When Mangus and his Atayal people settled on a remote mountain in Hsinchu County after a journey from Nantou County some 400 years ago, they may not have thought of it as a "Promised Land."
Today, however, 135 descendents of those early settlers have founded the first Israeli-style kibbutz "socialist commune" in an effort to protect their culture and tap the eco-tourist dollar.
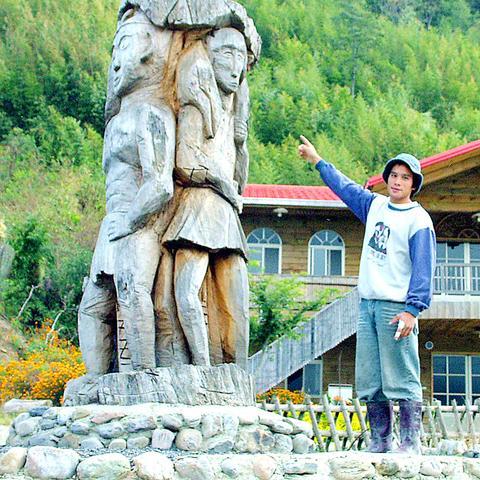

PHOTO: AFP
Reputedly the most isolated community in Taiwan, until recently the Smangus Atayal eked out a basic living from hunting and slash-and-burn agriculture on the mountain plateau sited at an altitude of 1,600m and surrounded by higher peaks.
Their way of life had seemed under threat as the youth of the tribe abandoned the mountain, lured by the opportunities in Taiwan's modern cities, where they often found themselves treated as second-class citizens.
Taiwan's 430,000 Aboriginals, whom anthropologists believe originally migrated from Malaysia or Indonesia, are among the country's most deprived communities.
Unemployment runs at 15 percent among them and 48 percent survive on less than NT$10,000 a month, a third of the average wage, according to independent lawmaker Kao Chin Su-mei (
More recently, however, the Atayal culture and a nearby grove of up to 1,000 ancient Formosan cypress trees, known as "divine trees," have drawn increasing numbers of eco-tourists to Smangus, an isolated village named after their ancestor.
"Thank our ancestors who gave us this land," says 69-year-old Icyh Sulong who is now head of the village.
Each week hundreds of tourists make the uncomfortable journey along bumpy mountain roads to see the giant trees and learn about the Atayal, who formerly hunted the local wildlife.
"My father had killed or captured 20-odd bears before he died," says 23-year-old Tqbil Icyan of his father Icyan.
While he died 20 years ago after a fall from a transport cable linking two mountains, the tribe believes the bears had their revenge.
"We believe those bears killed by my father avenged their death," Tqbil says.
The Atayal today see greater benefits from sparing the wildlife and tracking down tourist dollars instead.
"When I first visited Smangus 15 years ago, Atayal people shot birds to treat me," says writer Wu Chih-ching. "I told them if they want to attract more visitors to this remote village, they had to protect wild animals," adds Wu, who has advised on improvements to the villages.
The Atayal followed his advice but the transformation to eco-tourism was not without problems. When the Smangus people built their first tourist chalets about seven years ago, persistent squabbles arose over how to make the most of the new opportunities.
The disputes eventually prompted them to adopt a commune-style way of life, modeled on the Israeli kibbutz, although the tribe is Christian: a sign at the entrance of the village reads "Smangus is God's Tribe."
"The idea was inspired by the Bible" which encourages Christians to share their property, Taqbil says.
After a group of Atayal leaders visited Israel on a fact-finding trip early this year to see how Israelis operate their kibbutz communities, the Smangus residents decided to extend the communal lifestyle by sharing their land deeds.
"Now we feel the relationship among our people is much closer than before," Batu Icyh says happily.
Smangus adults work Monday through Thursday, with their jobs ranging from farming to maintaining roads and cooking. They are also required to spend Saturday and Sunday serving tourists living in their chalets while Friday is the day of rest.
In return, each adult receives a monthly salary of NT$10,000 from the communal Smangus coffers.
"I am able to save most of my monthly salary because it takes several hours to get to the nearest towns and there are few places to spend our money here," says Tqbil.
Smangus also boasts a modern restaurant where the residents are provided free meals. Nearly all other family expenses, such as medical bills and school fees, are also met by the communal coffers.
Unlike their parents, who had to walk several hours to attend the nearest school, Smangus children now take lessons in the village, which is also connected to the Internet.
Three Smangus families, attracted by its eco-tourism
success, have returned, a trend residents would not have dreamed of until recently.
Wu hopes the successes of the Smangu Atayal can be duplicated among the rest of Taiwan's Aboriginal communities, who are often marginalized in the predominantly Han Chinese society.
"The possibility cannot be ruled out. However, it may take time," Wu says. "At least the other Aboriginal tribes can learn something from Smangus."
May 26 to June 1 When the Qing Dynasty first took control over many parts of Taiwan in 1684, it roughly continued the Kingdom of Tungning’s administrative borders (see below), setting up one prefecture and three counties. The actual area of control covered today’s Chiayi, Tainan and Kaohsiung. The administrative center was in Taiwan Prefecture, in today’s Tainan. But as Han settlement expanded and due to rebellions and other international incidents, the administrative units became more complex. By the time Taiwan became a province of the Qing in 1887, there were three prefectures, eleven counties, three subprefectures and one directly-administered prefecture, with

Taiwan Power Co (Taipower, 台電) and the New Taipei City Government in May last year agreed to allow the activation of a spent fuel storage facility for the Jinshan Nuclear Power Plant in Shihmen District (石門). The deal ended eleven years of legal wrangling. According to the Taipower announcement, the city government engaged in repeated delays, failing to approve water and soil conservation plans. Taipower said at the time that plans for another dry storage facility for the Guosheng Nuclear Power Plant in New Taipei City’s Wanli District (萬里) remained stuck in legal limbo. Later that year an agreement was reached

What does the Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) in the Huang Kuo-chang (黃國昌) era stand for? What sets it apart from their allies, the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT)? With some shifts in tone and emphasis, the KMT’s stances have not changed significantly since the late 2000s and the era of former president Ma Ying-jeou (馬英九). The Democratic Progressive Party’s (DPP) current platform formed in the mid-2010s under the guidance of Tsai Ing-wen (蔡英文), and current President William Lai (賴清德) campaigned on continuity. Though their ideological stances may be a bit stale, they have the advantage of being broadly understood by the voters.

In a high-rise office building in Taipei’s government district, the primary agency for maintaining links to Thailand’s 108 Yunnan villages — which are home to a population of around 200,000 descendants of the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) armies stranded in Thailand following the Chinese Civil War — is the Overseas Community Affairs Council (OCAC). Established in China in 1926, the OCAC was born of a mandate to support Chinese education, culture and economic development in far flung Chinese diaspora communities, which, especially in southeast Asia, had underwritten the military insurgencies against the Qing Dynasty that led to the founding of