Yuto Naganuma looks silently as the cold sea breeze sweeps over the crumbling walls of the school where his little brother was lost in Japan’s devastating 2011 tsunami.
Ten years on, Naganuma and others like him form a generation whose young lives were shaped by what is known in Japan as the triple disaster: a powerful earthquake that sparked a terrifying tsunami and the worst nuclear accident since Chernobyl.
The children of the tsunami lost family, homes, schools and entire communities, and for some the experience sparked a drive to work in disaster awareness, or help children like them who have lived with tragedy.
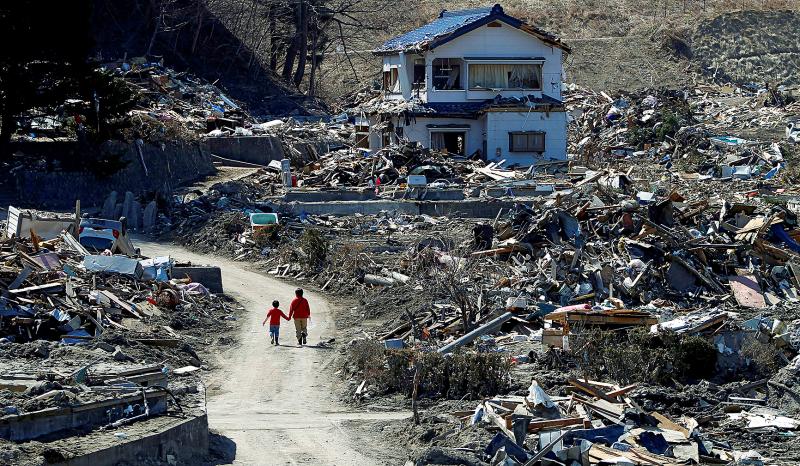

Photo: Reuters
Even a decade on, the devastation Naganuma suffered is raw.
“I lost my family, my community. Things that built who I am. I felt the tsunami carved away half of my body,” he said outside the Okawa Elementary School in northeast Japan, where his eight-year-old brother was killed.
He was among 74 children and 10 school staff killed in one of the worst tragedies of the disaster that left around 18,500 people dead or missing, swept away after staff failed to evacuate to higher ground.
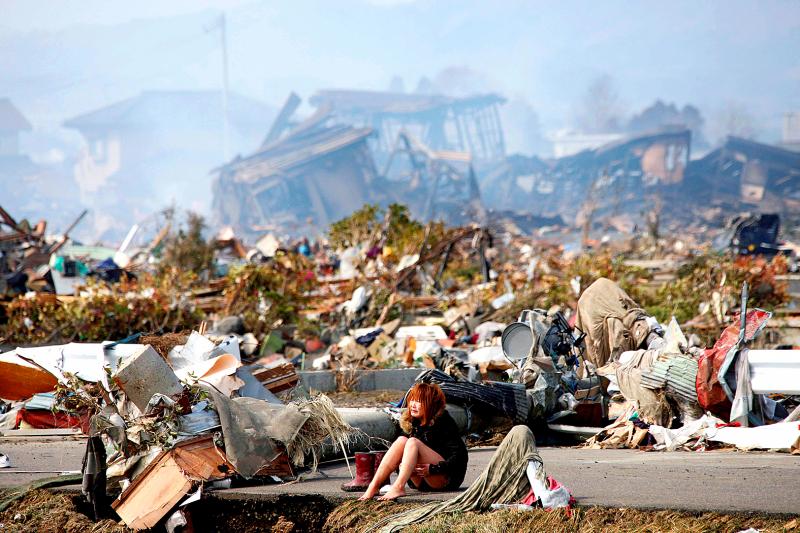

Photo: Reuters
Naganuma was just 16 at the time, but blamed himself for the loss.
Two days before the 9.0 magnitude quake struck, he felt a major 7.3 tremor on a local beach, which he saw later as a missed warning.
“I feel maybe my brother did not have to die. Had I warned people in the community, maybe they didn’t have to die,” he said as he gazed at gutted classrooms.
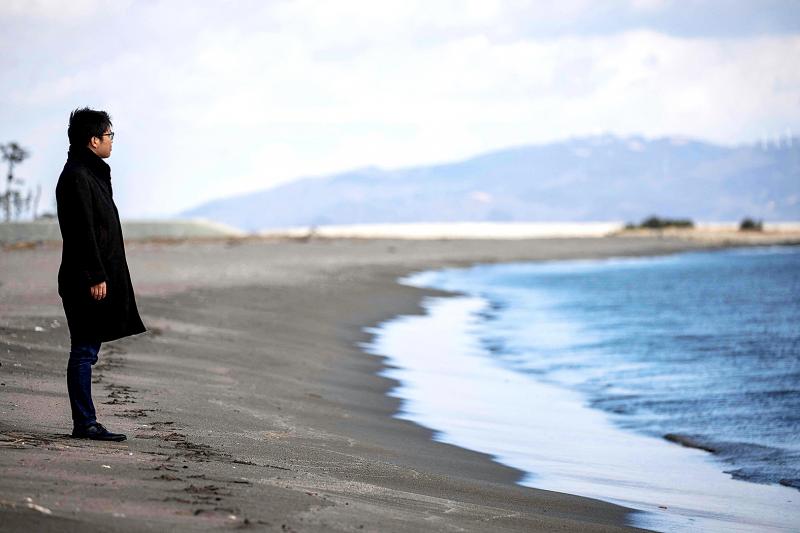

Photo: AFP
His grandmother and great-grandmother were also killed in the tsunami, as they waited for his brother’s school bus.
“I am filled with regret,” he said. “I let the day come without taking any action.”
‘LIVING BETWEEN DISASTERS’

Photo: Reuters
In the years after, Naganuma focused on leading a normal life, but he struggled with survivor’s guilt, wondering why he had been spared.
He enrolled in a teaching course at a university in another region but eventually moved to a school closer to his home to study disaster management.
He now gives tours at the school and lectures on disaster preparedness.
In Japan and elsewhere, “all of us are living in the time between disasters,” he said. “How we spend this time significantly changes the probability of survival when we face the next disaster.”
Nayuta Ganbe, 21, has also gradually come around to speaking about his experience of the tsunami.
He took shelter at his school with his mother and sister after a tsunami warning was issued following the quake.
They were meant to be on the third floor, but Ganbe went to retrieve his outdoor shoes, which Japanese students leave at the entrance.
As he held open the door for five men still coming towards the school, a torrent of water mixed with oily sludge and carrying debris and vehicles knocked the men over and pulled them down.
Ganbe was on slightly higher ground but the water, “thick like mayonnaise,” quickly flooded round him.
“It was like the water grabbed my ankles,” he said.
A man being carried away shouted and stretched his arm towards Ganbe, who stood paralyzed as the water surged.
“When his finger tips were completely submerged, I snapped out of it,” he said.
The aftermath of the disaster was barely less traumatic — Ganbe recalls finding a body days after, and a limb while walking to school, an experience not uncommon for children in the area at the time.
Media coverage emphasized polite evacuees and national solidarity, but Ganbe saw adults jump lines for food, pushing children aside. For several days after the tsunami he ate nothing.
Pupils were discouraged from talking about “missing” friends and some experienced panic attacks.
“Before you knew it, it became normal not to talk about it,” he said.
But three years after the disaster, he was asked to deliver a talk and began to process his memories, enduring flashbacks and sleepless nights.
‘TORN APART’
He now studies disaster sociology, investigating what makes people more likely to take the right steps to save themselves when crisis hits, and speaks to groups nationwide, in part to preserve memories that he fears are fading.
“Even in this area, the subject is becoming something that you see in textbooks,” he said.
He feels those who were adults at the time are often reluctant to stir up painful memories while younger people like his little sister remember only fragmented feelings of fear.
“Give it 20 years and we may see 20-year-olds, who were born after the disaster, who will leave home without knowing about it.”
The tsunami marked not only children caught up in its direct path, but also those affected by the nuclear disaster at Fukushima Daiichi.
Hazuki Shimizu lived in Namie, a few kilometers from the reactors that went into meltdown after the tsunami overwhelmed the plant’s cooling system.
She fled her home with her mother and sister on March 12, eventually ending up in Chiba, outside Tokyo.
“I was literally torn apart,” the 27-year-old recalled of watching the unfolding disaster from afar. “I couldn’t do anything.”
She was safe, but not always sheltered from pain. At the local city hall, her family was kept in the car park and monitored for radiation with Geiger counters when they came to register her for a new school.
And her new classmates were silent about the disaster.
“I just didn’t know why people were not talking about this... Why didn’t they care? I felt very isolated.”
As an adult, she moved back to the coastal region and now works for a group helping preserve memories of the tsunami.
“Once I became a disaster victim, I learned that it was very hard,” said Shimizu, who has also worked with groups offering children tutoring and community spaces.
“There are so many people who are experiencing sorrow and struggles,” she said. “We need to hear their voices and stand by them.”
June 23 to June 29 After capturing the walled city of Hsinchu on June 22, 1895, the Japanese hoped to quickly push south and seize control of Taiwan’s entire west coast — but their advance was stalled for more than a month. Not only did local Hakka fighters continue to cause them headaches, resistance forces even attempted to retake the city three times. “We had planned to occupy Anping (Tainan) and Takao (Kaohsiung) as soon as possible, but ever since we took Hsinchu, nearby bandits proclaiming to be ‘righteous people’ (義民) have been destroying train tracks and electrical cables, and gathering in villages
Swooping low over the banks of a Nile River tributary, an aid flight run by retired American military officers released a stream of food-stuffed sacks over a town emptied by fighting in South Sudan, a country wracked by conflict. Last week’s air drop was the latest in a controversial development — private contracting firms led by former US intelligence officers and military veterans delivering aid to some of the world’s deadliest conflict zones, in operations organized with governments that are combatants in the conflicts. The moves are roiling the global aid community, which warns of a more militarized, politicized and profit-seeking trend

The wide-screen spectacle of Formula One gets a gleaming, rip-roaring workout in Joseph Kosinski’s F1, a fine-tuned machine of a movie that, in its most riveting racing scenes, approaches a kind of high-speed splendor. Kosinski, who last endeavored to put moviegoers in the seat of a fighter jet in Top Gun: Maverick, has moved to the open cockpits of Formula One with much the same affection, if not outright need, for speed. A lot of the same team is back. Jerry Bruckheimer produces. Ehren Kruger, a co-writer on Maverick, takes sole credit here. Hans Zimmer, a co-composer previously, supplies the thumping

Dr. Y. Tony Yang, Associate Dean of Health Policy and Population Science at George Washington University, argued last week in a piece for the Taipei Times about former president Ma Ying-jeou (馬英九) leading a student delegation to the People’s Republic of China (PRC) that, “The real question is not whether Ma’s visit helps or hurts Taiwan — it is why Taiwan lacks a sophisticated, multi-track approach to one of the most complex geopolitical relationships in the world” (“Ma’s Visit, DPP’s Blind Spot,” June 18, page 8). Yang contends that the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) has a blind spot: “By treating any