It is admired the world over as an exquisite depiction of maternal grief. But Michelangelo’s Pieta has overshadowed two other moving sculptures on the same subject by the Renaissance giant.
That is why Florence’s Opera del Duomo museum in Italy is putting on display together for the first time all three versions of the Virgin Mary mourning over the body of her son Jesus Christ.
The Tuscan museum’s original Bandini goes on show Thursday alongside casts of the Pieta and Rondanini, which are on loan from the Vatican Museums.
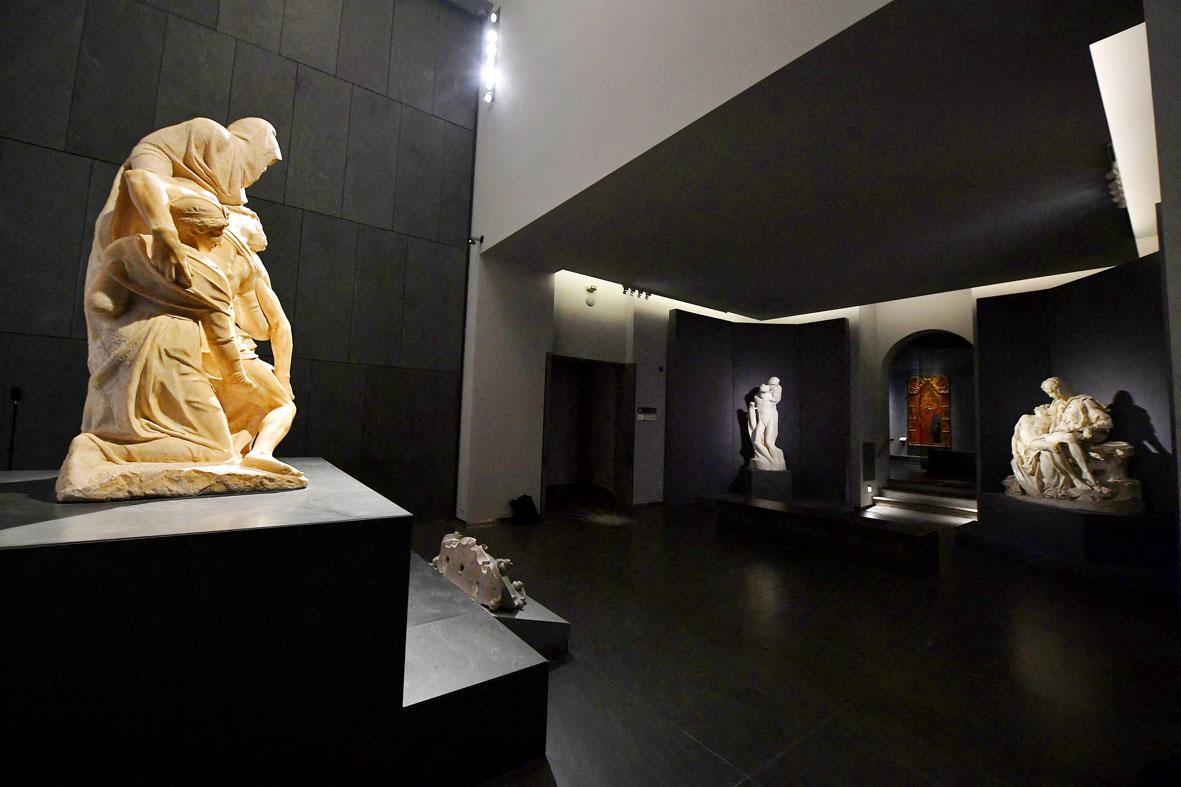

Photo: REUTERS
Positioned to face each other in an intimate setting, there are striking contrasts between these variations, which mark different phases in the life of the artist, who died aged 88 in 1564.
The museum’s director, Timothy Verdon, said it was a unique opportunity to “observe Michelangelo’s intellectual maturation on the theme of the sacred.”
The exhibition, which runs until Aug. 1, “highlights the link between life and art in this religious sculptor, who served the popes for most of his career.”
The Pieta housed at the Vatican — masterfully executed when Michelangelo was not yet 25 years old — amazed his contemporaries, who were dazzled by the beauty of this virgin, clothed in billowing drapery.
The artist rejected criticism that his Mary was too youthful, saying purity kept women beautiful.
Mary cradles her 33-year old son, whose serene expression suggests he could almost be sleeping in a nod to the coming resurrection — the rising of Jesus from the dead in Christian belief.
This sculpture was damaged by a Hungarian hammer-wielding attacker in 1972, and the restored work of art is now protected behind bulletproof glass.
Centuries earlier, Michelangelo himself — dissatisfied with the Bandini, his second pieta — attacked it with a hammer, leaving marks which can still be seen today on Jesus’ shoulder and Mary’s hand.
This version was done when the then-72-year old artist was suffering from depression. Convinced death was near, Michelangelo took a vow of poverty and placed religion at the center of his life.
He lent his own features and beard to the character of Nicodemus, who dominates the Bandini, shielding Jesus, Mary Magdalene and Mary, who here has lost her earlier timeless beauty.
The Rondanini is without doubt the most surprising: stunningly modern, this stripped-down sculpture, about two meters high, was begun around 1552, when the artist was nearly 80 years old.
It was found in his home in Rome, where he worked until his death. Juxtaposing the three works “allows us to measure the evolution of Michelangelo’s style over the 50 years that separate the first pieta from the other two, and the even more drastic and striking change between the last two,” Verdon said.
The last pieta feels unfinished and far removed from the aesthetic canons of the time, but experts also see it as a message of faith and the importance of looking beyond appearances to the essential.
Gone is the rich drapery, gone are the supporting characters.
Mary and her son, whose faces and bodies are reduced to sketches, are once again represented alone in an extreme simplicity that reinforces the spiritual power of Michelangelo Buonarroti’s last work.
May 26 to June 1 When the Qing Dynasty first took control over many parts of Taiwan in 1684, it roughly continued the Kingdom of Tungning’s administrative borders (see below), setting up one prefecture and three counties. The actual area of control covered today’s Chiayi, Tainan and Kaohsiung. The administrative center was in Taiwan Prefecture, in today’s Tainan. But as Han settlement expanded and due to rebellions and other international incidents, the administrative units became more complex. By the time Taiwan became a province of the Qing in 1887, there were three prefectures, eleven counties, three subprefectures and one directly-administered prefecture, with

President William Lai (賴清德) yesterday delivered an address marking the first anniversary of his presidency. In the speech, Lai affirmed Taiwan’s global role in technology, trade and security. He announced economic and national security initiatives, and emphasized democratic values and cross-party cooperation. The following is the full text of his speech: Yesterday, outside of Beida Elementary School in New Taipei City’s Sanxia District (三峽), there was a major traffic accident that, sadly, claimed several lives and resulted in multiple injuries. The Executive Yuan immediately formed a task force, and last night I personally visited the victims in hospital. Central government agencies and the

Among Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) villages, a certain rivalry exists between Arunothai, the largest of these villages, and Mae Salong, which is currently the most prosperous. Historically, the rivalry stems from a split in KMT military factions in the early 1960s, which divided command and opium territories after Chiang Kai-shek (蔣介石) cut off open support in 1961 due to international pressure (see part two, “The KMT opium lords of the Golden Triangle,” on May 20). But today this rivalry manifests as a different kind of split, with Arunothai leading a pro-China faction and Mae Salong staunchly aligned to Taiwan.
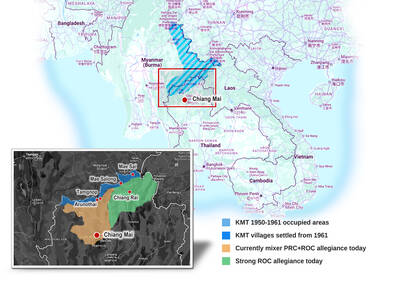
As with most of northern Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) settlements, the village of Arunothai was only given a Thai name once the Thai government began in the 1970s to assert control over the border region and initiate a decades-long process of political integration. The village’s original name, bestowed by its Yunnanese founders when they first settled the valley in the late 1960s, was a Chinese name, Dagudi (大谷地), which literally translates as “a place for threshing rice.” At that time, these village founders did not know how permanent their settlement would be. Most of Arunothai’s first generation were soldiers