Shoji Morimoto has what some would see as a dream job: he gets paid to do pretty much nothing.
The 38-year-old Tokyo resident charges 10,000 yen (US$71) an hour to accompany clients and simply exist as a companion.
“Basically, I rent myself out. My job is to be wherever my clients want me to be and to do nothing in particular,” Morimoto said, adding that he had handled some 4,000 sessions in the past four years.
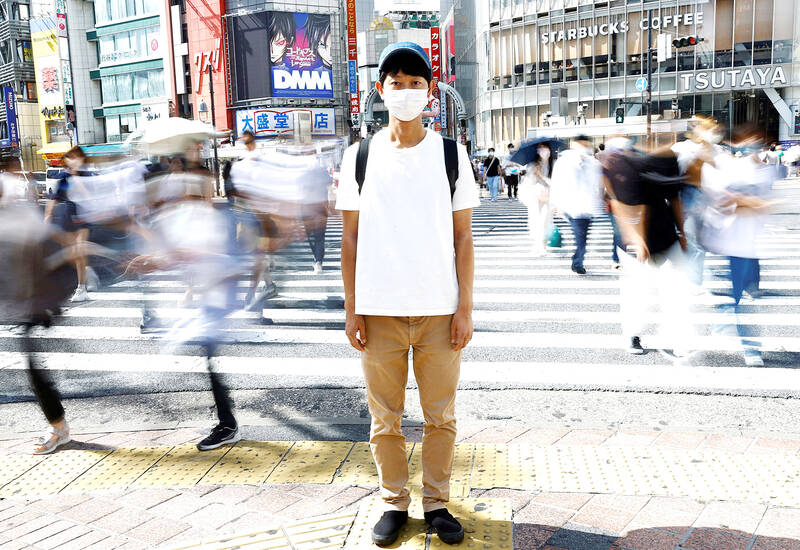

Photo: REUTERS
With a lanky build and average looks, Morimoto now boasts nearly a quarter of a million followers on Twitter, where he finds most of his clients. Roughly a quarter of them are repeat customers, including one who has hired him 270 times.
His job has taken him to a park with a person who wanted to play on a see-saw. He has also beamed and waved through a train window at a complete stranger who wanted a send-off.
Doing nothing doesn’t mean Morimoto will do anything. He has turned down offers to move a fridge and go to Cambodia, and doesn’t take any requests of a sexual nature.
Last week, Morimoto sat opposite Aruna Chida, a 27-year-old data analyst clad in a sari, having a sparse conversation over tea and cakes.
Chida wanted to wear the Indian garment out in public but was worried it might embarrass her friends. So she turned to Morimoto for companionship.
“With my friends I feel I have to entertain them, but with the rental-guy (Morimoto) I don’t feel the need to be chatty,” she said.
Before Morimoto found his true calling, he worked at a publishing company and was often chided for “doing nothing.”
“I started wondering what would happen if I provided my ability to ‘do nothing’ as a service to clients,” he said.
The companionship business is now Morimoto’s sole source of income, with which he supports his wife and child. Although he declined to disclose how much he makes, he said he sees about one or two clients a day. Before the pandemic, it was three or four a day.
As he spent a Wednesday doing nothing of note in Tokyo, Morimoto reflected on the bizarre nature of his job and appeared to question a society that values productivity and derides uselessness.
“People tend to think that my ‘doing nothing’ is valuable because it is useful (for others) ... But it’s fine to really not do anything. People do not have to be useful in any specific way,” he said.
Google unveiled an artificial intelligence tool Wednesday that its scientists said would help unravel the mysteries of the human genome — and could one day lead to new treatments for diseases. The deep learning model AlphaGenome was hailed by outside researchers as a “breakthrough” that would let scientists study and even simulate the roots of difficult-to-treat genetic diseases. While the first complete map of the human genome in 2003 “gave us the book of life, reading it remained a challenge,” Pushmeet Kohli, vice president of research at Google DeepMind, told journalists. “We have the text,” he said, which is a sequence of

On a harsh winter afternoon last month, 2,000 protesters marched and chanted slogans such as “CCP out” and “Korea for Koreans” in Seoul’s popular Gangnam District. Participants — mostly students — wore caps printed with the Chinese characters for “exterminate communism” (滅共) and held banners reading “Heaven will destroy the Chinese Communist Party” (天滅中共). During the march, Park Jun-young, the leader of the protest organizer “Free University,” a conservative youth movement, who was on a hunger strike, collapsed after delivering a speech in sub-zero temperatures and was later hospitalized. Several protesters shaved their heads at the end of the demonstration. A

In August of 1949 American journalist Darrell Berrigan toured occupied Formosa and on Aug. 13 published “Should We Grab Formosa?” in the Saturday Evening Post. Berrigan, cataloguing the numerous horrors of corruption and looting the occupying Republic of China (ROC) was inflicting on the locals, advocated outright annexation of Taiwan by the US. He contended the islanders would welcome that. Berrigan also observed that the islanders were planning another revolt, and wrote of their “island nationalism.” The US position on Taiwan was well known there, and islanders, he said, had told him of US official statements that Taiwan had not

We have reached the point where, on any given day, it has become shocking if nothing shocking is happening in the news. This is especially true of Taiwan, which is in the crosshairs of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), uniquely vulnerable to events happening in the US and Japan and where domestic politics has turned toxic and self-destructive. There are big forces at play far beyond our ability to control them. Feelings of helplessness are no joke and can lead to serious health issues. It should come as no surprise that a Strategic Market Research report is predicting a Compound