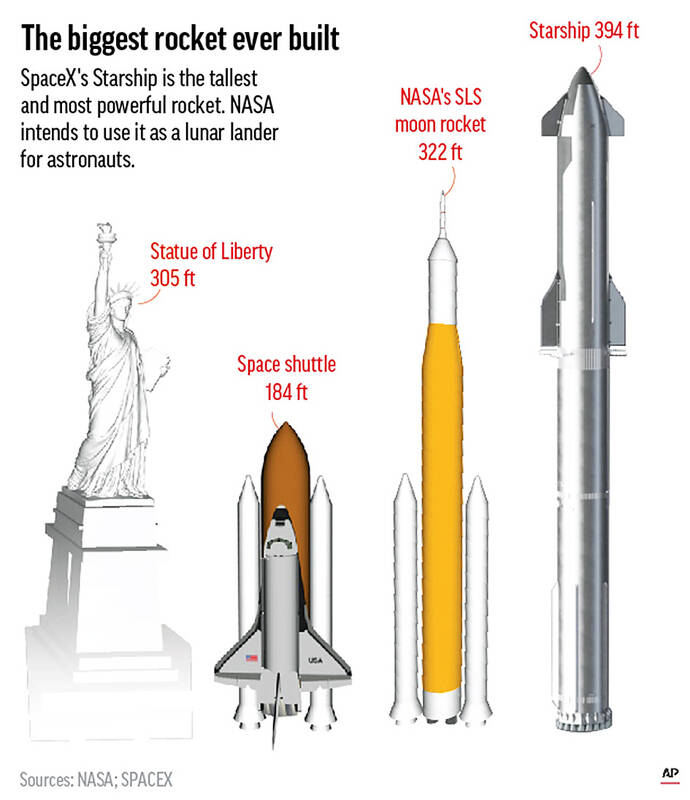
Photo: AP
Given its muscle, Starship could lift as much as 250 tons and accommodate 100 people on a trip to Mars. The six-engine spacecraft accounts for 50 meters of its height. Musk anticipates using Starship to launch satellites into low-Earth orbit, including his own Starlinks for Internet service, before strapping anyone in.
Starship easily eclipses NASA’s moon rockets — the Saturn V from the bygone Apollo era and the Space Launch System from the Artemis program that logged its first lunar trip late last year. It also outflanks the former Soviet Union’s N1 moon rocket, which never made it past a minute into flight, exploding with no one aboard.
GAME PLAN
The test flight will last 90 minutes, and fall short of a full orbit of Earth. If Starship reaches the three-minute mark after launch, the booster will be commanded to separate and fall into the Gulf of Mexico. The spacecraft would continue eastward, passing over the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans before ditching near Hawaii.
Starship is designed to be fully reusable but nothing will be saved from the test flight. Harvard astrophysicist and spacecraft tracker Jonathan McDowell will be more excited whenever Starship actually lands and returns intact from orbit. It will be “a profound development in spaceflight if and when Starship is debugged and operational,” he said.
LAUNCH PAD
Starship will take off from a remote site on the southernmost tip of Texas near Boca Chica Beach. It’s just below South Padre Island, and about 20 miles from Brownsville.
Down the road from the launch pad is the complex where SpaceX has been developing and building Starship prototypes for the past several years. The complex, called Starbase, has more than 1,800 employees, who live in Brownsville or elsewhere in the Rio Grande Valley.
The Texas launch pad is equipped with giant robotic arms — called chopsticks — to eventually grab a returning booster as it lands. SpaceX is retooling one of its two Florida launch pads to accommodate Starships down the road. Florida is where SpaceX’s Falcon rockets blast off with crew, space station cargo and satellites for NASA and other customers.
THE ODDS
As usual, Musk is remarkably blunt about his chances, giving even odds, at best, that Starship will reach orbit on its first flight. But with a fleet of Starships under construction at Starbase, he estimates an 80 percent chance that one of them will attain orbit by year’s end.
He expects it will take a couple years to achieve full and rapid reusability.
CUSTOMERS
With Starship, the California-based SpaceX is focusing on the moon for now, with a US$3 billion NASA contract to land astronauts on the lunar surface as early as 2025, using the upper stage spacecraft.
It will be the first moon landing by astronauts in more than 50 years.
The moonwalkers will leave Earth via NASA’s Orion capsule and Space Launch System rocket, and then transfer to Starship in lunar orbit for the descent to the surface, and then back to Orion. To reach the moon and beyond, Starship will first need to refuel in low-Earth orbit.
SpaceX envisions an orbiting depot with window-less Starships as tankers. But Starship isn’t just for NASA. A private crew will be the first to fly Starship, orbiting Earth. Two private flights to the moon would follow — no landings, just flyarounds.
OTHER PLAYERS
There are other new rockets on the horizon. Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin is readying the New Glenn rocket for its orbital debut from Cape Canaveral, Florida, in the next year or so.
Named after the first American to orbit the world, John Glenn, the rocket towers over the company’s current New Shepard rocket, named for Mercury astronaut Alan Shepard’s 1961 suborbital hop.
NASA will use New Glenn to send a pair of spacecraft to Mars in 2024. United Launch Alliance expects its new Vulcan rocket to make its inaugural launch later this year, hoisting a private lunar lander to the moon at NASA’s behest. Europe’s Arianespace is close to launching its new, upgraded Ariane 6 rocket from French Guiana in South America. And NASA’s Space Launch System moon rocket that will carry astronauts will morph into ever bigger versions.

In the March 9 edition of the Taipei Times a piece by Ninon Godefroy ran with the headine “The quiet, gentle rhythm of Taiwan.” It started with the line “Taiwan is a small, humble place. There is no Eiffel Tower, no pyramids — no singular attraction that draws the world’s attention.” I laughed out loud at that. This was out of no disrespect for the author or the piece, which made some interesting analogies and good points about how both Din Tai Fung’s and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co’s (TSMC, 台積電) meticulous attention to detail and quality are not quite up to

April 21 to April 27 Hsieh Er’s (謝娥) political fortunes were rising fast after she got out of jail and joined the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) in December 1945. Not only did she hold key positions in various committees, she was elected the only woman on the Taipei City Council and headed to Nanjing in 1946 as the sole Taiwanese female representative to the National Constituent Assembly. With the support of first lady Soong May-ling (宋美齡), she started the Taipei Women’s Association and Taiwan Provincial Women’s Association, where she

It is one of the more remarkable facts of Taiwan history that it was never occupied or claimed by any of the numerous kingdoms of southern China — Han or otherwise — that lay just across the water from it. None of their brilliant ministers ever discovered that Taiwan was a “core interest” of the state whose annexation was “inevitable.” As Paul Kua notes in an excellent monograph laying out how the Portuguese gave Taiwan the name “Formosa,” the first Europeans to express an interest in occupying Taiwan were the Spanish. Tonio Andrade in his seminal work, How Taiwan Became Chinese,

Mongolian influencer Anudari Daarya looks effortlessly glamorous and carefree in her social media posts — but the classically trained pianist’s road to acceptance as a transgender artist has been anything but easy. She is one of a growing number of Mongolian LGBTQ youth challenging stereotypes and fighting for acceptance through media representation in the socially conservative country. LGBTQ Mongolians often hide their identities from their employers and colleagues for fear of discrimination, with a survey by the non-profit LGBT Centre Mongolia showing that only 20 percent of people felt comfortable coming out at work. Daarya, 25, said she has faced discrimination since she