Phishing scams have grown up from the unsophisticated swindles of the past in which fake Nigerian princes e-mailed victims, who were told they would get a big windfall if they just provide their bank account number.
Even as authorities try to stamp out that con and other e-mail and online scams, scammers are getting more wily and finding new loopholes to exploit.
The vast majority of e-mail is spam and an unknown percentage of that is meant to defraud. The scale of electronic fraud means that the criminals can make huge profits even if only a small percentage of people are duped.
Phishing commonly refers to hoax e-mails purportedly from banks or other trustworthy sources that seek to trick recipients into revealing bank or credit card account numbers and passwords.
The US government scored a big victory in November when the Web hosting company McColo Corp was taken offline. Estimates vary, but the Washington Post said that 75 percent of spam worldwide had been sent through that single company.
But the spam e-mails offering celebrity diets, cheap printer ink, erased credit card debt and amazing orgasms found a new way to inboxes, according to Google’s security subsidiary Postini.
Now spammers use a variety of computers to send out spam e-mails to obscure their origins, meaning that a dramatic McColo-style takedown will be harder to reproduce, said Adam Swidler, product marketing manager for Google’s Postini.
And they’ve largely abandoned scams that are easy to see through — like the Nigerian prince — in favor of sophisticated “location-based spam,” which directs the victim to a Web site discussing a local disaster or similar issue. If they click on the offered video, the Web site downloads a virus to the user’s computer, Google said in a blog on security.
Tim Cranton, a Microsoft cybersecurity expert, said there was no way to know how much money is stolen.
“We don’t have a way to estimate numbers because there are so many victims that you’re not aware of,” he said.
E-con artists are getting more sophisticated in approaching potential victims. One tactic has been to write spam that purports to come from a trusted source, like Paypal.
When Paypal, which is owned by eBay, learned that spammers were using its name, they put a digital signature on their e-mails and asked providers like Yahoo and Google to block any e-mail purporting to come from them that did not have that signature.
“We know how many they throw away and it’s approximately speaking about 10 million a month,” said Michael Barrett, Paypal’s chief information security officer. “If the consumer never sees the e-mail in the first place then it’s hard for them to get victimized.”
“Phishing was not just impacting consumers, in terms of general loss, it was impacting their view of the safety of the Internet and … indirectly damaging our brand,” he said.
Security experts say they are seeing more and more shifts from outright fraud, where the victim will hand over their money, to the use of malware, basically malicious software that, among other things, collects passwords and credit card numbers for thieves.
“Those will then be sold on the underground market,” said David Marcus, a threat research expert at McAfee computer security firm.
The person purchasing the passwords and card numbers will use that information to make purchases, get cash or create fake identities. The Federal Bureau of Investigation, working with police in the UK, Turkey and Germany, shut down one such online forum called Dark Market last October that, at its peak, had more than 2,500 registered members, the FBI said at the time.
But experts agreed that they didn’t expect the problem to go away anytime soon and that more people out of work could mean more people falling for scams.
Marcus said many of the scams were nothing more than the digital equivalent of confidence tricks, although on a massive scale that could net some scammers more than US$100,000 a month.
“These things only have to be 2 percent successful,” he said. “Those campaigns are sent out to tens of millions of people at the same time.”
Also See: The GhostNet in the machine
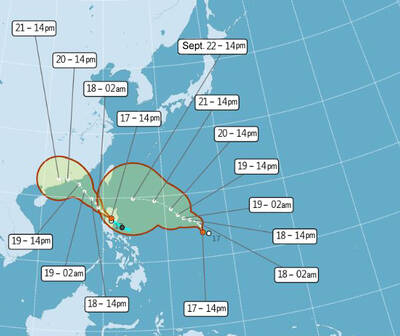
One of two tropical depressions that formed off Taiwan yesterday morning could turn into a moderate typhoon by the weekend, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said yesterday. Tropical Depression No. 21 formed at 8am about 1,850km off the southeast coast, CWA forecaster Lee Meng-hsuan (李孟軒) said. The weather system is expected to move northwest as it builds momentum, possibly intensifying this weekend into a typhoon, which would be called Mitag, Lee said. The radius of the storm is expected to reach almost 200km, she said. It is forecast to approach the southeast of Taiwan on Monday next week and pass through the Bashi Channel

NO CHANGE: The TRA makes clear that the US does not consider the status of Taiwan to have been determined by WWII-era documents, a former AIT deputy director said The American Institute in Taiwan’s (AIT) comments that World War-II era documents do not determine Taiwan’s political status accurately conveyed the US’ stance, the US Department of State said. An AIT spokesperson on Saturday said that a Chinese official mischaracterized World War II-era documents as stating that Taiwan was ceded to the China. The remarks from the US’ de facto embassy in Taiwan drew criticism from the Ma Ying-jeou Foundation, whose director said the comments put Taiwan in danger. The Chinese-language United Daily News yesterday reported that a US State Department spokesperson confirmed the AIT’s position. They added that the US would continue to

The number of Chinese spouses applying for dependent residency as well as long-term residency in Taiwan has decreased, the Mainland Affairs Council said yesterday, adding that the reduction of Chinese spouses staying or living in Taiwan is only one facet reflecting the general decrease in the number of people willing to get married in Taiwan. The number of Chinese spouses applying for dependent residency last year was 7,123, down by 2,931, or 29.15 percent, from the previous year. The same census showed that the number of Chinese spouses applying for long-term residency and receiving approval last year stood at 2,973, down 1,520,

EASING ANXIETY: The new guide includes a section encouraging people to discuss the threat of war with their children and teach them how to recognize disinformation The Ministry of National Defense’s All-Out Defense Mobilization Agency yesterday released its updated civil defense handbook, which defines the types of potential military aggression by an “enemy state” and self-protection tips in such scenarios. The agency has released three editions of the handbook since 2022, covering information from the preparation of go-bags to survival tips during natural disasters and war. Compared with the previous edition, released in 2023, the latest version has a clearer focus on wartime scenarios. It includes a section outlining six types of potential military threats Taiwan could face, including destruction of critical infrastructure and most undersea cables, resulting in