Three Mile Island, the site of the US’ worst nuclear accident, would restart operations to provide power to Microsoft Corp, US electricity company Constellation Energy Corp announced on Friday.
Microsoft would use the capability to deliver its expanding artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud services, which are putting pressure on local electricity providers as tech giants build more power-hungry data centers.
The 20-year agreement involves restarting Unit 1, which “operated at industry-leading levels of safety and reliability for decades before being shut down for economic reasons exactly five years ago,” Constellation said in a statement.
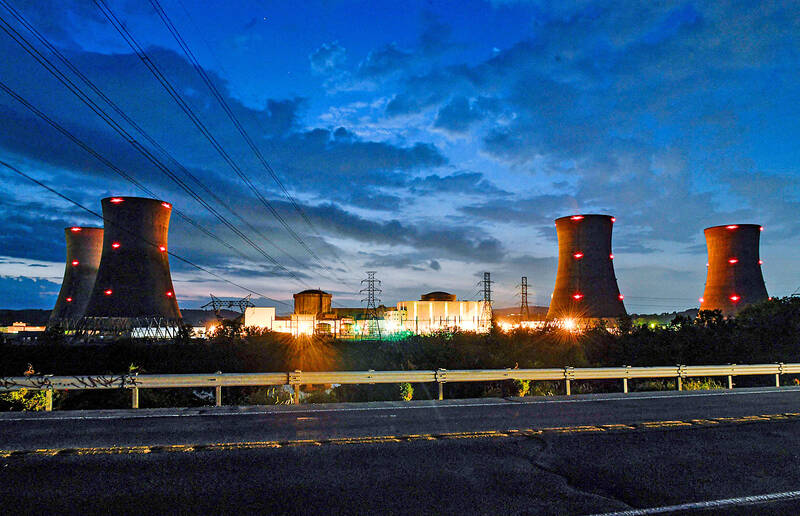

Photo: AFP
Unit 1 was not involved in the 1979 partial nuclear meltdown at the Pennsylvania site.
Before its premature retirement in 2019, the plant could power more than 800,000 average homes.
Microsoft would use this energy to support power grids in the mid-Atlantic states around Washington DC, a region considered an internet crossroads.
Microsoft vice president of energy Bobby Hollis said that Three Mile Island’s nuclear energy would bolster a power grid covering 13 states.
This area faces severe strain from data centers’ massive energy consumption, raising concerns about grid stability as AI demands increase.
Tech giants such as Microsoft, Amazon, and Google are rapidly expanding their data center capabilities to meet the AI revolution’s computing needs while also scouring the globe for sources of electricity.
Hollis said the project was part of a “multi-technology approach” to sourcing power — which also includes wind and solar energy — and “an essential pathway to achieving our goal of becoming carbon negative by 2030.”
Microsoft earlier this year signed a deal with Canada’s Brookfield Asset Management Ltd to develop more than 10.5 gigawatts of new wind and solar farms, marking one of the largest corporate purchases of renewable energy to date.
Constellation Energy expects the Three Mile Island reactor to go back online in 2028.
Seen as a more consistent source of power than solar and wind, many tech companies are betting on nuclear energy’s rapid development to meet AI’s electricity demands.
Amazon Web Services agreed in March to invest US$650 million in a data center campus powered by another 40-year-old Pennsylvania nuclear plant.
Tech companies are also interested in small modular reactors, which are more compact and potentially easier to deploy — with big investments by Microsoft founder Bill Gates in the sector.
However, this technology is still in its infancy and lacks regulatory approval, leading companies to seek out existing nuclear power options.
Nuclear energy has staunch opponents due to concerns about radioactive waste disposal, the potential for catastrophic accidents, and the high costs associated with plant construction and decommissioning.
The 1979 partial meltdown of Unit 2 at Three Mile Island caused panic in the US and brought the expansion of nuclear energy to a standstill.
The US Nuclear Regulatory Commission deemed it the “most serious accident in US commercial nuclear power plant operating history,” although it also said there were no detectable health effects on workers or the public from the small radioactive releases.

Merida Industry Co (美利達) has seen signs of recovery in the US and European markets this year, as customers are gradually depleting their inventories, the bicycle maker told shareholders yesterday. Given robust growth in new orders at its Taiwanese factory, coupled with its subsidiaries’ improving performance, Merida said it remains confident about the bicycle market’s prospects and expects steady growth in its core business this year. CAUTION ON CHINA However, the company must handle the Chinese market with great caution, as sales of road bikes there have declined significantly, affecting its revenue and profitability, Merida said in a statement, adding that it would
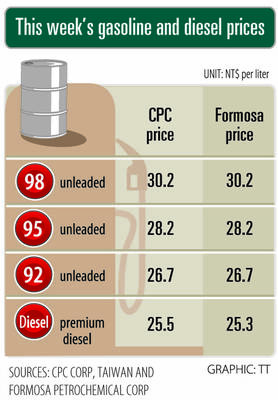
i Gasoline and diesel prices at fuel stations are this week to rise NT$0.1 per liter, as tensions in the Middle East pushed crude oil prices higher last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. International crude oil prices last week rose for the third consecutive week due to an escalating conflict between Israel and Iran, as the market is concerned that the situation in the Middle East might affect crude oil supply, CPC and Formosa said in separate statements. Front-month Brent crude oil futures — the international oil benchmark — rose 3.75 percent to settle at US$77.01

RISING: Strong exports, and life insurance companies’ efforts to manage currency risks indicates the NT dollar would eventually pass the 29 level, an expert said The New Taiwan dollar yesterday rallied to its strongest in three years amid inflows to the nation’s stock market and broad-based weakness in the US dollar. Exporter sales of the US currency and a repatriation of funds from local asset managers also played a role, said two traders, who asked not to be identified as they were not authorized to speak publicly. State-owned banks were seen buying the greenback yesterday, but only at a moderate scale, the traders said. The local currency gained 0.77 percent, outperforming almost all of its Asian peers, to close at NT$29.165 per US dollar in Taipei trading yesterday. The

RECORD LOW: Global firms’ increased inventories, tariff disputes not yet impacting Taiwan and new graduates not yet entering the market contributed to the decrease Taiwan’s unemployment rate last month dropped to 3.3 percent, the lowest for the month in 25 years, as strong exports and resilient domestic demand boosted hiring across various sectors, the Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (DGBAS) said yesterday. After seasonal adjustments, the jobless rate eased to 3.34 percent, the best performance in 24 years, suggesting a stable labor market, although a mild increase is expected with the graduation season from this month through August, the statistics agency said. “Potential shocks from tariff disputes between the US and China have yet to affect Taiwan’s job market,” Census Department Deputy Director Tan Wen-ling