What’s small, yellow, loves bananas and promotes the rule of law? A Minion, at least according to an edited version of the latest animated film featuring supervillain Gru and his army of tiny sidekicks being screened in China. The fifth instalment of the lucrative Despicable Me franchise, Minions: The Rise of Gru, premiered in China this month, several weeks after the film opened in US cinemas.
But while the international version of the kung fu-filled family-friendly romp set in 1970s San Francisco tells the story of how the dastardly Gru cut his teeth as a tween criminal, filmgoers in China are treated to an alternative ending in which the good guys win.
A series of subtitled still images inserted into the credits sequence on mainland Chinese screens reassures audiences that police catch Gru’s law-breaking mentor Wild Knuckles and lock him up for 20 years after a failed heist.
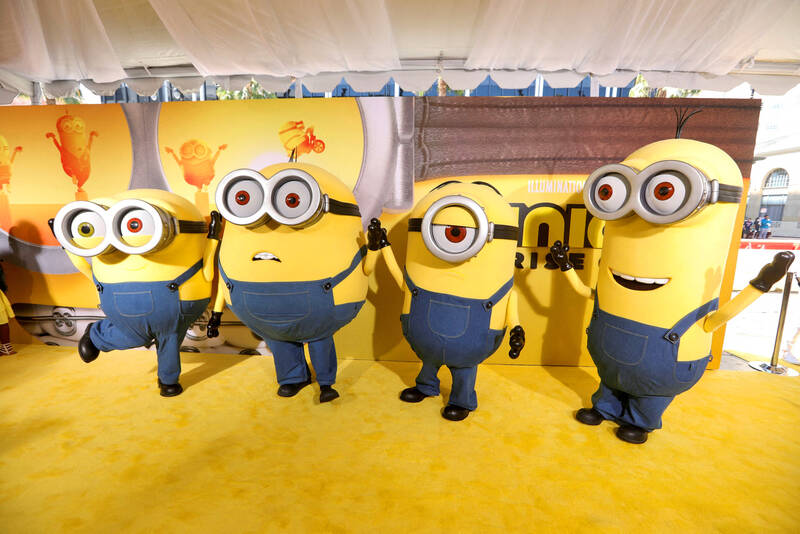

Photo: Reuters
International viewers simply see Knuckles give police the slip by faking his death earlier in the film’s concluding scenes, but in the Chinese version he puts his con artist skills to positive use in prison, where he follows his “love of acting” and sets up a theatrical troupe.
As for Gru, he “eventually became one of the good guys,” devoted to raising his family, the Chinese ending says.
It is not the first time a popular foreign film has been altered for cinemas in China, where the entertainment industry faces some of the world’s strictest censorship rules and is tasked with promoting “healthy” values.
David Fincher’s 1999 cult classic Fight Club starring Brad Pitt and Edward Norton was given similar treatment when Chinese streaming platform Tencent Video in January uploaded a version where police shut down the protagonist’s plan to bring down modern civilization.
And the highly anticipated return of US sitcom Friends to Chinese streaming platforms in February prompted fury among fans after viewers noticed a LGBTQ plotline was cut.
It is unclear if the Minions ending was altered due to censors’ demands or if producers considered it a more palatable conclusion for the Chinese market.
Universal did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
Social media reaction to the Chinese Minions ending was mixed, with one person on the Twitter-like Weibo social media platform saying they had gone to the cinema specifically to see the new ending but was disappointed that it was “just subtitles.”
Other fans were upset by the discontinuity between young Gru’s virtuous transformation in the new film, a prequel, and his continued villainous behavior in the other films, set in the present day.
“We can only say that the Gru of the main films lives in another parallel Minion universe,” one Weibo user complained.
May 26 to June 1 When the Qing Dynasty first took control over many parts of Taiwan in 1684, it roughly continued the Kingdom of Tungning’s administrative borders (see below), setting up one prefecture and three counties. The actual area of control covered today’s Chiayi, Tainan and Kaohsiung. The administrative center was in Taiwan Prefecture, in today’s Tainan. But as Han settlement expanded and due to rebellions and other international incidents, the administrative units became more complex. By the time Taiwan became a province of the Qing in 1887, there were three prefectures, eleven counties, three subprefectures and one directly-administered prefecture, with

President William Lai (賴清德) yesterday delivered an address marking the first anniversary of his presidency. In the speech, Lai affirmed Taiwan’s global role in technology, trade and security. He announced economic and national security initiatives, and emphasized democratic values and cross-party cooperation. The following is the full text of his speech: Yesterday, outside of Beida Elementary School in New Taipei City’s Sanxia District (三峽), there was a major traffic accident that, sadly, claimed several lives and resulted in multiple injuries. The Executive Yuan immediately formed a task force, and last night I personally visited the victims in hospital. Central government agencies and the

Among Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) villages, a certain rivalry exists between Arunothai, the largest of these villages, and Mae Salong, which is currently the most prosperous. Historically, the rivalry stems from a split in KMT military factions in the early 1960s, which divided command and opium territories after Chiang Kai-shek (蔣介石) cut off open support in 1961 due to international pressure (see part two, “The KMT opium lords of the Golden Triangle,” on May 20). But today this rivalry manifests as a different kind of split, with Arunothai leading a pro-China faction and Mae Salong staunchly aligned to Taiwan.
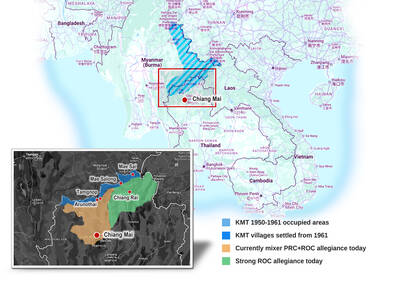
As with most of northern Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) settlements, the village of Arunothai was only given a Thai name once the Thai government began in the 1970s to assert control over the border region and initiate a decades-long process of political integration. The village’s original name, bestowed by its Yunnanese founders when they first settled the valley in the late 1960s, was a Chinese name, Dagudi (大谷地), which literally translates as “a place for threshing rice.” At that time, these village founders did not know how permanent their settlement would be. Most of Arunothai’s first generation were soldiers