Kenzo Takada, the iconic French-Japanese fashion designer famed for his jungle-infused designs and free-spirited aesthetic that channeled global travel, has died. He was 81.
The family said in a statement to French media Sunday that Takada died from complications from COVID-19 in a hospital in Neuilly-sur-Seine, near Paris. A public relations officer for Kenzo’s brand confirmed that Takada died, but didn’t give a cause of death.
“It is with immense sadness that KENZO has learned of the passing of our founder,” the fashion house said in a statement. “For half a century, Mr. Takada has been an emblematic personality in the fashion industry — always infusing creativity and color into the world.”
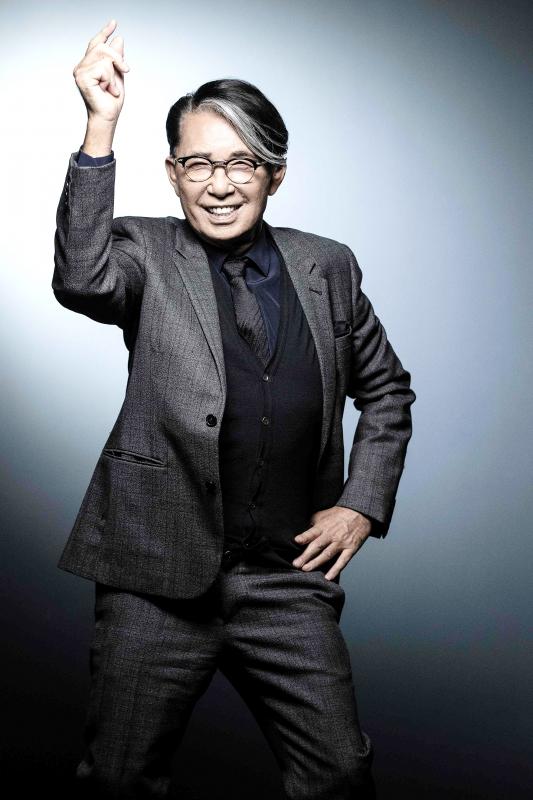

Photo: AFP
Takada’s death came at the tail end of Paris Fashion Week, whose nine-day calendar is undertaking an unusual fashion season for spring-summer 2021 because of the coronavirus pandemic. It was only days ago that the Kenzo fashion house unveiled its bee-themed collection here.
Though Takada had been retired from his house since 1999 to pursue a career in art, Kenzo remains one of the most respected fixtures of high Paris fashion. Since 1993, the Kenzo brand has been owned by the French luxury goods company LVMH.
“His amazing energy, kindness, talent and smile were contagious,” said Kenzo artistic director Felipe Oliveira Baptista, who unveiled the bee-themed collection to fashion editors Wednesday. “His kindred spirit will live forever.”
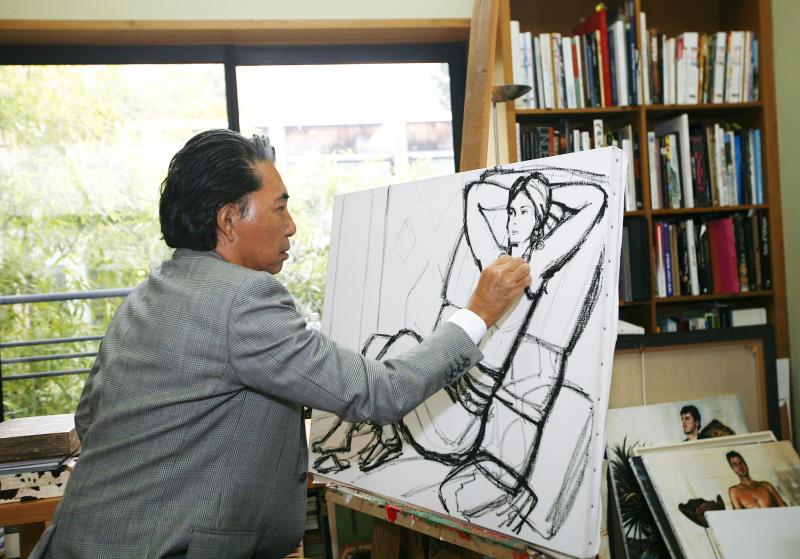

Photo: AP
Kenzo’s styles used bold color, clashing prints and were inspired by travels all over the world.
“Kenzo Takada has, from the 1970s, infused into fashion a tone of poetic lightness and sweet freedom which inspired many designers after him,” said Bernard Arnault, chairman and chief executive of LVMH.
Takada was born on Feb. 27, 1939, in Himeji, in the Hyogo Prefecture in Japan to hoteliers, but after reading his sisters’ fashion magazines his love of fashion began.
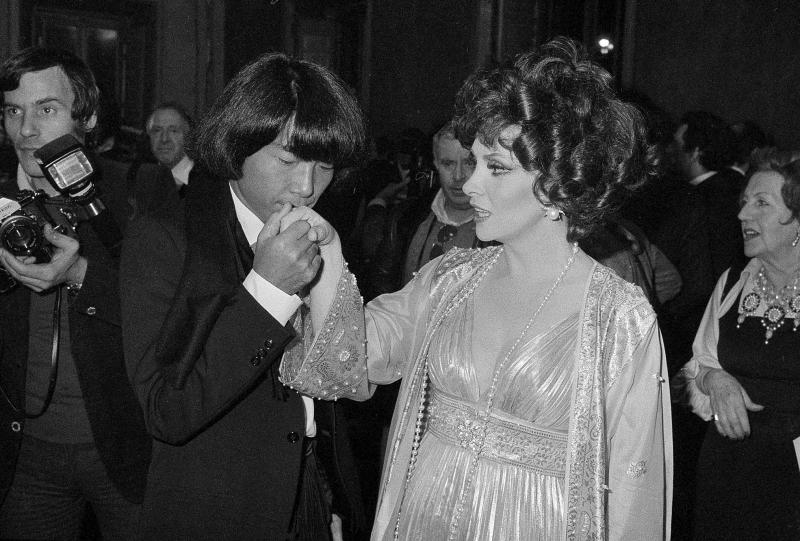

Photo: AP
Studying at the Bunka College of Fashion in Tokyo, Takada had a brief stint working in Japan, before relocating to Paris in 1965, to work as a freelance designer.
In Paris, he took over a boutique in 1970 and crystallized his future ready-to-wear aesthetic inspired in its decoration by the jungle scenes of painter Henri Rousseau, which he merged with Asian styles. It became influential.
But it was lowly beginnings: Takada’s first collection at the store called was made entirely out of cotton because he had little money. But the clothes spoke for themselves and a model of his was put on the cover of Elle magazine. A short time after, pioneering shoulder forms, large armholes, dungarees, smock tent dresses, innovative shoulder shapes, and his store was featured in US Vogue. Kenzo showed collections in New York and Tokyo in 1971.
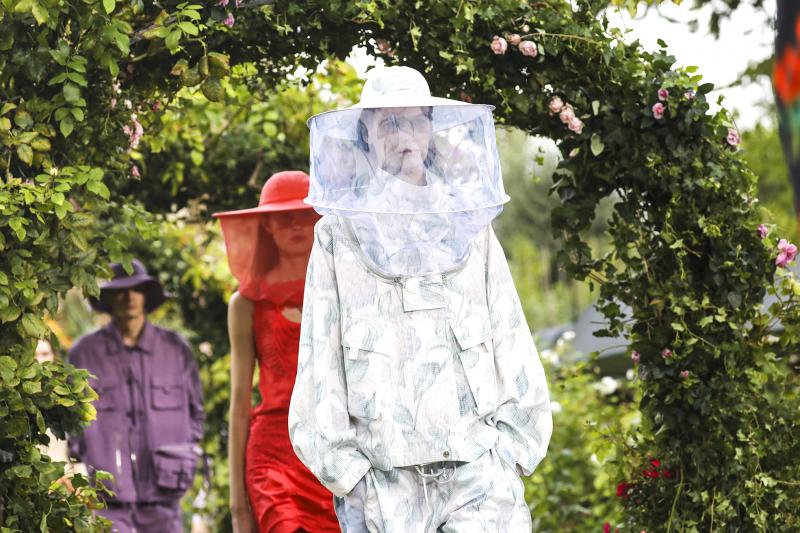

Photo: AP
Yves Saint Laurent was an important inspiration in his work, Takada has said. Takada shared Saint Laurent’s penchant for theatrics. in 1978 and 1979, he showed in a circus tent, and it featured himself riding an elephant, and performers rode horses wearing see-through uniforms.
Takada’s love of travel and use of ethnic influences were strong features in his three decades atop his house. His contribution to style was significant. He championed a youthful aesthetic and unstructured form, and did away with zippers to liberate silhouettes. His signatures were of wider sleeves and arm holes, that harked to historic styles in his home continent of Asia.
May 26 to June 1 When the Qing Dynasty first took control over many parts of Taiwan in 1684, it roughly continued the Kingdom of Tungning’s administrative borders (see below), setting up one prefecture and three counties. The actual area of control covered today’s Chiayi, Tainan and Kaohsiung. The administrative center was in Taiwan Prefecture, in today’s Tainan. But as Han settlement expanded and due to rebellions and other international incidents, the administrative units became more complex. By the time Taiwan became a province of the Qing in 1887, there were three prefectures, eleven counties, three subprefectures and one directly-administered prefecture, with

Taiwan Power Co (Taipower, 台電) and the New Taipei City Government in May last year agreed to allow the activation of a spent fuel storage facility for the Jinshan Nuclear Power Plant in Shihmen District (石門). The deal ended eleven years of legal wrangling. According to the Taipower announcement, the city government engaged in repeated delays, failing to approve water and soil conservation plans. Taipower said at the time that plans for another dry storage facility for the Guosheng Nuclear Power Plant in New Taipei City’s Wanli District (萬里) remained stuck in legal limbo. Later that year an agreement was reached

What does the Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) in the Huang Kuo-chang (黃國昌) era stand for? What sets it apart from their allies, the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT)? With some shifts in tone and emphasis, the KMT’s stances have not changed significantly since the late 2000s and the era of former president Ma Ying-jeou (馬英九). The Democratic Progressive Party’s (DPP) current platform formed in the mid-2010s under the guidance of Tsai Ing-wen (蔡英文), and current President William Lai (賴清德) campaigned on continuity. Though their ideological stances may be a bit stale, they have the advantage of being broadly understood by the voters.

In a high-rise office building in Taipei’s government district, the primary agency for maintaining links to Thailand’s 108 Yunnan villages — which are home to a population of around 200,000 descendants of the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) armies stranded in Thailand following the Chinese Civil War — is the Overseas Community Affairs Council (OCAC). Established in China in 1926, the OCAC was born of a mandate to support Chinese education, culture and economic development in far flung Chinese diaspora communities, which, especially in southeast Asia, had underwritten the military insurgencies against the Qing Dynasty that led to the founding of