The author of a sci-fi manga about to hit shelves in Japan admits he has “absolutely zero” drawing talent, so turned to artificial intelligence to create the dystopian saga.
All the futuristic contraptions and creatures in Cyberpunk: Peach John were intricately rendered by Midjourney, a viral AI tool that has sent the art world into a spin, along with others such as Stable Diffusion and DALL-E 2.
As Japan’s first fully AI-drawn manga, the work has raised questions over the threat technology could pose to jobs and copyright in the nation’s multi-billion-dollar comic book industry.
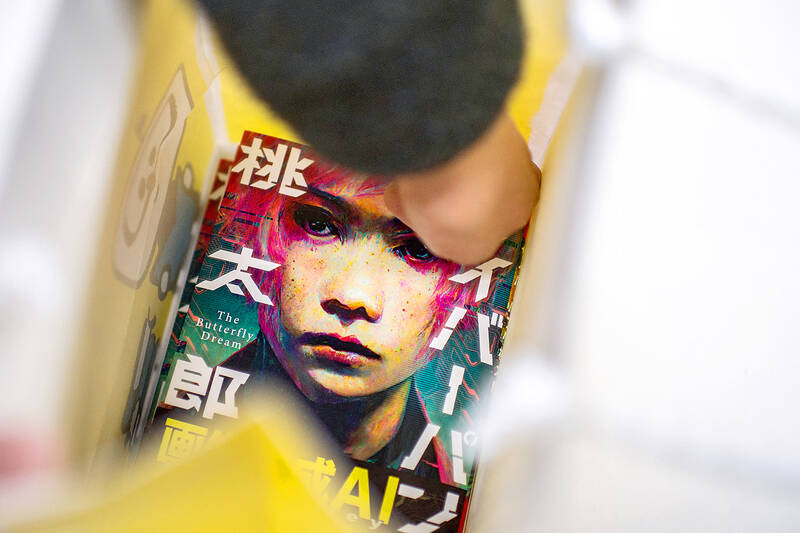

Photo: AFP
It took the author, who goes by the pen name Rootport, just six weeks to finish the over-100-page manga, which would have taken a skilled artist a year to complete, he said.
“It was a fun process, it reminded me of playing the lottery,” the 37-year-old said.
Rootport, a writer who has previously worked on manga plots, entered combinations of text prompts such as “pink hair,” “Asian boy” and “stadium jacket” to conjure up images of the story’s hero in around a minute.
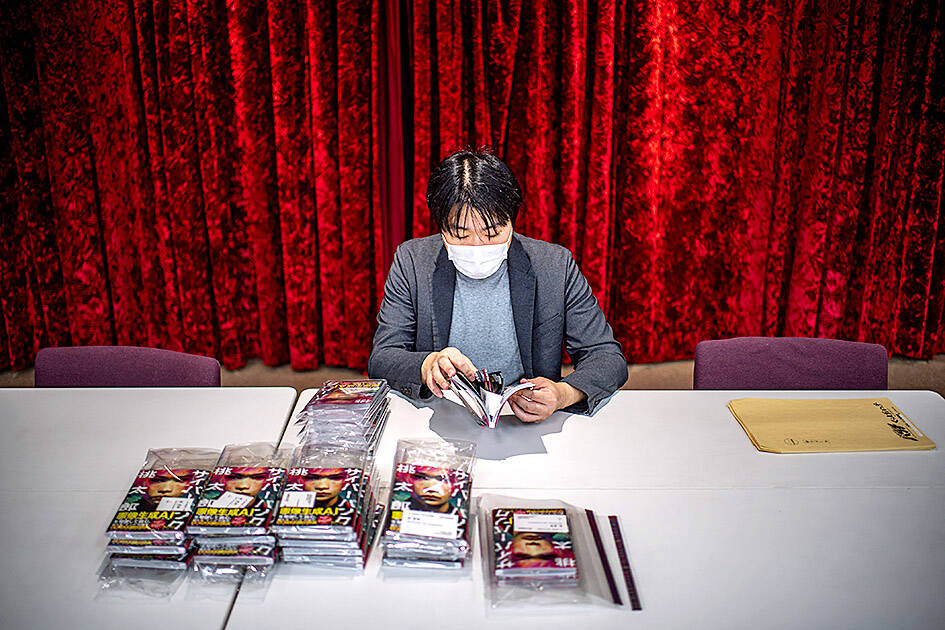

Photo: AFP
He then laid out the best frames in comic-book format to produce the book, which has already sparked a buzz online ahead of its March 9 release by Shinchosha, a major publishing house.
Unlike traditional black-and-white manga, his brainchild is fully colored, although the faces of the same character sometimes appear in markedly different forms. Still, AI image generators have “paved the way for people without artistic talent to make inroads” into the manga industry — provided they have good stories to tell, the author said.
Rootport said he felt a sense of fulfillment when his text instructions, which he describes as magic “spells,” created an image that chimed with what he had imagined.

Photo: AFP
“But is it the same satisfaction you’d feel when you’ve drawn something by hand from scratch? Probably not.”
SOUL SEARCHING
Midjourney was developed in the US and soared to popularity worldwide after its launch last year.
Like other AI text-to-image generators, its fantastical, absurd and sometimes creepy inventions can be strikingly sophisticated, provoking soul-searching among artists.
The tools have also run into legal difficulties, with the London-based start-up behind Stable Diffusion facing lawsuits alleging the software scraped large amounts of copyrighted material from the web without permission.
Some Japanese lawmakers have raised concerns over artists’ rights, although experts say copyright infringements are unlikely if AI art is made using simple text prompts, with little human creativity.
Other people have warned that the technology could steal jobs from junior manga artists, who painstakingly paint background images for each scene.
When Netflix released a Japanese animated short in January using AI-generated backgrounds, it was lambasted online for not hiring human animators.
“The possibility that manga artists’ assistants will be replaced [by AI] isn’t zero,” Keio University professor Satoshi Kurihara said.
In 2020, Kurihara and his team published an AI-aided comic in the style of late manga pioneer Osamu Tezuka.
For that project, humans drew almost everything, but since then AI art has become “top notch” and is “bound to” influence the manga industry’s future, he said.
‘HUMANS STILL DOMINATE’
Some manga artists welcome the new possibilities offered by the technology.
“I don’t really see AI as a threat — rather, I think it can be a great companion,” said Madoka Kobayashi, whose career spans over 30 years.
Artificial intelligence can “help me visualize what I have in mind, and suggest rough ideas, which I then challenge myself to improve,” she said.
The author, who also trains aspiring manga artists at a Tokyo academy, argues that manga isn’t just built on aesthetics, but also on cleverly devised plots.
In that arena, “I’m confident humans still dominate.”
Even so, she recoils at copying directly from computer-generated images, because “I don’t know whose artwork they’re based on.”
At Tokyo Design Academy, Kobayashi uses figurines to help improve the students’ pencil drawings, including details ranging from muscles to creases in clothes and hair whorls.
“AI art is great... but I find human drawings more appealing, precisely because they are ‘messy,’” said 18-year-old student Ginjiro Uchida.
Computer programs don’t always capture the deliberately exaggerated hands or faces of a real manga artist, and “humans still have a better sense of humor,” he said.
Three major publishers declined to comment when asked whether they thought AI could disrupt Japan’s human-driven manga production process.
Rootport doubts fully AI-drawn manga will ever become mainstream, because real artists are better at making sure their illustrations fit the context.
But, “I also don’t think manga completely unaided by AI will remain dominant forever.”
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them

Politically charged thriller One Battle After Another won six prizes, including best picture, at the British Academy Film Awards on Sunday, building momentum ahead of Hollywood’s Academy Awards next month. Blues-steeped vampire epic Sinners and gothic horror story Frankenstein won three awards each, while Shakespearean family tragedy Hamnet won two including best British film. One Battle After Another, Paul Thomas Anderson’s explosive film about a group of revolutionaries in chaotic conflict with the state, won awards for directing, adapted screenplay, cinematography and editing, as well as for Sean Penn’s supporting performance as an obsessed military officer. “This is very overwhelming and wonderful,” Anderson