SEPT. 14 to SEPT. 20
When then-county commissioner Chen Ding-nan (陳定南) announced that movie theaters in Yilan County no longer needed to play the national anthem before each showing, the authorities were displeased.
It was Sept. 13, 1988, over a year after the lifting of martial law, but the decades-old tradition where moviegoers had to stand and sing the anthem still endured.
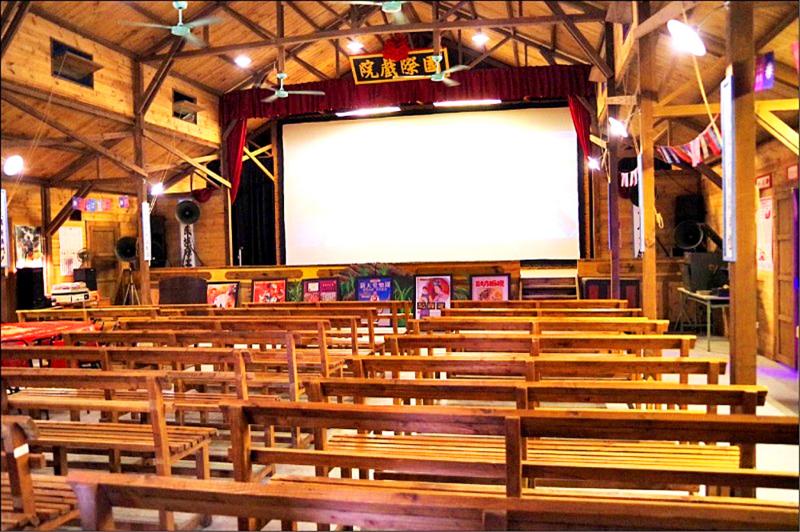

Photo: Tseng Nai-chiang, Taipei Times
Of course, Chen sugarcoated his decision: “Considering the environment of the theater, the contents of the movies and the reactions of the audience, we believe that it’s actually disrespectful to play the anthem before each showing. We should ensure that the dignity of the national anthem is no longer degraded, and in addition, there is no law mandating that theaters must play the national anthem,” he stated.
The national authorities didn’t buy it, and the next day the now-shuttered Government Information Office (GIO) ordered the Yilan County Government to correct its decision on grounds of violating Article 15 of the Motion Picture Act. Chen blasted the request, arguing that Article 15 only mandated that government promotional videos be shown after the national anthem clip and before the movie — it did not directly require theaters to play the national anthem.
“The GIO’s argument is fallacious,” he told the media. “How can I correct something that has no legal basis?”
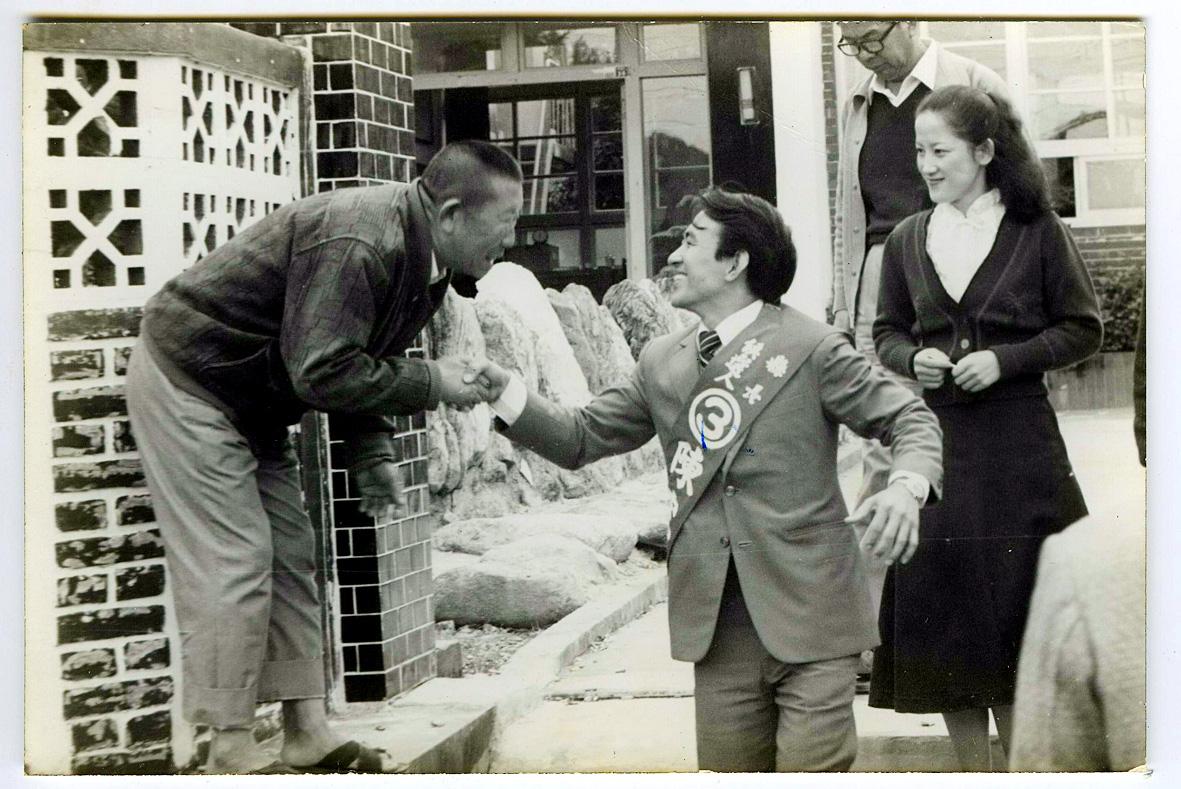

Photo courtesy of Chen Ding-nan Digital Archives
It was not the first time Chen defied authoritarian-era institutions, as the Liberty Times (Taipei Times’ sister paper) ran the story with the headline, “Chen Ding-nan strikes again (陳定南又出新招),” adding that the GIO was left “dumbfounded.” Shortly after being elected to his second term in 1986, he abolished the New Year’s Day flag-raising ceremony and later did away with the Human Resources Second Office (人二室) that essentially served as the thought police in every public institution. He also destroyed “loyalty records” that kept tabs on all local government office and school staff.
An intense debate ensued, but there was no stopping the tide, especially with the lifting in April 1991 of the Temporary Provisions Effective During the Period of National Mobilization for Suppression of the Communist Rebellion (動員戡亂時期臨時條款), which provided the basis for authoritarian rule. In July of the same year, the government abolished the law where people could be arrested for refusing to stand during the anthem, and by the mid-1990s, the practice was no more.
DISPLAY OF PATRIOTISM

Photo: Tseng Nai-chiang, Taipei Times
When the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) first took over Taiwan after World War II, they let each movie theater decide whether to play the national anthem before each showing. It wasn’t until 1951 that the Taiwan Garrison Command ordered all theaters to comply.
The government launched the “Anti-Communist, Anti-Soviet Movement” in 1952, where then-president Chiang Kai-shek (蔣介石) directly ordered that short “educational videos” be shown before movie screenings to boost public loyalty and support. The movement’s cultural committee in 1953 reiterated that all movie theaters needed to play the national anthem and that all audience members needed to stand up and stand still for its entire duration.
At first, due to reports that people were sitting down before the last note of the anthem concluded, the government asked movie theaters to urge their customers to rectify this behavior. Other issues included poor audio or video quality, which the government deemed degrading toward the anthem. By 1954, it appears that the national anthem had become a universal practice in all movie theaters across Taiwan.
Whether people actually complied with the orders to “stand still” is another issue. In 1966, the United Daily News reported that audience behavior had become increasingly frivolous during the national anthem: “People just treat it as a mere formality and no longer take the practice seriously,” it stated. “There are many who don’t even stand properly, showing bad posture, and many sit down before the end of the song. There are also those who stand for the whole song, but continue to smoke, eat popsicles and melon seeds and even joke with other people.”
By March 1988, the United Daily News reported that people were running off to the bathrooms or buying food during the anthem, while others would arrive in the middle of the song and walk around looking for a seat. Martial law had already ended then, and the newspaper surmised that people were disrupting the anthem on purpose in protest. It questioned the need to play the anthem before every showing, suggesting that perhaps playing it once in the morning and once in the evening was enough.
SPLIT OPINION
Chen’s decision split public opinion, and the reports from each newspaper varied greatly. The state-run Central Daily News (中央日報) cited a government-sponsored survey where 74 percent of respondents agreed that the national anthem should be played before each showing. Some respondents said that it should be played just once per day before the first showing, while others said it should be played once in the morning and once in the evening.
Furthermore, 45.5 percent said that they enjoyed the national anthem video, while only 12.4 percent said that they did not like it.
“Every citizen must support their country and love their flag and national anthem,” the article quoted the GIO as saying. “Playing the national anthem in theaters and standing for it is a good tradition that should be maintained.”
The article also ran a joint statement by several theater association presidents: “Singing the national anthem is the duty of the citizens, and a concrete way to display one’s patriotism. Theaters should not abolish the practice.”
On the other hand, the Liberty Times noted that “most experts reacted positively” to Chen’s move. National Cheng Chi University’s then-journalism department head Wang Chi (汪琪) said, “If a practice has become merely a formality, I don’t think we need to insist on doing it anymore. It doesn’t matter if not playing the national anthem violates the law or not. Society has been changing rapidly in the past year, and there are already a number of media laws that need to be reviewed and updated to fit the times.”
Despite the government’s pushback, the Yilan Movie Theater Association on Sept. 20 voted to stop playing the national anthem. This led to a domino effect and other theater associations petitioned their local governments to follow Yilan’s lead. The GIO stood its ground, arguing that the US also requires people to stand for its national anthem before sports matches.
In early 1995, then-Taipei mayor Chen Shui-bian (陳水扁) allowed the city’s theaters to decide themselves whether to play the anthem or not — but in November of the same year, a high school student was reportedly punished by his school for not standing during the anthem. The mayor was not happy with the school and expressed his displeasure during a city council meeting.
By the end of 1996, the GIO finally relented, and this four-decade-old ritual was finally no more.
Taiwan in Time, a column about Taiwan’s history that is published every Sunday, spotlights important or interesting events around the nation that either have anniversaries this week or are tied to current events.
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

For many centuries from the medieval to the early modern era, the island port of Hirado on the northwestern tip of Kyushu in Japan was the epicenter of piracy in East Asia. From bases in Hirado the notorious wokou (倭寇) terrorized Korea and China. They raided coastal towns, carrying off people into slavery and looting everything from grain to porcelain to bells in Buddhist temples. Kyushu itself operated a thriving trade with China in sulfur, a necessary ingredient of the gunpowder that powered militaries from Europe to Japan. Over time Hirado developed into a full service stop for pirates. Booty could

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them

Politically charged thriller One Battle After Another won six prizes, including best picture, at the British Academy Film Awards on Sunday, building momentum ahead of Hollywood’s Academy Awards next month. Blues-steeped vampire epic Sinners and gothic horror story Frankenstein won three awards each, while Shakespearean family tragedy Hamnet won two including best British film. One Battle After Another, Paul Thomas Anderson’s explosive film about a group of revolutionaries in chaotic conflict with the state, won awards for directing, adapted screenplay, cinematography and editing, as well as for Sean Penn’s supporting performance as an obsessed military officer. “This is very overwhelming and wonderful,” Anderson